Slide 1
... Law of Gravitation Appears to be a universal law. Extends to an infinite distance. Near the Earth’s surface, the force is called “gravitational force,” or “weight W.” ...
... Law of Gravitation Appears to be a universal law. Extends to an infinite distance. Near the Earth’s surface, the force is called “gravitational force,” or “weight W.” ...
Rigid Body Dynamics chapter 10 continues
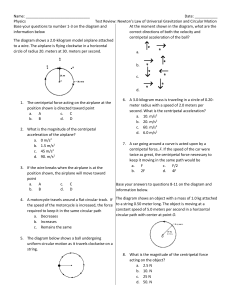
... and the coefficients of friction with the road surface are s = 0.800 and k = 0.600. Assuming that the weight is evenly distributed on the four wheels, calculate the maximum torque that can be exerted by the engine on a driving wheel, without spinning the wheel. If you wish, you may assume the car is ...
... and the coefficients of friction with the road surface are s = 0.800 and k = 0.600. Assuming that the weight is evenly distributed on the four wheels, calculate the maximum torque that can be exerted by the engine on a driving wheel, without spinning the wheel. If you wish, you may assume the car is ...
Newtonian Mechanics
... book known as Principia. The full Latin title of the book1 may be translated into English as Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy. The theory that the planets (including Earth) revolve around the sun was published by Nicolaus Copernicus in 1543. This was a revolutionary idea! The picture of ...
... book known as Principia. The full Latin title of the book1 may be translated into English as Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy. The theory that the planets (including Earth) revolve around the sun was published by Nicolaus Copernicus in 1543. This was a revolutionary idea! The picture of ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Only motion in a straight line is motion that is not changing its direction. Movement in a circle is actually a continuous changing of directions. Therefore, it must be undergoing an acceleration. Ask what force is acting on the yo-yo to change its direction. In an open discussion, explain to stude ...
... Only motion in a straight line is motion that is not changing its direction. Movement in a circle is actually a continuous changing of directions. Therefore, it must be undergoing an acceleration. Ask what force is acting on the yo-yo to change its direction. In an open discussion, explain to stude ...
Lecture 1: Rotation of Rigid Body
... unexpected speedup called a glitch. One explanation is that a glitch occurs when the crust of the neutron star settles slightly, decreasing the moment of inertia about the rotation axis. A neutron star with angular speed 0=70.4 rad/s underwent such a glitch in October 1975 that increased its angula ...
... unexpected speedup called a glitch. One explanation is that a glitch occurs when the crust of the neutron star settles slightly, decreasing the moment of inertia about the rotation axis. A neutron star with angular speed 0=70.4 rad/s underwent such a glitch in October 1975 that increased its angula ...
Chapter 5-6
... 18. Walker3 6.P.066. [549531] Show Details A 2.0 kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at an angle of 65° above the horizontal. The upper end of the box is attached to a spring with a force constant of 16 N/m, as shown in Figure 6-38. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and the ...
... 18. Walker3 6.P.066. [549531] Show Details A 2.0 kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at an angle of 65° above the horizontal. The upper end of the box is attached to a spring with a force constant of 16 N/m, as shown in Figure 6-38. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and the ...
Forces and The Laws of Motion
... • When the net external force on an object is zero, its acceleration is zero • Conversely, an object that is not accelerating has no net force acting on it • Net force is vector sum of all forces: • Bodies at rest will stay at rest and bodies in motion will stay in straight-line motion at a constant ...
... • When the net external force on an object is zero, its acceleration is zero • Conversely, an object that is not accelerating has no net force acting on it • Net force is vector sum of all forces: • Bodies at rest will stay at rest and bodies in motion will stay in straight-line motion at a constant ...
Force and Newton` s Laws Study Guide
... 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the obj ...
... 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the obj ...
Chapters 5&6
... • Hooke’s law can be applied not to springs only, but to all elastic materials and objects ...
... • Hooke’s law can be applied not to springs only, but to all elastic materials and objects ...
Angular Momentum (AIS)
... same anywhere on the body, it does not matter which point of rotation we choose for our summation of torques • Best to choose a point that is easiest to solve (The location of one of our unknown forces) ...
... same anywhere on the body, it does not matter which point of rotation we choose for our summation of torques • Best to choose a point that is easiest to solve (The location of one of our unknown forces) ...
PHYSICS
... quizzes, and homework will have open-ended questions and problems in which students will be evaluated on the processes and reasoning they employ to arrive at their answers. This course is student-centered in that students are required to be active learners and participate in numerous learning experi ...
... quizzes, and homework will have open-ended questions and problems in which students will be evaluated on the processes and reasoning they employ to arrive at their answers. This course is student-centered in that students are required to be active learners and participate in numerous learning experi ...
Force and Acceleration
... For example, when we are traveling in a bus, and bus is going at fast speed. The driver suddenly applies the brake and we are unable to control ourselves and our body plunges forward. It is because the bus and our body are moving at constant velocity. That is why in cars etc. we use seat belts. So t ...
... For example, when we are traveling in a bus, and bus is going at fast speed. The driver suddenly applies the brake and we are unable to control ourselves and our body plunges forward. It is because the bus and our body are moving at constant velocity. That is why in cars etc. we use seat belts. So t ...