Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction
... Future: direct auditory stimulation of auditory cortex, repetitive transmagnetic stimulation, tinnitus retraining therapy ...
... Future: direct auditory stimulation of auditory cortex, repetitive transmagnetic stimulation, tinnitus retraining therapy ...
Tetrapods
... Body Density - Girdles – • In fish, the pectoral girdle is attached to the skull. • Early tetrapods developed a stronger shoulder ...
... Body Density - Girdles – • In fish, the pectoral girdle is attached to the skull. • Early tetrapods developed a stronger shoulder ...
Sensation and Perception Chapter 4
... guitar strings, transfer the surrounding mediumair-as the vibrating objects push the molecules of the medium back and forth. In space, there is no air, so the sound wave would have no ...
... guitar strings, transfer the surrounding mediumair-as the vibrating objects push the molecules of the medium back and forth. In space, there is no air, so the sound wave would have no ...
Exam 3 Sample 2003
... a. exercise decreases the sensitivity of the receptors. b. in a muscular body, the receptors are buried deeper in the skin. c. they have become used to lower levels of pain after constant exposure. d. they want to appear as tough as male athletes. Endorphins are a. morphine-like substances that natu ...
... a. exercise decreases the sensitivity of the receptors. b. in a muscular body, the receptors are buried deeper in the skin. c. they have become used to lower levels of pain after constant exposure. d. they want to appear as tough as male athletes. Endorphins are a. morphine-like substances that natu ...
senses - Greer Middle College
... WINDOW, and vibrations cause the perilymph to vibrate; the hair cells here transmit this vibration. Therefore the HAIR CELLS in this region are receptors for HEARING. As you age, hair cells become damaged (loud music can speed this process along). Older people usually can’t hear frequencies that you ...
... WINDOW, and vibrations cause the perilymph to vibrate; the hair cells here transmit this vibration. Therefore the HAIR CELLS in this region are receptors for HEARING. As you age, hair cells become damaged (loud music can speed this process along). Older people usually can’t hear frequencies that you ...
Chordates - LBHS Biology | The study of life
... – horns composed of core of bone surrounded by keratin sheath ...
... – horns composed of core of bone surrounded by keratin sheath ...
Module 10
... Cochlea Basilar membrane Hair cells Auditory nerve Semicircular canals (3) – motion sensors Otoliths- orientation & acceleration sensors ...
... Cochlea Basilar membrane Hair cells Auditory nerve Semicircular canals (3) – motion sensors Otoliths- orientation & acceleration sensors ...
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT AMPHIBIANS
... How are the exit openings different in MALE and FEMALE mammals? Which part of the brain is largest in mammals? What do the brain parts do? What is the function of fur/hair? Where are BILE, TRYPSIN, AMYLASE, INSULIN, GLUCAGON, & THYROXIN, made? What is the function of these substances? How is GLUCAGO ...
... How are the exit openings different in MALE and FEMALE mammals? Which part of the brain is largest in mammals? What do the brain parts do? What is the function of fur/hair? Where are BILE, TRYPSIN, AMYLASE, INSULIN, GLUCAGON, & THYROXIN, made? What is the function of these substances? How is GLUCAGO ...
the auditory system
... Hearing the Sound Make sure you read this slide. Transmitting the Sound What happens inside the cochlea? Please make sure you include the concepts of basilar membrane, oval window, and hair cells in your response. ...
... Hearing the Sound Make sure you read this slide. Transmitting the Sound What happens inside the cochlea? Please make sure you include the concepts of basilar membrane, oval window, and hair cells in your response. ...
Otoacoustic Emissions
... Supported by almost simultaneous discovery of OHC motility Movement into Clinical Use: ...
... Supported by almost simultaneous discovery of OHC motility Movement into Clinical Use: ...
Chordate Test Review Pre AP
... ______Reptilia________. Ectothermic animals do not produce or store a lot of heat. Their body temperatures will change to match their surroundings. Ectothermic animals have ___3____ heart chambers. In most ____reptiles_______, the heart is partly divided. The exceptions to this are the _____ crocod ...
... ______Reptilia________. Ectothermic animals do not produce or store a lot of heat. Their body temperatures will change to match their surroundings. Ectothermic animals have ___3____ heart chambers. In most ____reptiles_______, the heart is partly divided. The exceptions to this are the _____ crocod ...
Chapter-24
... First vertebrates able to complete their life cycle on dry land • Water-conserving skin and kidneys • Amniote eggs (four membranes) • Allow amniote embryo to develop away from water • Active life-styles ...
... First vertebrates able to complete their life cycle on dry land • Water-conserving skin and kidneys • Amniote eggs (four membranes) • Allow amniote embryo to develop away from water • Active life-styles ...
Hearing Conservation
... Can You Imagine? Not being able to: Hear what the other person is saying? Listen to the sound of music? Listen to the sound of nature? Being afflicted with: Uncomfortable ringing in your ears? Abnormal sounds that interfere with your sleep? ...
... Can You Imagine? Not being able to: Hear what the other person is saying? Listen to the sound of music? Listen to the sound of nature? Being afflicted with: Uncomfortable ringing in your ears? Abnormal sounds that interfere with your sleep? ...
hearing loss in older adults
... Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we can suggest to patients if they can’t afford hearing aids. ...
... Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we can suggest to patients if they can’t afford hearing aids. ...
Influence of hearing sounds Materials:
... Why is hearing influential for cognitive development? (how our brains develop) b. What are some dominant sounds that we depend on for survival? EARS: contain structures for both the sense of hearing and the sense of balance. The eighth cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve made up of the auditory a ...
... Why is hearing influential for cognitive development? (how our brains develop) b. What are some dominant sounds that we depend on for survival? EARS: contain structures for both the sense of hearing and the sense of balance. The eighth cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve made up of the auditory a ...
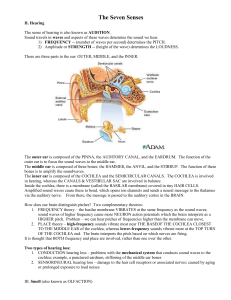
II. Hearing
... Amplified sound waves cause these to bend, which opens ion channels and sends a neural message to the thalamus via the auditory nerve. From there, the message is passed to the auditory cortex in the BRAIN. How does our brain distinguish pitches? Two complementary theories: 1. FREQUENCY theory – the ...
... Amplified sound waves cause these to bend, which opens ion channels and sends a neural message to the thalamus via the auditory nerve. From there, the message is passed to the auditory cortex in the BRAIN. How does our brain distinguish pitches? Two complementary theories: 1. FREQUENCY theory – the ...
Mammals starts with?
... 14. Animals with a cloaca have a vent; animals without a cloaca have a R __ __ __ __ __ to hold waiting digestive waste and a A __ __ __ as an exit opening. 15. Unlike birds, mammals have a urinary B __ __ __ __ __ __ to store urine made from urea. 16. First chamber of the stomach in a cow, goat, or ...
... 14. Animals with a cloaca have a vent; animals without a cloaca have a R __ __ __ __ __ to hold waiting digestive waste and a A __ __ __ as an exit opening. 15. Unlike birds, mammals have a urinary B __ __ __ __ __ __ to store urine made from urea. 16. First chamber of the stomach in a cow, goat, or ...
Vertebrates
... • Develop from an amniotic egg – Yolk provides nourishment for developing embryo – Amnion is a membrane filled with fluid that cushions and prevents it from desiccation – Leathery shell for protection ...
... • Develop from an amniotic egg – Yolk provides nourishment for developing embryo – Amnion is a membrane filled with fluid that cushions and prevents it from desiccation – Leathery shell for protection ...
PSY 342: Review for Exam 3 Chapter 11: Sound and the Auditory
... Human hearing range is 20-20,000 Hertz Ear structures (outer, middle and inner ear) Outer ear: pinna and auditory canal (protects tympanic membrane or ear drum) Middle ear: tympanic membrane and three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations Inner ear: Cochlea which contains the Organ of ...
... Human hearing range is 20-20,000 Hertz Ear structures (outer, middle and inner ear) Outer ear: pinna and auditory canal (protects tympanic membrane or ear drum) Middle ear: tympanic membrane and three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations Inner ear: Cochlea which contains the Organ of ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EAR
... Reduce sound by producing an acoustical barrier to sound transmission Reduce high frequencies more than low ...
... Reduce sound by producing an acoustical barrier to sound transmission Reduce high frequencies more than low ...
1145010Module Hearing 08JS
... contains the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs Cochlea coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses Hair cells line the basilar membrane ...
... contains the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs Cochlea coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses Hair cells line the basilar membrane ...