Eighth International Conference on Geometry, Integrability and Quantization
... such as the position and momentum. ...
... such as the position and momentum. ...
Homework 2
... and initial momentum p0 = 0. The scattered photon has the wave vector k. Based on the conservation of the relativistic energy and momentum, determine the shift λ − λ0 of the wave length of the scattered photon as a function of the scattering angle θ between k and k0 . (Remark: Special relativity yie ...
... and initial momentum p0 = 0. The scattered photon has the wave vector k. Based on the conservation of the relativistic energy and momentum, determine the shift λ − λ0 of the wave length of the scattered photon as a function of the scattering angle θ between k and k0 . (Remark: Special relativity yie ...
The Relativistic Quantum World
... that particles (electrons) “are carried” by waves. Original idea: a physical wave Quantum mechanics: probability wave! Particle wavelength: ...
... that particles (electrons) “are carried” by waves. Original idea: a physical wave Quantum mechanics: probability wave! Particle wavelength: ...
Document
... from Niels Bohr who explained experimentally observed discrete nature of atomic spectrum of Hydrogen. In spite of its immediate success in providing theoretical account of the spectrum and other nature of Hydrogen atom, a complete understanding of Bohr’s atom came only after de Broglie’s conjecture ...
... from Niels Bohr who explained experimentally observed discrete nature of atomic spectrum of Hydrogen. In spite of its immediate success in providing theoretical account of the spectrum and other nature of Hydrogen atom, a complete understanding of Bohr’s atom came only after de Broglie’s conjecture ...
[2011 question paper]
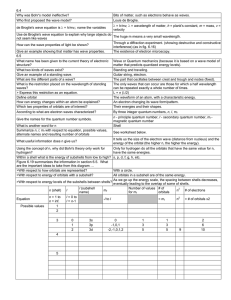
... (b) Find the value of A such that the particle can be found somewhere in [−∞, ∞] with probability one. (c) Find the expectation value of position hxi and standard deviation of position q ∆x = hx2 i − hxi2 in the above initial gaussian wave packet state. (d) Write down the free particle Schrödinger ...
... (b) Find the value of A such that the particle can be found somewhere in [−∞, ∞] with probability one. (c) Find the expectation value of position hxi and standard deviation of position q ∆x = hx2 i − hxi2 in the above initial gaussian wave packet state. (d) Write down the free particle Schrödinger ...
InorgCh2.1
... a) Rutherford and Moseley quickly discovered the charge of the nucleus i. Electron beams aimed at an element caused X-rays to be emitted ii. The square root of the X-ray frequency emitted had a linear relationship with about half of the atomic mass of the element iii. This number was clearly Z, the ...
... a) Rutherford and Moseley quickly discovered the charge of the nucleus i. Electron beams aimed at an element caused X-rays to be emitted ii. The square root of the X-ray frequency emitted had a linear relationship with about half of the atomic mass of the element iii. This number was clearly Z, the ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... 10. What type of spectra would be created by exciting xenon gas? 11. What element did Bohr use to support his theory on bright line spectra? 12. Energy of a photon is directly proportional to what wave property? 13. What is a spectrum? 14. What two forms of energy can generally be used to excite an ...
... 10. What type of spectra would be created by exciting xenon gas? 11. What element did Bohr use to support his theory on bright line spectra? 12. Energy of a photon is directly proportional to what wave property? 13. What is a spectrum? 14. What two forms of energy can generally be used to excite an ...
Lecture 25: Wave mechanics
... if we were to describe position and momentum of “quantum size” particle it will be difficult to measure both the quantities simultaneously. That is, the act of measuring position of a particle, say by shining a light on it, will influence the momentum of the particle creating uncertainty in both the ...
... if we were to describe position and momentum of “quantum size” particle it will be difficult to measure both the quantities simultaneously. That is, the act of measuring position of a particle, say by shining a light on it, will influence the momentum of the particle creating uncertainty in both the ...
Final “Intro Quantum Mechanics”
... (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his constant. (b) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the structure of atoms, as classical physics gives the w ...
... (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his constant. (b) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the structure of atoms, as classical physics gives the w ...
Quantum Mechanics and the Bohr Model - slater science
... • Using the line as the midpoint draw two waves superimposed on each other. Both waves should have the same amplitude but different frequencies. • Draw another horizontal line and two waves with the same wavelength but different amplitudes. ...
... • Using the line as the midpoint draw two waves superimposed on each other. Both waves should have the same amplitude but different frequencies. • Draw another horizontal line and two waves with the same wavelength but different amplitudes. ...
Handout
... Experiments confirm that electron behave like waves and interfere with themselves - particles are waves! ...
... Experiments confirm that electron behave like waves and interfere with themselves - particles are waves! ...
Chapter2. Elements of quantum mechanics
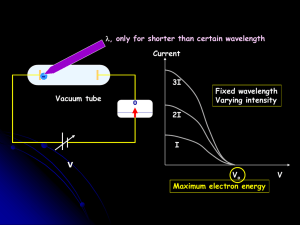
... An observation by Plank : radiation from a heated sample is emitted in discrete units of energy, called quanta ; the energy units were described by h, where is the frequency of the radiation, and h is a quantity called Plank’s constant En=nhν=nћω, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J·s, ћ=h/2π Quantization of ligh ...
... An observation by Plank : radiation from a heated sample is emitted in discrete units of energy, called quanta ; the energy units were described by h, where is the frequency of the radiation, and h is a quantity called Plank’s constant En=nhν=nћω, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J·s, ћ=h/2π Quantization of ligh ...







![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881811_1-8ef23f7493d56bc511a2c01dcc81fc96-300x300.png)