Physics C: Mechanics - Piscataway High School
... 1. Understand the kinematics of simple harmonic motion so they can: a. Sketch or identify a graph of displacement as a function of time, and determine from such a graph the amplitude, period and frequency of the motion. b. Identify points in the motion where the velocity is zero or achieves its maxi ...
... 1. Understand the kinematics of simple harmonic motion so they can: a. Sketch or identify a graph of displacement as a function of time, and determine from such a graph the amplitude, period and frequency of the motion. b. Identify points in the motion where the velocity is zero or achieves its maxi ...
ch07-4 - Physics-YISS
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
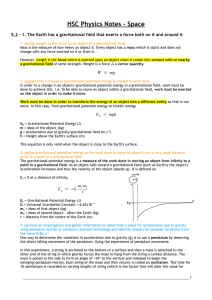
Gravity: the Laws of Motions
... Mass and Weight • Mass is a measure of how much material is in an object. • Weight is the force exterted by gravity on a massive body (body with mass), e.g. placed on the surface of Earth • Weight is a measure of the gravitational force exerted on that material. • Thus, mass is constant for an obje ...
... Mass and Weight • Mass is a measure of how much material is in an object. • Weight is the force exterted by gravity on a massive body (body with mass), e.g. placed on the surface of Earth • Weight is a measure of the gravitational force exerted on that material. • Thus, mass is constant for an obje ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... 1. C&J page 172 (middle), Check Your Understanding #12: …fuel tank… 2. Two people throw a baseball m = 0.5 kg, with a speed of 10 m/s back and forth with 30 round trips. How much energy must be transferred to the baseball to accomplish this motion? ...
... 1. C&J page 172 (middle), Check Your Understanding #12: …fuel tank… 2. Two people throw a baseball m = 0.5 kg, with a speed of 10 m/s back and forth with 30 round trips. How much energy must be transferred to the baseball to accomplish this motion? ...
F = 0 x = 0 F =
... complete rotation. Heartbeats are an example of periodic behavior. If you look at heartbeats on an electrocardiogram, they make a regular pattern. The pattern that the heart obeys is rather complicated. In this section, we’re going to be dealing with a specific type of periodic motion called simple ...
... complete rotation. Heartbeats are an example of periodic behavior. If you look at heartbeats on an electrocardiogram, they make a regular pattern. The pattern that the heart obeys is rather complicated. In this section, we’re going to be dealing with a specific type of periodic motion called simple ...
Review - Flipped Physics
... those forces a third law action/reaction pair? If not, what are the pairs? ...
... those forces a third law action/reaction pair? If not, what are the pairs? ...
Conservation of Energy - Physics Introductory Labs at Stony Brook
... 3. Level the air track by carefully adjusting the single leveling screw at one end of the track. Rotating the screw will tilt the track one way or the other, so adjust it until the glider remains nearly stationary on the air track. Be sure to tighten the wing nut on the leveling screw when the track ...
... 3. Level the air track by carefully adjusting the single leveling screw at one end of the track. Rotating the screw will tilt the track one way or the other, so adjust it until the glider remains nearly stationary on the air track. Be sure to tighten the wing nut on the leveling screw when the track ...
Honors Physics - Practice Final Exam
... circular path. If the maximum tension that the string can withstand is 350 N, what is the maximum speed of the mass if the string is not to break? A. 700 m/s C. 19 m/s B. 26 m/s D. 13 m/s 54. An object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. Consider the direction of the object’s velocity and ...
... circular path. If the maximum tension that the string can withstand is 350 N, what is the maximum speed of the mass if the string is not to break? A. 700 m/s C. 19 m/s B. 26 m/s D. 13 m/s 54. An object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. Consider the direction of the object’s velocity and ...
Physics-1 Recitation-7
... moment of inertia I. One end of the mass m is connected to a spring of force constant k, and the other end is fastened to a cord wrapped around the pulley. The pulley axle and the incline are frictionless. If the pulley is wound conterclockwise so that the spring is stretched a distance d from its u ...
... moment of inertia I. One end of the mass m is connected to a spring of force constant k, and the other end is fastened to a cord wrapped around the pulley. The pulley axle and the incline are frictionless. If the pulley is wound conterclockwise so that the spring is stretched a distance d from its u ...