Phy_103_-3
... the fluid. For example, a large rock at the bottom of a stream would be easily lifted compare to lifting it from the ground. As the rock breaks through the surface of the water, it becomes heavier. This phenomenon is as a result of upward force called the buoyant force (upthrust) acting on the rock ...
... the fluid. For example, a large rock at the bottom of a stream would be easily lifted compare to lifting it from the ground. As the rock breaks through the surface of the water, it becomes heavier. This phenomenon is as a result of upward force called the buoyant force (upthrust) acting on the rock ...
Chapter 3 Fluid dynamics
... a factor of 16. This relation is familiar to physicians in connection with the selection of needles for hypodermic syringes (皮下注射管). Needle size is much more important than thumb pressure in determining the flow rate from the needle; doubling the needle diameter has the same effect as increasing the ...
... a factor of 16. This relation is familiar to physicians in connection with the selection of needles for hypodermic syringes (皮下注射管). Needle size is much more important than thumb pressure in determining the flow rate from the needle; doubling the needle diameter has the same effect as increasing the ...
v = F/A - VCOMcc
... • When flow is laminar, all elements of the fluid move in streamlines that are parallel to the axis of the tube • In turbulent flow the elements of the fluid move irregularly in axial, radial, and circumferential directions • Though blood flow is generally laminar, it can become turbulent under cert ...
... • When flow is laminar, all elements of the fluid move in streamlines that are parallel to the axis of the tube • In turbulent flow the elements of the fluid move irregularly in axial, radial, and circumferential directions • Though blood flow is generally laminar, it can become turbulent under cert ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 11: Endocrine System Directions
... 13. What would reverse the alarm and resistance stages? If the stimulus was removed (see #10), or if the epinephrine, norepinephrine, CRH, ACTH, and cortisol were reduced in quantity. 14. Re-draw this as a negative feedback mechanism. Use figure 11.17 to help you with format. Be sure to include: STI ...
... 13. What would reverse the alarm and resistance stages? If the stimulus was removed (see #10), or if the epinephrine, norepinephrine, CRH, ACTH, and cortisol were reduced in quantity. 14. Re-draw this as a negative feedback mechanism. Use figure 11.17 to help you with format. Be sure to include: STI ...
Pressure Pressure
... The area of the left piston is 10 mm2; that of the right piston 10,000 mm 2. What force must be exerted on the left piston to keep the 10,000N car on the right at the same height? ...
... The area of the left piston is 10 mm2; that of the right piston 10,000 mm 2. What force must be exerted on the left piston to keep the 10,000N car on the right at the same height? ...
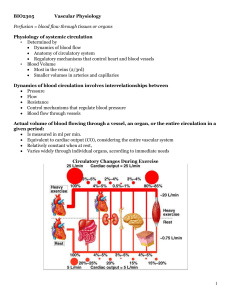
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... Peripheral Resistance • = Resistance of the arterial system • For blood to flow into peripheral capillaries the pressure gradient must be great enough to overcome peripheral resistance • 3 sources of peripheral resistance – Vascular resistance (resistance of blood vessels) ...
... Peripheral Resistance • = Resistance of the arterial system • For blood to flow into peripheral capillaries the pressure gradient must be great enough to overcome peripheral resistance • 3 sources of peripheral resistance – Vascular resistance (resistance of blood vessels) ...