Chapter 4 - Planet Holloway
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
Chapter 5 Lectures
... Mass is one of the single most misunderstood concepts in chemistry and physics. It is not the same as “weight,” although the two measurements are related. Mass is a measure of the amount of inertia that a body has—it’s a measure of how hard it is to change an object’s motion. The more mass you have, ...
... Mass is one of the single most misunderstood concepts in chemistry and physics. It is not the same as “weight,” although the two measurements are related. Mass is a measure of the amount of inertia that a body has—it’s a measure of how hard it is to change an object’s motion. The more mass you have, ...
Chapter 5 Rotational Motion File
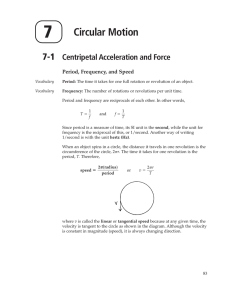
... • Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction • When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular acceleration – The tangential (linear) speed ...
... • Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction • When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular acceleration – The tangential (linear) speed ...
B. Multiple Choice Questions
... 4. Block A is heavier than Block B. The force F is the same in both configurations. The surface is frictionless. The acceleration of Block A A.) is larger than Block B. A B.) is smaller than Block B. F C.) is the same as Block B. D.) can not be determined. E.) none of the above. F ...
... 4. Block A is heavier than Block B. The force F is the same in both configurations. The surface is frictionless. The acceleration of Block A A.) is larger than Block B. A B.) is smaller than Block B. F C.) is the same as Block B. D.) can not be determined. E.) none of the above. F ...
Wednesday, Feb. 6, 2002
... A ball of mass m is attached to the end of a cord of length R. The ball is moving in a vertical circle. Determine the tension of the cord at any instant when the speed of the ball is v and the cord makes an angle q with vertical. ...
... A ball of mass m is attached to the end of a cord of length R. The ball is moving in a vertical circle. Determine the tension of the cord at any instant when the speed of the ball is v and the cord makes an angle q with vertical. ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... 1. Open Logger Pro file “Force Probe”. Go to Experiment, Data Collection, change the “Sampling Rate” to 200 samples per second. ZERO the force probe while it is in the horizontal position. 2. Start the ball from its optimal location on the ramp – the place that gets you the best speed. Let the ball ...
... 1. Open Logger Pro file “Force Probe”. Go to Experiment, Data Collection, change the “Sampling Rate” to 200 samples per second. ZERO the force probe while it is in the horizontal position. 2. Start the ball from its optimal location on the ramp – the place that gets you the best speed. Let the ball ...
File
... A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magnitude given by F = bv, where t is the speed of the ball and b is a positive constant. The magnitude of the acceleration a of the ball at any time is equal to which of the foll ...
... A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magnitude given by F = bv, where t is the speed of the ball and b is a positive constant. The magnitude of the acceleration a of the ball at any time is equal to which of the foll ...
Forces and Motion - Catawba County Schools
... Projectile Motion is the motion of a falling object (projectile) after it is given an initial forward velocity. * Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile. * The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward vertical force of gravity causes the ball to fol ...
... Projectile Motion is the motion of a falling object (projectile) after it is given an initial forward velocity. * Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile. * The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward vertical force of gravity causes the ball to fol ...
Forces
... • A book resting on a table has the force of gravity pulling it toward the Earth, but the book is not moving or accelerating, so there must be opposing forces acting on the book. This force is caused by the table and is known as the normal force. . Normal Force is the force of an object pushing back ...
... • A book resting on a table has the force of gravity pulling it toward the Earth, but the book is not moving or accelerating, so there must be opposing forces acting on the book. This force is caused by the table and is known as the normal force. . Normal Force is the force of an object pushing back ...
Newton`s Laws PPT for HTML
... Newton’s First Law of Motion “The Law of Inertia” “An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue to move at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by a net external force.” The property of an object that causes it to resist changes in its motion is called inertia. Iner ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion “The Law of Inertia” “An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue to move at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by a net external force.” The property of an object that causes it to resist changes in its motion is called inertia. Iner ...
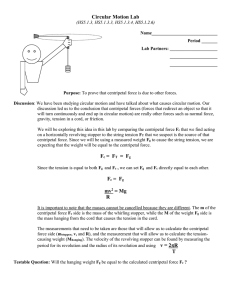
Circular Motion Lab
... 1. Measure the mass of the stopper and convert this mass to kilograms 2. For each trial measure: the mass that you are hanging off the end of the string in kilograms the time it takes to swing the stopper in 10 complete circles at a constant radius (this will be divided by 10 to obtain the perio ...
... 1. Measure the mass of the stopper and convert this mass to kilograms 2. For each trial measure: the mass that you are hanging off the end of the string in kilograms the time it takes to swing the stopper in 10 complete circles at a constant radius (this will be divided by 10 to obtain the perio ...
Newton
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. • Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. • As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to a ...
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. • Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. • As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to a ...
Application of Forces
... Angular moment follows Newton’s first law (which in this case is known as the ‘conservation of angular momentum.’ A body will continue spinning unless a force (e.g. air resistance, friction) acts on it. ...
... Angular moment follows Newton’s first law (which in this case is known as the ‘conservation of angular momentum.’ A body will continue spinning unless a force (e.g. air resistance, friction) acts on it. ...
HonorsReview
... The questions are based on all the topics that have been covered during the school year. The focus is on constant velocity, Uniform acceleration, Forces balanced and Unbalanced, Projectile motion, circular motion, energy, and Momentum, Impulse. During the school year we have used different represent ...
... The questions are based on all the topics that have been covered during the school year. The focus is on constant velocity, Uniform acceleration, Forces balanced and Unbalanced, Projectile motion, circular motion, energy, and Momentum, Impulse. During the school year we have used different represent ...
Chapter 14 - Simple Harmonic Motion
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
No Slide Title
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...