Chapter 8 Getting Things to Move: Momentum and Kinetic Energy
... You probably won’t be asked to solve questions of this kind on physics tests because, in addition to being two simultaneous equations, the second equation has a lot of squared velocities in it. But it’s one you may see in homework. When you do the math, you get v f1 = ...
... You probably won’t be asked to solve questions of this kind on physics tests because, in addition to being two simultaneous equations, the second equation has a lot of squared velocities in it. But it’s one you may see in homework. When you do the math, you get v f1 = ...
SHM - Red Hook Central Schools
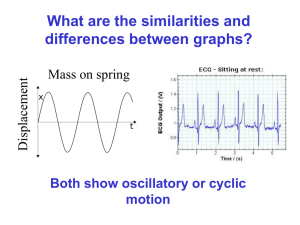
... pendulum in a mathematically identical way to the mass on a spring. ...
... pendulum in a mathematically identical way to the mass on a spring. ...
Solutions Guide - Blue Valley Schools
... 20. An object moving with a constant velocity has a non-zero velocity and a zero acceleration at the same time. So a car driving at constant speed on a straight, level roadway would meet this condition. 21. The object starts with a constant velocity in the positive direction. At about t = 17 s, when ...
... 20. An object moving with a constant velocity has a non-zero velocity and a zero acceleration at the same time. So a car driving at constant speed on a straight, level roadway would meet this condition. 21. The object starts with a constant velocity in the positive direction. At about t = 17 s, when ...
Newton 2nd law1
... • Suppose the pilot announces that the plane is flying at a constant 900 km/h and the thrust of the engines is a constant 80,000 N. What is the acceleration of the airplane? • Zero, b/c velocity is constant • What is the combined force of air resistance that acts on the plane’s outside surface? • 80 ...
... • Suppose the pilot announces that the plane is flying at a constant 900 km/h and the thrust of the engines is a constant 80,000 N. What is the acceleration of the airplane? • Zero, b/c velocity is constant • What is the combined force of air resistance that acts on the plane’s outside surface? • 80 ...
Halliday 9th chapter 9
... form an air cavity around the top of the foot. To avoid having to pull the foot back up against water drag in order to complete the step, the lizard withdraws the foot before water can flow into the air cavity. If the lizard is not to sink, the average upward impulse on the lizard during this full a ...
... form an air cavity around the top of the foot. To avoid having to pull the foot back up against water drag in order to complete the step, the lizard withdraws the foot before water can flow into the air cavity. If the lizard is not to sink, the average upward impulse on the lizard during this full a ...
Kinematics - Vicphysics
... an object causes the object to accelerate (change its velocity). The amount of acceleration that occurs depends on the size of the force and the mass of the object. Large forces cause large accelerations. Objects with large mass accelerate less when they experience the same force as a small mass. Th ...
... an object causes the object to accelerate (change its velocity). The amount of acceleration that occurs depends on the size of the force and the mass of the object. Large forces cause large accelerations. Objects with large mass accelerate less when they experience the same force as a small mass. Th ...
Green`s function methods
... Consider a free particle subjected to an external x(t ) 0 dt ' (t - t ') f (t ') 0 udv force satisfying the Diff Eq: x F (t ) / m f (t ). Let dv f (t ') dt ' and u -(t '- t ) t' Assume x(0) x(0) 0 and f (t t0 ) 0. We v(t ) f (t '') dt '' ; du dt ' ...
... Consider a free particle subjected to an external x(t ) 0 dt ' (t - t ') f (t ') 0 udv force satisfying the Diff Eq: x F (t ) / m f (t ). Let dv f (t ') dt ' and u -(t '- t ) t' Assume x(0) x(0) 0 and f (t t0 ) 0. We v(t ) f (t '') dt '' ; du dt ' ...
Linear Momentum and Collisions
... D E = D K + D U = -fkd if friction forces are doing work on the system. The total amount of energy in the system is still constant, but the change in mechanical energy goes into “internal energy” or heat. ...
... D E = D K + D U = -fkd if friction forces are doing work on the system. The total amount of energy in the system is still constant, but the change in mechanical energy goes into “internal energy” or heat. ...