Physics Stations
... Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another w ...
... Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another w ...
Monday, September 24, 2007
... We’ve been learning kinematics; describing motion without understanding what the cause of the motion is. Now we are going to learn dynamics!! FORCE is what causes an object to move. Can someone tell me The above statement is not entirely correct. Why? what FORCE is? Because when an object is moving ...
... We’ve been learning kinematics; describing motion without understanding what the cause of the motion is. Now we are going to learn dynamics!! FORCE is what causes an object to move. Can someone tell me The above statement is not entirely correct. Why? what FORCE is? Because when an object is moving ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... a) A crate of mass m is on the flat bed of a pick up truck. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the truck is m. The truck is traveling at the constant velocity of magnitude V1. Draw the free body diagram for the crate. b) The truck starts to accelerate with an acceleration ac. Draw the ...
... a) A crate of mass m is on the flat bed of a pick up truck. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the truck is m. The truck is traveling at the constant velocity of magnitude V1. Draw the free body diagram for the crate. b) The truck starts to accelerate with an acceleration ac. Draw the ...
saint patrick`s high school
... 1. READ each question very carefully. There are no marks for answering a question not asked or for neglecting to answer a question. 2. Mark all answers directly on this paper. Use scrap paper if necessary, but it will not be marked. 3. Scientific calculators and rulers are allowed. 4. Write down as ...
... 1. READ each question very carefully. There are no marks for answering a question not asked or for neglecting to answer a question. 2. Mark all answers directly on this paper. Use scrap paper if necessary, but it will not be marked. 3. Scientific calculators and rulers are allowed. 4. Write down as ...
Word
... 14) If you were to travel to the moon, you would cross a certain spot at which the net gravitational force on you (from the earth and the moon anyway) would be zero. Where would this spot be located; closer to earth, closer to the moon, or equal distance from both? Explain. Since the earth is much ...
... 14) If you were to travel to the moon, you would cross a certain spot at which the net gravitational force on you (from the earth and the moon anyway) would be zero. Where would this spot be located; closer to earth, closer to the moon, or equal distance from both? Explain. Since the earth is much ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
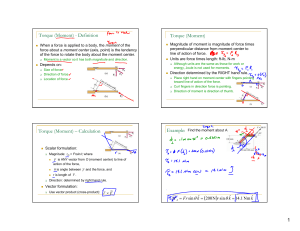
... Example: Hoisting a Crate A motor is used to lift a crate with the dual pulley system shown below. The combined moment of inertia of the dual pulley is 46.0 kg·m2. The crate has a mass of 451 kg. A tension of 2150 N is maintained in the cable attached to the motor. Find the angular acceleration of t ...
... Example: Hoisting a Crate A motor is used to lift a crate with the dual pulley system shown below. The combined moment of inertia of the dual pulley is 46.0 kg·m2. The crate has a mass of 451 kg. A tension of 2150 N is maintained in the cable attached to the motor. Find the angular acceleration of t ...
File
... Net force is the vector sum (so both mag & direction) of all the forces acting on an object at one time Last chapter we called this Resultant Force – FR If an object’s Fnet = 0, then the object satisfies the condition in Newton’s 1st Law to be maintaining its state of motion - either at rest or ...
... Net force is the vector sum (so both mag & direction) of all the forces acting on an object at one time Last chapter we called this Resultant Force – FR If an object’s Fnet = 0, then the object satisfies the condition in Newton’s 1st Law to be maintaining its state of motion - either at rest or ...
Newton*s 1st Law * Objectives:
... If two individual forces are of equal magnitude and opposite direction, then the forces are said to be balanced. ...
... If two individual forces are of equal magnitude and opposite direction, then the forces are said to be balanced. ...
Unit 1
... on an object, the greater its change in motion; however, the same amount of force applied to an object with less mass results in a greater acceleration. • While Newton’s second law describes a single object, forces always come in equal and opposite pairs due to interaction between objects. Give exam ...
... on an object, the greater its change in motion; however, the same amount of force applied to an object with less mass results in a greater acceleration. • While Newton’s second law describes a single object, forces always come in equal and opposite pairs due to interaction between objects. Give exam ...
(the terminal velocity is smaller for larger cross
... 1.Force is a vector 2.The direction of acceleration vector is the same as the direction of the force vector 3.The magnitude of the force and acceleration are related by a constant which depends on number of blocks ...
... 1.Force is a vector 2.The direction of acceleration vector is the same as the direction of the force vector 3.The magnitude of the force and acceleration are related by a constant which depends on number of blocks ...
A Net Force
... If there is no horizontally applied force, then the object will be: • stationary (v = 0 m/s) • or in motion, sliding along a frictionless surface at a constant velocity (v = constant). •Under both circumstances, Fnet = 0 N since there is no acceleration. ...
... If there is no horizontally applied force, then the object will be: • stationary (v = 0 m/s) • or in motion, sliding along a frictionless surface at a constant velocity (v = constant). •Under both circumstances, Fnet = 0 N since there is no acceleration. ...
Episode 209 - Teaching Advanced Physics
... Why does a piece of paper fall more slowly under gravity than a piece of chalk if the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects? (Demonstrate this.) If an object is falling through the air with constant velocity, what can you say about the net force on the object? How do the forces on ...
... Why does a piece of paper fall more slowly under gravity than a piece of chalk if the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects? (Demonstrate this.) If an object is falling through the air with constant velocity, what can you say about the net force on the object? How do the forces on ...