mechanics - Hertfordshire Grid for Learning
... 2. Calculate the total energy before the motion and compare it with the total energy after the motion. Since Work done = Change in energy. Therefore the difference in total energy is accounted for by the work done against friction.. ...
... 2. Calculate the total energy before the motion and compare it with the total energy after the motion. Since Work done = Change in energy. Therefore the difference in total energy is accounted for by the work done against friction.. ...
Chapter 6
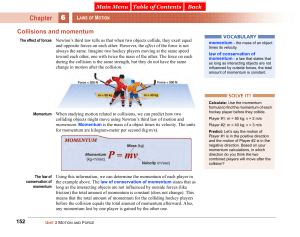
... and opposite forces on each other. However, the effect of the force is not always the same. Imagine two hockey players moving at the same speed toward each other, one with twice the mass of the other. The force on each during the collision is the same strength, but they do not have the same change i ...
... and opposite forces on each other. However, the effect of the force is not always the same. Imagine two hockey players moving at the same speed toward each other, one with twice the mass of the other. The force on each during the collision is the same strength, but they do not have the same change i ...
HERE
... the following statements is true according to Newton’s third law of motion? A. Each object exerts a force on the other, and the two forces are equal and in opposite directions. B. Each object exerts a force on the other, and the two forces are the same in magnitude and direction. C. Each object exer ...
... the following statements is true according to Newton’s third law of motion? A. Each object exerts a force on the other, and the two forces are equal and in opposite directions. B. Each object exerts a force on the other, and the two forces are the same in magnitude and direction. C. Each object exer ...
Chapter 6 Forces in Motion
... Acceleration Stops at the Terminal Velocity • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
... Acceleration Stops at the Terminal Velocity • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
Energy - Sakshi Education
... 23. A spherically ball of mass 20kg is stationary at the top of a hill of height 100m. It rolls down a smooth surface to the ground, then climbs up another hill of height 30m and finally rolls down to a horizontal base at a height of 20m above the ground. The velocity attained by the ball is b) 20ms ...
... 23. A spherically ball of mass 20kg is stationary at the top of a hill of height 100m. It rolls down a smooth surface to the ground, then climbs up another hill of height 30m and finally rolls down to a horizontal base at a height of 20m above the ground. The velocity attained by the ball is b) 20ms ...
PEKA 5
... 1. Arrange the apparatus as shown in the diagram. Compensate for friction. 2. Measure the mass of the trolley using the triple beam balance provided. Record the value. 2. Switch on the ticker timer. Use a 50g slotted weight for a constant force. 3. Release the slotted weight to fall freely to the gr ...
... 1. Arrange the apparatus as shown in the diagram. Compensate for friction. 2. Measure the mass of the trolley using the triple beam balance provided. Record the value. 2. Switch on the ticker timer. Use a 50g slotted weight for a constant force. 3. Release the slotted weight to fall freely to the gr ...