Newton`s 2nd Law Problems
... skateboard at the beginning of the interval and is removed at the end. The skateboard takes 8.5 s to travel the 1.0 m distance, and it then coasts for another 1.25 m before coming to rest. Calculate the force applied to the skateboard, and the constant frictional force apposing its motion. (2.6 x 10 ...
... skateboard at the beginning of the interval and is removed at the end. The skateboard takes 8.5 s to travel the 1.0 m distance, and it then coasts for another 1.25 m before coming to rest. Calculate the force applied to the skateboard, and the constant frictional force apposing its motion. (2.6 x 10 ...
Chapter-9 Rotational Dynamics
... 2.Draw a free-body diagram that shows all the external forces acting on the object. 3.Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4.Apply the equations that specify the balance of forces at equilibrium: SFx = 0 and SFy = 0. 5.Select a conven ...
... 2.Draw a free-body diagram that shows all the external forces acting on the object. 3.Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4.Apply the equations that specify the balance of forces at equilibrium: SFx = 0 and SFy = 0. 5.Select a conven ...
Projectile motion and drag
... This section shows the use of a spreadsheet to calculate the properties of the motion of an object projected vertically upwards and affected by air resistance. Velocity at any point = v Drag force is proportional to v2 Drag force = Cv2 where C is the drag coefficient [= 0.00077 in this case] Acceler ...
... This section shows the use of a spreadsheet to calculate the properties of the motion of an object projected vertically upwards and affected by air resistance. Velocity at any point = v Drag force is proportional to v2 Drag force = Cv2 where C is the drag coefficient [= 0.00077 in this case] Acceler ...
File
... 20. An exceptional standing jump would raise a person 0.80m off the ground. To do this, what force must a 70kg person exert against the ground? 21. Calculate the force of gravity between two bowling balls each of which has a mass of 8.0kg, when they are 0.50m apart (centre to centre.) 22. Calculate ...
... 20. An exceptional standing jump would raise a person 0.80m off the ground. To do this, what force must a 70kg person exert against the ground? 21. Calculate the force of gravity between two bowling balls each of which has a mass of 8.0kg, when they are 0.50m apart (centre to centre.) 22. Calculate ...
PowerPoint
... 2. The cannon ball because it’s heavier. 3. Both the same since he used the same kick. 4. The soccer ball, but for some other reason. 5. The cannon ball, but for some other reason. 6. Both the same, but for some other reason. ...
... 2. The cannon ball because it’s heavier. 3. Both the same since he used the same kick. 4. The soccer ball, but for some other reason. 5. The cannon ball, but for some other reason. 6. Both the same, but for some other reason. ...
Unit 3 Vocabulary words
... Acceleration - change in velocity divided by the amount of time needed for that change to take place; occurs when an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction Balanced forces – forces that are equal but opposite in direction; when they act on an object, they cancel each other out, and no ch ...
... Acceleration - change in velocity divided by the amount of time needed for that change to take place; occurs when an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction Balanced forces – forces that are equal but opposite in direction; when they act on an object, they cancel each other out, and no ch ...
Gravity
... Why do all objects have the same free-fall acceleration? Newton’s second law shows that acceleration depends on both the force on an object and its mass. A heavier object experiences a greater gravitational force than a lighter object. However, a heavier object is also harder to accelerate beca ...
... Why do all objects have the same free-fall acceleration? Newton’s second law shows that acceleration depends on both the force on an object and its mass. A heavier object experiences a greater gravitational force than a lighter object. However, a heavier object is also harder to accelerate beca ...
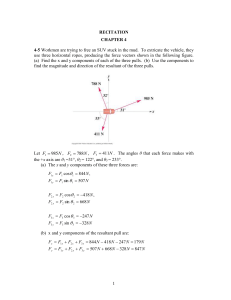
Recitation Ch 4-1
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
Document
... a) Many Possible Experiments. For example, students could decide to pull with the same force on various air gliders of different masses with spring scales to determine if the acceleration depends on 1/m. b) The best experiment should create the best chance of disproving the relationship a = ΣF/m c) ...
... a) Many Possible Experiments. For example, students could decide to pull with the same force on various air gliders of different masses with spring scales to determine if the acceleration depends on 1/m. b) The best experiment should create the best chance of disproving the relationship a = ΣF/m c) ...
blue exam answers
... After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside the exam and turn in at the front of the lecture room. No form number is necessary. No section # is necessary. Pl ...
... After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside the exam and turn in at the front of the lecture room. No form number is necessary. No section # is necessary. Pl ...
Physics I - Rose
... information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of the object. The sensation from the textbook is about five times the sensation from the pound weight. So we conclude th ...
... information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of the object. The sensation from the textbook is about five times the sensation from the pound weight. So we conclude th ...
Name Date ______ Block ___ Physics Final Study Guide part 2
... 10. For an object moving along a trajectory, the horizontal velocity of the object __________ as the position changes. 11. What is the vertical change in position of an object that is dropped and that of an identical object that is thrown horizontally from the same height? 12. In trajectory motion, ...
... 10. For an object moving along a trajectory, the horizontal velocity of the object __________ as the position changes. 11. What is the vertical change in position of an object that is dropped and that of an identical object that is thrown horizontally from the same height? 12. In trajectory motion, ...
Physics Final Exam Study Guide
... Unit 2- Vectors and Projectiles - rules for adding vectors - vector vs. scalar quantities - determine magnitude and direction of a vector - determine vertical and horizontal components of a projectile launched at an angle - describe horizontal and vertical velocity changes of a projectile during its ...
... Unit 2- Vectors and Projectiles - rules for adding vectors - vector vs. scalar quantities - determine magnitude and direction of a vector - determine vertical and horizontal components of a projectile launched at an angle - describe horizontal and vertical velocity changes of a projectile during its ...
Name: Date: Period: Study Guide for Quiz Directions: Answer each
... 8. When you want to jump from one building to another and clearing the jump nicely without getting hurt, which Newton’s law does this apply to? What are you building in order to clear the jump nicely (Hint: Starts with an M)? ...
... 8. When you want to jump from one building to another and clearing the jump nicely without getting hurt, which Newton’s law does this apply to? What are you building in order to clear the jump nicely (Hint: Starts with an M)? ...