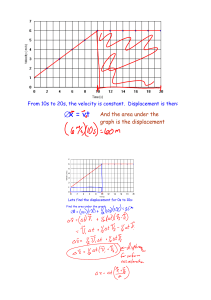
When objects are thrown or launched at an
... Imagine that Adam can watch the apple only. What path will Adam see it take? Remember that the apple has the same horizontal velocity as the car. From Adam’s frame of reference, or point of view, the path will be curved like that of the launched golf ball. Will Jami see the same path? Jami and the ...
... Imagine that Adam can watch the apple only. What path will Adam see it take? Remember that the apple has the same horizontal velocity as the car. From Adam’s frame of reference, or point of view, the path will be curved like that of the launched golf ball. Will Jami see the same path? Jami and the ...
Straw Tower
... Tension: The stress/force felt when an object is being pulled apart (outward). If a tennis ball is suspended near the top of the tower by a net of tape, the tape is under tension because the weight of the tennis ball is pulling on the tape. Torque: It is a force that tends to rotate or turn things. ...
... Tension: The stress/force felt when an object is being pulled apart (outward). If a tennis ball is suspended near the top of the tower by a net of tape, the tape is under tension because the weight of the tennis ball is pulling on the tape. Torque: It is a force that tends to rotate or turn things. ...
Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Gravitation
... the car enters the turn, your inertia makes to tend to move along the original straightline path. This movement is in accordance with Newton’s first law, which states that the natural tendency of a body is to continue moving in a straight line. ...
... the car enters the turn, your inertia makes to tend to move along the original straightline path. This movement is in accordance with Newton’s first law, which states that the natural tendency of a body is to continue moving in a straight line. ...
mi11
... distance, maximum, conserved, v / r, different, , velocity, torque, I, second, force, angle Spinning around When we want to describe the movement of an object we can talk about its velocity and its acceleration. But what about something like a CD which stays in the same place but spins around? Diff ...
... distance, maximum, conserved, v / r, different, , velocity, torque, I, second, force, angle Spinning around When we want to describe the movement of an object we can talk about its velocity and its acceleration. But what about something like a CD which stays in the same place but spins around? Diff ...
Chapter 3 Forces and Motion
... How a resultant force can give rise to motion in a circle The effect of air resistance on a moving object How force, mass and acceleration are related How a force changes an object’s momentum How to calculate the resultant of two or more vectors ...
... How a resultant force can give rise to motion in a circle The effect of air resistance on a moving object How force, mass and acceleration are related How a force changes an object’s momentum How to calculate the resultant of two or more vectors ...
Physics 102 Introduction to Physics
... Units of mass = kg English Units of weight = pounds (lb) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 2.2 lb In metric units, weight is expressed in Newtons (N) The acceleration of gravity is g = 9.8 m/s2 (or about 10 m/s2) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 9.8 N (or about 10 N) Problem: What is the weight of ...
... Units of mass = kg English Units of weight = pounds (lb) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 2.2 lb In metric units, weight is expressed in Newtons (N) The acceleration of gravity is g = 9.8 m/s2 (or about 10 m/s2) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 9.8 N (or about 10 N) Problem: What is the weight of ...
notes about solving friction problems
... surfaces; it can never be below zero and is usually less than 1. The coefficient of friction for rubber tires on pavement is about 0.8; for skates on ice it is about 0.1. Our Toolbox so far… We can now include this friction equation in our toolbox, since it is pretty useful to us. (There is one more ...
... surfaces; it can never be below zero and is usually less than 1. The coefficient of friction for rubber tires on pavement is about 0.8; for skates on ice it is about 0.1. Our Toolbox so far… We can now include this friction equation in our toolbox, since it is pretty useful to us. (There is one more ...
Physics 111 Practice Problems
... another cord from the ceiling (Fig. 5-33a). What is the reading on the scale, which is marked in weight units? (b) In Fig. 5-33b the salami is supported by a cord that runs around a pulley and to a scale. The opposite end of the scale is attached by a cord to a wall. What is the reading on the scale ...
... another cord from the ceiling (Fig. 5-33a). What is the reading on the scale, which is marked in weight units? (b) In Fig. 5-33b the salami is supported by a cord that runs around a pulley and to a scale. The opposite end of the scale is attached by a cord to a wall. What is the reading on the scale ...
Notes - UMD Physics
... Then the centripetal acceleration, also called the lateral acceleration, is calculated as a multiple of the free-fall acceleration g. A Dodge Viper GTS can negotiate a skidpad of radius 61.0 m at 86.5 km/h (53.7 mph). Calculate its maximum lateral acceleration. ...
... Then the centripetal acceleration, also called the lateral acceleration, is calculated as a multiple of the free-fall acceleration g. A Dodge Viper GTS can negotiate a skidpad of radius 61.0 m at 86.5 km/h (53.7 mph). Calculate its maximum lateral acceleration. ...
Chapter 4-physics - Mrs. Krusa`s Wikispace
... Example: A 50.0 kg bucket is being lifted by a rope. The rope will not break if the tension is 525 N or less. The bucket started at rest, and after being lifted 3.0 m, it is moving at 3.0 m/s. If the acceleration is constant, is the rope in danger of breaking? ...
... Example: A 50.0 kg bucket is being lifted by a rope. The rope will not break if the tension is 525 N or less. The bucket started at rest, and after being lifted 3.0 m, it is moving at 3.0 m/s. If the acceleration is constant, is the rope in danger of breaking? ...
Newton`s Second Law NOTES
... objects. This is particularly apparent at the scale of the atom. An electron, mass 9.1 x 10-31 kg, experiences a force of 1.6 x 10-17 N in a typical electric field at the earth’s surface. From rest, how much time would it take for the electron to reach a speed of 3.0 x 106 m/s, 1% of the speed of li ...
... objects. This is particularly apparent at the scale of the atom. An electron, mass 9.1 x 10-31 kg, experiences a force of 1.6 x 10-17 N in a typical electric field at the earth’s surface. From rest, how much time would it take for the electron to reach a speed of 3.0 x 106 m/s, 1% of the speed of li ...
mj force and motion - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Change in distance per unit of time • A vector is a number (a magnitude) together with a direction (compare with scalar). A vector can be represented by an arrow whose length represents the magnitude and the direction represents the direction. • Magnitude- the property of relative size or extent ( ...
... • Change in distance per unit of time • A vector is a number (a magnitude) together with a direction (compare with scalar). A vector can be represented by an arrow whose length represents the magnitude and the direction represents the direction. • Magnitude- the property of relative size or extent ( ...
Newtons 1st Law of Motion
... •All objects were classified into categories of earth, water, air, or fire. •“Natural motion” occurred when an object sought to return to its “natural place” after being moved from it by some type of “violent motion.” •To keep an object moving would require a force. ...
... •All objects were classified into categories of earth, water, air, or fire. •“Natural motion” occurred when an object sought to return to its “natural place” after being moved from it by some type of “violent motion.” •To keep an object moving would require a force. ...
How Do I Move? - tpsexercisescience12
... Occurs when a body moves along a circular path, through the same angle, in the same direction, and at the same time ...
... Occurs when a body moves along a circular path, through the same angle, in the same direction, and at the same time ...