2005 C Mechanics 1. (a) ____ increases
... resistance) and this net force equals Ma according to Newton's Second Law of Motion. Since F is decreasing as the ball moves upward, the net force decreases, thus, the acceleration decreases (b) -Mg - kv = Ma -g - ...
... resistance) and this net force equals Ma according to Newton's Second Law of Motion. Since F is decreasing as the ball moves upward, the net force decreases, thus, the acceleration decreases (b) -Mg - kv = Ma -g - ...
Newton`s 2nd Law - Resources
... different forces, the one with the greater force will accelerate faster. It also depends on the mass of an object. The more mass the slower it accelerates. If two objects have the same force acting upon them, but different masses the object with the greater mass will not accelerate as quickly as ...
... different forces, the one with the greater force will accelerate faster. It also depends on the mass of an object. The more mass the slower it accelerates. If two objects have the same force acting upon them, but different masses the object with the greater mass will not accelerate as quickly as ...
Newtons Laws PPT
... •Resolve vectors into components •Write equations of motion by adding and subtracting vectors to find the NET FORCE. Always write larger force – smaller force. •Solve for any unknowns ...
... •Resolve vectors into components •Write equations of motion by adding and subtracting vectors to find the NET FORCE. Always write larger force – smaller force. •Solve for any unknowns ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... 3. Uniform Circular Motion: - I can: distinguish between reference systems (inertial and non-inertial) with respect to real and apparent forces acting within such systems (e.g. apparent force in a rotating frame, apparent gravitational force in a vertically accelerating frame) analyse, in qualit ...
... 3. Uniform Circular Motion: - I can: distinguish between reference systems (inertial and non-inertial) with respect to real and apparent forces acting within such systems (e.g. apparent force in a rotating frame, apparent gravitational force in a vertically accelerating frame) analyse, in qualit ...
“Who Wants To Be A Millionaire?” Inertia Style Created by Claire
... B)Speed and direction C)A force that happens when things rub against each other D)Change in position The answer is C. ...
... B)Speed and direction C)A force that happens when things rub against each other D)Change in position The answer is C. ...
Newton`s laws, forces
... there may be several forces; add them. there is only one acceleration. ...
... there may be several forces; add them. there is only one acceleration. ...
Centripetal Force
... 2. Adjust the pointer in the base so that it is about midway between its two extreme radial poistions. Measure the distance from the pointer to the axis of rotation. You will find the distance by measuring the center of the shaft to the center of the slider. 3. Adjust the length of the string suppo ...
... 2. Adjust the pointer in the base so that it is about midway between its two extreme radial poistions. Measure the distance from the pointer to the axis of rotation. You will find the distance by measuring the center of the shaft to the center of the slider. 3. Adjust the length of the string suppo ...
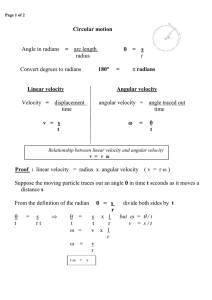
Circular motion - Leaving Cert Physics
... Relationship between linear velocity and angular velocity ...
... Relationship between linear velocity and angular velocity ...
Name: Notes - 4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a
... B. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on Earth? C. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on the Moon? 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12 ...
... B. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on Earth? C. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on the Moon? 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12 ...
force
... 3. Write the net force equations for the forces (x and y). They should all be equal to zero. 4. Write the net torque equation. It should also be equal to zero. Choosing a strategic axis of rotation eliminates unknown forces. 5. Solve for the unknowns. ...
... 3. Write the net force equations for the forces (x and y). They should all be equal to zero. 4. Write the net torque equation. It should also be equal to zero. Choosing a strategic axis of rotation eliminates unknown forces. 5. Solve for the unknowns. ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
Physics - John Madejski Academy
... exert on each other are equal and opposite. If you push on a wall, there is a normal contact force pushing back with the same force. This is an equilibrium situation – neither object moves. If two people on roller-skates push against each other, they will both feel the same size force and so acceler ...
... exert on each other are equal and opposite. If you push on a wall, there is a normal contact force pushing back with the same force. This is an equilibrium situation – neither object moves. If two people on roller-skates push against each other, they will both feel the same size force and so acceler ...
Physical Science Gravity
... • Explain that gravitational force becomes stronger as the masses increase and rapidly become weaker as the distance between the masses increases, F=G(m1m2/d2) • Evaluate the concept that free-fall acceleration near Earth’s surface is independent of the mass of the falling object • Demonstrate mathe ...
... • Explain that gravitational force becomes stronger as the masses increase and rapidly become weaker as the distance between the masses increases, F=G(m1m2/d2) • Evaluate the concept that free-fall acceleration near Earth’s surface is independent of the mass of the falling object • Demonstrate mathe ...
F g - Humble ISD
... NOTE: MASS and WEIGHT are NOT the same thing. MASS never changes When an object moves to a different planet. What is the weight of an 85.3-kg person on earth? On Mars=3.2 m/s/s)? ...
... NOTE: MASS and WEIGHT are NOT the same thing. MASS never changes When an object moves to a different planet. What is the weight of an 85.3-kg person on earth? On Mars=3.2 m/s/s)? ...
111
... Use: The acceleration of gravity g = 10 m/s2 and The universal gravitational constant G = 6.67x10-11 N.m2/kg2. The density of pure water = 1 g/cm3 = 1000 kg/m3 1) Which one of the following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at constant velocit ...
... Use: The acceleration of gravity g = 10 m/s2 and The universal gravitational constant G = 6.67x10-11 N.m2/kg2. The density of pure water = 1 g/cm3 = 1000 kg/m3 1) Which one of the following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at constant velocit ...
Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Problems: SHOW YOUR WORK
... _____ 28. When you turn suddenly to the left in a car your body is pushed to the right. _____ 29. A tractor pulling a full trailer will accelerate slower then a tractor pulling an empty trailer. _____ 30. A rocket lifts because an unbalanced force is acted upon it. _____ 31. The acceleration of the ...
... _____ 28. When you turn suddenly to the left in a car your body is pushed to the right. _____ 29. A tractor pulling a full trailer will accelerate slower then a tractor pulling an empty trailer. _____ 30. A rocket lifts because an unbalanced force is acted upon it. _____ 31. The acceleration of the ...
1 - FreeScienceStuff.com
... A Inertia B Friction C Gravity D A net force 8. In a head-on car crash, passengers not wearing seat belts continue to move forward with the same ___________ that the car had prior to impact. ...
... A Inertia B Friction C Gravity D A net force 8. In a head-on car crash, passengers not wearing seat belts continue to move forward with the same ___________ that the car had prior to impact. ...