Forces
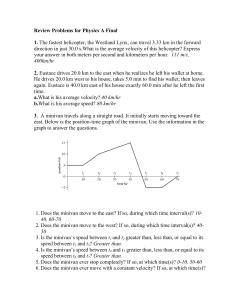
... Air resistance creates a resistive force opposite to the force of gravity. The faster an object falls, the bigger the resistive force. Eventually the upwards resistive force becomes as big as the downwards gravitational force. The two forces are equal and opposite, so there is no net force. When the ...
... Air resistance creates a resistive force opposite to the force of gravity. The faster an object falls, the bigger the resistive force. Eventually the upwards resistive force becomes as big as the downwards gravitational force. The two forces are equal and opposite, so there is no net force. When the ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... 2. If you push harder, is the change in motion smaller or larger? 3. Do you think this is a direct or inverse relationship? 4. Assume that you have a bowling ball and a baseball, each suspended from a different rope. If you hit each of these balls with a full swing of a baseball bat, which ball will ...
... 2. If you push harder, is the change in motion smaller or larger? 3. Do you think this is a direct or inverse relationship? 4. Assume that you have a bowling ball and a baseball, each suspended from a different rope. If you hit each of these balls with a full swing of a baseball bat, which ball will ...
Newton_sFirstLawo1ch
... some time off for a little putt-putt golf. The 15th hole at the Hole-In-One PuttPutt Golf Course has a large metal rim that putters must use to guide their ball towards the hole. Mr. S guides a golf ball around the metal rim When the ball leaves the rim, which path (1, 2, or 3) will the golf ball fo ...
... some time off for a little putt-putt golf. The 15th hole at the Hole-In-One PuttPutt Golf Course has a large metal rim that putters must use to guide their ball towards the hole. Mr. S guides a golf ball around the metal rim When the ball leaves the rim, which path (1, 2, or 3) will the golf ball fo ...
Powerpoint Slides - Faculty Web Sites
... 1. Newton’s 1st Law: An object at rest, remains at rest, OR if in motion, travels in a straight line at constant velocity, UNLESS acted on by a net force. ...
... 1. Newton’s 1st Law: An object at rest, remains at rest, OR if in motion, travels in a straight line at constant velocity, UNLESS acted on by a net force. ...
document
... under discussion could be moving. In fact, Anna suggests that if friction and air resistance could be ignored (because of their negligible size), the object could be moving in a horizontal direction. According to Anna, an object experiencing forces as described at the right could be experiencing a h ...
... under discussion could be moving. In fact, Anna suggests that if friction and air resistance could be ignored (because of their negligible size), the object could be moving in a horizontal direction. According to Anna, an object experiencing forces as described at the right could be experiencing a h ...
Conceptual Physics 2.2 PP
... An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion with the same speed and direction UNLESS acted on by a force. ...
... An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion with the same speed and direction UNLESS acted on by a force. ...
Dependence of central force on angular velocity
... The yellow digital display at the lower left shows the theoretical central force based on the values entered for the car mass, radial distance from the rotational axis and the current measured angular velocity. This can be continuously compared to the current force displayed in the upper left of the ...
... The yellow digital display at the lower left shows the theoretical central force based on the values entered for the car mass, radial distance from the rotational axis and the current measured angular velocity. This can be continuously compared to the current force displayed in the upper left of the ...
Chapter 5 Lectures
... Mass is one of the single most misunderstood concepts in chemistry and physics. It is not the same as “weight,” although the two measurements are related. Mass is a measure of the amount of inertia that a body has—it’s a measure of how hard it is to change an object’s motion. The more mass you have, ...
... Mass is one of the single most misunderstood concepts in chemistry and physics. It is not the same as “weight,” although the two measurements are related. Mass is a measure of the amount of inertia that a body has—it’s a measure of how hard it is to change an object’s motion. The more mass you have, ...
Motion in one and two dimensions
... All motions are relative.The motion (velocity) of an object depends on which frame of reference is used to measure it. We say the measured velocity is relative to the chosen frame of reference. Usually the ground is the preferred choice as the reference frame and very often it is not specifically me ...
... All motions are relative.The motion (velocity) of an object depends on which frame of reference is used to measure it. We say the measured velocity is relative to the chosen frame of reference. Usually the ground is the preferred choice as the reference frame and very often it is not specifically me ...
Chapter 4 - Planet Holloway
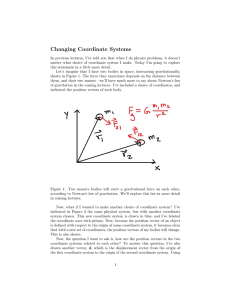
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...