Editorial Comment Hyperthermia: A Hyperadrenergic
... taken by the two species to this "terminus." In this editorial, attention is directed to important differences as well as similarities in how human and other mammalian cardiovascular systems cope with a noncompensible thermal stress; some consequences of this stress are discussed as well. When anima ...
... taken by the two species to this "terminus." In this editorial, attention is directed to important differences as well as similarities in how human and other mammalian cardiovascular systems cope with a noncompensible thermal stress; some consequences of this stress are discussed as well. When anima ...
The Heart, Day 4 (Professor Powerpoint)
... Amount of muscle stretching affects the force of contractions (e.g. pulling a rubber band) Starlings Law of the Heart “Stretch” builds up resistance against the blood ♦ More blood is pushed out ...
... Amount of muscle stretching affects the force of contractions (e.g. pulling a rubber band) Starlings Law of the Heart “Stretch” builds up resistance against the blood ♦ More blood is pushed out ...
Key for Week 1 Course Packet Page 1
... d. Comparative – Study focused on comparing anatomy between different organisms. Example: Examination of forelimbs of vertebrate animals. II. Physiology – That branch of science dealing with the study of body functions. A. Systemic – Body Systems. Example: Cardiac physiology B. Immunology – Body Def ...
... d. Comparative – Study focused on comparing anatomy between different organisms. Example: Examination of forelimbs of vertebrate animals. II. Physiology – That branch of science dealing with the study of body functions. A. Systemic – Body Systems. Example: Cardiac physiology B. Immunology – Body Def ...
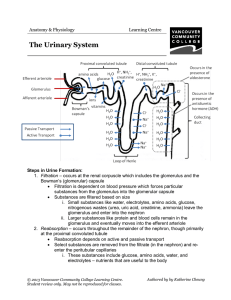
Urinary System - VCC Library - Vancouver Community College
... dilute because there is more water than normal. 3. If red blood cells or proteins were present in your urine, you should be concerned because a normally functioning kidney would not allow these large substances to enter into the glomerular capsule and end up in urine. 4. ACE inhibitor would prevent ...
... dilute because there is more water than normal. 3. If red blood cells or proteins were present in your urine, you should be concerned because a normally functioning kidney would not allow these large substances to enter into the glomerular capsule and end up in urine. 4. ACE inhibitor would prevent ...
Midterm 2 - Creighton Biology
... a. An autoimmune disease that causes antibodies to inhibit activation of receptors for adrenocorticotropic hormone. b. An autoimmune disease that causes antibodies to permanently activate receptors for adrenocorticotropic hormone. c. A tumor in the adrenal cortex that causes it to hypersecrete corti ...
... a. An autoimmune disease that causes antibodies to inhibit activation of receptors for adrenocorticotropic hormone. b. An autoimmune disease that causes antibodies to permanently activate receptors for adrenocorticotropic hormone. c. A tumor in the adrenal cortex that causes it to hypersecrete corti ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... Blood flow can increase 7-8 times as a result of vasodilation of metarterioles and precapillary sphincters in response to increased rate of metabolism ...
... Blood flow can increase 7-8 times as a result of vasodilation of metarterioles and precapillary sphincters in response to increased rate of metabolism ...
File
... • Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells • Gas exchange (lungs) • Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract) • Urine formation (kidneys) • Rate of flow is precisely the right amount to provide for proper function Velocity of Blood Flow • Changes as it travels throug ...
... • Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells • Gas exchange (lungs) • Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract) • Urine formation (kidneys) • Rate of flow is precisely the right amount to provide for proper function Velocity of Blood Flow • Changes as it travels throug ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • The rate of blood flow to each tissue of the body is almost always precisely controlled in relation to the tissue need. • The cardiac output is controlled mainly by the sum of all the local tissue flows. • Arterial pressure regulation is generally independent of either local blood flow control or ...
... • The rate of blood flow to each tissue of the body is almost always precisely controlled in relation to the tissue need. • The cardiac output is controlled mainly by the sum of all the local tissue flows. • Arterial pressure regulation is generally independent of either local blood flow control or ...
Diving response - CMA
... response to submerging is the slowing down of the heart (10-25%). The heart rate of aquatic mammals slows down even more dramatic. Slowing the heart rate lessens the need for bloodstream oxygen, leaving more to be used in the other organs. Under high pressure capillaries in the extremities start clo ...
... response to submerging is the slowing down of the heart (10-25%). The heart rate of aquatic mammals slows down even more dramatic. Slowing the heart rate lessens the need for bloodstream oxygen, leaving more to be used in the other organs. Under high pressure capillaries in the extremities start clo ...
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... In clinical settings, blood pressure usually refers to blood pressure in the main arteries, which varies during the cardiac cycle, as shown in 10th Martini Figure 21-9 (Pressures within the Systemic Circuit). The systolic blood pressure is the peak of arterial pressure generated during ventricular c ...
... In clinical settings, blood pressure usually refers to blood pressure in the main arteries, which varies during the cardiac cycle, as shown in 10th Martini Figure 21-9 (Pressures within the Systemic Circuit). The systolic blood pressure is the peak of arterial pressure generated during ventricular c ...