Rotational motion
... Tension did positive rotational work (it made the Yo-Yo spin faster) Tension did negative translational work (it made the Yo-Yo move more slowly) ... the net work done by tension was zero. This happened because the string was stationary, and thus enforced a = ±αr. This is also true in rolling motion ...
... Tension did positive rotational work (it made the Yo-Yo spin faster) Tension did negative translational work (it made the Yo-Yo move more slowly) ... the net work done by tension was zero. This happened because the string was stationary, and thus enforced a = ±αr. This is also true in rolling motion ...
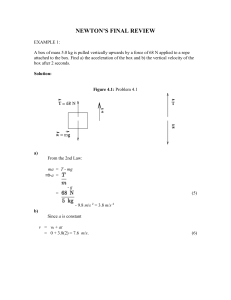
Final Newtons Review
... e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 3, then the new accelerati ...
... e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 3, then the new accelerati ...
chapter11
... The instantaneous angular momentum of a particle relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector and its instantaneous linear momentum. ...
... The instantaneous angular momentum of a particle relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector and its instantaneous linear momentum. ...
doc
... . It can also be seen from the example that a change in angular position (a rotation) about a given axis is equivalent to a change in angular position (a rotation) about any other parallel axis. It is important to create a clear understanding of the above paragraph here and now. We often use words ...
... . It can also be seen from the example that a change in angular position (a rotation) about a given axis is equivalent to a change in angular position (a rotation) about any other parallel axis. It is important to create a clear understanding of the above paragraph here and now. We often use words ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... time elapsed = duration of an event – there is a beginning, a middle, and an end to any event. distance = path length displacement = change in position mass = measure of inertia or resistance to change in state of motion ...
... time elapsed = duration of an event – there is a beginning, a middle, and an end to any event. distance = path length displacement = change in position mass = measure of inertia or resistance to change in state of motion ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 0.034 m/s2 at the equator—and it can be neglected for most purposes. Our additional centripetal acceleration due to the motion of the Earth around the Sun is even smaller, about 0.002 m/s2. Hereafter, unless otherwise stated, we will take it for granted that the reference frames in which we express ...
... 0.034 m/s2 at the equator—and it can be neglected for most purposes. Our additional centripetal acceleration due to the motion of the Earth around the Sun is even smaller, about 0.002 m/s2. Hereafter, unless otherwise stated, we will take it for granted that the reference frames in which we express ...
SPH3U: Forces, Mass and Motion
... An alternative and convenient way (and the one we will use) to find the net force is by changing the vector equation into a scalar equation. Use the sign convention indicated in the diagram above. Forces acting in the positive x-direction are labelled positive and forces acting in the negative x-di ...
... An alternative and convenient way (and the one we will use) to find the net force is by changing the vector equation into a scalar equation. Use the sign convention indicated in the diagram above. Forces acting in the positive x-direction are labelled positive and forces acting in the negative x-di ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... time elapsed = duration of an event – there is a beginning, a middle, and an end to any event. distance = path length displacement = change in position mass = measure of inertia or resistance to change in state of motion ...
... time elapsed = duration of an event – there is a beginning, a middle, and an end to any event. distance = path length displacement = change in position mass = measure of inertia or resistance to change in state of motion ...
Lecture 4
... addition. • Vector components • Mathematical description of vector addition (addition of components) • Unit Vectors 95.141, F2010, Lecture 4 ...
... addition. • Vector components • Mathematical description of vector addition (addition of components) • Unit Vectors 95.141, F2010, Lecture 4 ...