SOLUTION:
... but the ball deflects to the right as shown and passes behind B as previously described. This is not a centrifugal-force effect, for the latter acts radially outward. Instead, this effect acts sideways, perpendicular to v , and is called a Coriolis acceleration; it is said to be due to the Coriolis ...
... but the ball deflects to the right as shown and passes behind B as previously described. This is not a centrifugal-force effect, for the latter acts radially outward. Instead, this effect acts sideways, perpendicular to v , and is called a Coriolis acceleration; it is said to be due to the Coriolis ...
Document
... a) the force of gravity, which is directed downward b) the force which is directed radially outward from the center of the circle c) the tension in the chains of the swing, which is directed upward d) answers b and c only e) answers a and c only ...
... a) the force of gravity, which is directed downward b) the force which is directed radially outward from the center of the circle c) the tension in the chains of the swing, which is directed upward d) answers b and c only e) answers a and c only ...
How? Newton`s second law of motion
... equal, they are not balanced because they act on different objects. ...
... equal, they are not balanced because they act on different objects. ...
Chapter 10 - galileo.harvard.edu
... wheel has a net forward velocity: 2v v zero not enough information to say back ...
... wheel has a net forward velocity: 2v v zero not enough information to say back ...
Chapter 4 - faculty at Chemeketa
... • the greater its force of attraction toward the Earth. • the smaller its tendency to move i.e., the greater its inertia. So, the acceleration is the same. It is equal to the acceleration due to gravity: 10 m/s2 (precisely 9.8 m/s2). ...
... • the greater its force of attraction toward the Earth. • the smaller its tendency to move i.e., the greater its inertia. So, the acceleration is the same. It is equal to the acceleration due to gravity: 10 m/s2 (precisely 9.8 m/s2). ...
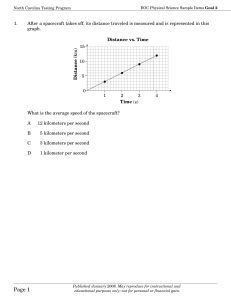
Page 1 - NC Department of Public Instruction
... the same time, another student drops ball B from the same height without any horizontal velocity. Neglecting air resistance, which best describes the results? ...
... the same time, another student drops ball B from the same height without any horizontal velocity. Neglecting air resistance, which best describes the results? ...
Pull my Strings: Normal Forces, Force Vectors
... 1. Draw the picture showing the forces on the block. What are they? 2. Draw the free-body diagram. 3. Write down Newton’s law, Fnet = M a 4. Think about the problem. When does the acceleration become greater than zero? ...
... 1. Draw the picture showing the forces on the block. What are they? 2. Draw the free-body diagram. 3. Write down Newton’s law, Fnet = M a 4. Think about the problem. When does the acceleration become greater than zero? ...
Centripetal Force Video Script
... Did you say that velocity involves both speed and direction and that during circular motion, direction is always changing? That means velocity is changing. According to Newton’s 2nd Law, acceleration requires a net force. And that’s the centripetal force. Now there are four variables that could affe ...
... Did you say that velocity involves both speed and direction and that during circular motion, direction is always changing? That means velocity is changing. According to Newton’s 2nd Law, acceleration requires a net force. And that’s the centripetal force. Now there are four variables that could affe ...
Physics 1401 - Exam 2 Chapter 5N-New
... (a) The lighter one has one fourth as much kinetic energy as the other does. (b) The lighter one has one half as much kinetic energy as the other does. (c) The lighter one has the same kinetic energy as the other does. (d) The lighter one has twice as much kinetic energy as the other does. (e) The l ...
... (a) The lighter one has one fourth as much kinetic energy as the other does. (b) The lighter one has one half as much kinetic energy as the other does. (c) The lighter one has the same kinetic energy as the other does. (d) The lighter one has twice as much kinetic energy as the other does. (e) The l ...
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems ANSWERS FACT
... FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A “change in state of motion” means a change in an object’s velocity, therefore inertia can also be defined as the tendency of an object to resist acceleration. Inertial mass is a measure of an object’s inertia. In oth ...
... FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A “change in state of motion” means a change in an object’s velocity, therefore inertia can also be defined as the tendency of an object to resist acceleration. Inertial mass is a measure of an object’s inertia. In oth ...