Honors Physics Unit 5 Notes
... to push her toward the door From the frame of the Earth, the car applies a leftward force on the passenger The outward force is often called a centrifugal force ...
... to push her toward the door From the frame of the Earth, the car applies a leftward force on the passenger The outward force is often called a centrifugal force ...
Motion and Forces Study Guide
... the teacher in class if there are any questions. Motion is change in position over a period of time. Frame of referenceWhenever you describe something that is moving, you are comparing it with something that is assumed to be stationary, or not moving. The background or object that is used for compar ...
... the teacher in class if there are any questions. Motion is change in position over a period of time. Frame of referenceWhenever you describe something that is moving, you are comparing it with something that is assumed to be stationary, or not moving. The background or object that is used for compar ...
Document
... The correct unit for weight force is the newton (N). What is your metric weight? (reminder 1 kg=~2.2 lb.) Divide your weight by 2.2 lbs to convert it to mass, then multiply by 9.8m/sec2. This will give your wt. in newtons. ...
... The correct unit for weight force is the newton (N). What is your metric weight? (reminder 1 kg=~2.2 lb.) Divide your weight by 2.2 lbs to convert it to mass, then multiply by 9.8m/sec2. This will give your wt. in newtons. ...
Force - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force • If the net force = 0, then the object’s state motion will remain unchanged ...
... • An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force • If the net force = 0, then the object’s state motion will remain unchanged ...
Forces and Motion
... The fluid friction experienced by objects falling through the air. The product of an object’s mass and velocity. The motion of a falling object when the only force acting on it is gravity. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two surfaces rub against each other. The tendency of an o ...
... The fluid friction experienced by objects falling through the air. The product of an object’s mass and velocity. The motion of a falling object when the only force acting on it is gravity. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two surfaces rub against each other. The tendency of an o ...
Newton`s Laws - Dr. Robert MacKay
... • The acceleration of an object describes how fast its velocity changes. • If an object travels in a straight line with constant speed the acceleration is zero. • Whenever an object either changes speed of changes direction it is accelerating. ...
... • The acceleration of an object describes how fast its velocity changes. • If an object travels in a straight line with constant speed the acceleration is zero. • Whenever an object either changes speed of changes direction it is accelerating. ...
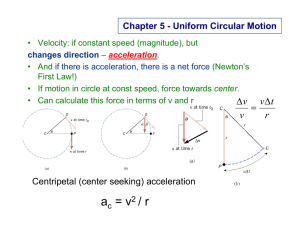
Centripetal acceleration
... center of the circular path and perpendicular to it. • Realize that Fto center=mac=mv2/r ...
... center of the circular path and perpendicular to it. • Realize that Fto center=mac=mv2/r ...
Lecture 3 The Physics of Objects in Motion
... – Proposed that the Earth revolved around the Sun from observations of the motion of planets. – Because the concept of inertia was unknown at his time, the idea of a moving Earth was difficult to comprehend. ...
... – Proposed that the Earth revolved around the Sun from observations of the motion of planets. – Because the concept of inertia was unknown at his time, the idea of a moving Earth was difficult to comprehend. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law Note
... motion can be described (words, graphs, diagrams, numbers, etc.) were discussed. In this unit (Newton's Laws of Motion), the ways in which motion can be explained will be discussed. Isaac Newton (a 17th century scientist) put forth a variety of laws which explain why objects move (or don't move) as ...
... motion can be described (words, graphs, diagrams, numbers, etc.) were discussed. In this unit (Newton's Laws of Motion), the ways in which motion can be explained will be discussed. Isaac Newton (a 17th century scientist) put forth a variety of laws which explain why objects move (or don't move) as ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... continue the motion they already have unless they are acted on by a net force. If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
... continue the motion they already have unless they are acted on by a net force. If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
Kinematics Distance X Total length travelled (direction doesn`t affect
... *Instantaneous speed = magnitude of instantaneous velocity, but average speed magnitude of average velocity Acceleration ...
... *Instantaneous speed = magnitude of instantaneous velocity, but average speed magnitude of average velocity Acceleration ...
1020 Test review
... On earth’s surface, all falling balls accelerate downward at 9.8 meter/second2 ...
... On earth’s surface, all falling balls accelerate downward at 9.8 meter/second2 ...
Work - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... kinetic and potential energy). (We will learn more about energy soon!) Work is done only if an object moves. When the work is done upon the object, that object gains energy Work is only done on an object when the force and displacement are in the same direction. ...
... kinetic and potential energy). (We will learn more about energy soon!) Work is done only if an object moves. When the work is done upon the object, that object gains energy Work is only done on an object when the force and displacement are in the same direction. ...