ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... stove burner or the light from a light bulb. Max Planck (1900) hypothesized that energy can be released or absorbed by atoms in certain amounts. He called these amounts quanta. A quantum is the smallest amount of energy that can be absorbed or released as EMR The relationship is: E = h where h ...
... stove burner or the light from a light bulb. Max Planck (1900) hypothesized that energy can be released or absorbed by atoms in certain amounts. He called these amounts quanta. A quantum is the smallest amount of energy that can be absorbed or released as EMR The relationship is: E = h where h ...
Ch 7 Lecture Notes
... 1. The presence of ______________ rather than a complete spectrum when elements were heated. ...
... 1. The presence of ______________ rather than a complete spectrum when elements were heated. ...
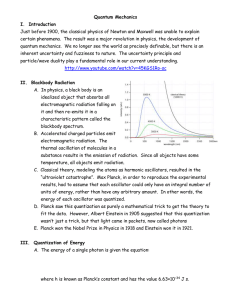
Quantization of Energy
... impacted by relativity and the photoelectric effect, both of which had been introduced in his lifetime. The photoelectric effect pointed to the particle properties of light, which had been considered to be a wave phenomenon. He wondered if electons and other "particles" might exhibit wave properties ...
... impacted by relativity and the photoelectric effect, both of which had been introduced in his lifetime. The photoelectric effect pointed to the particle properties of light, which had been considered to be a wave phenomenon. He wondered if electons and other "particles" might exhibit wave properties ...
Charged Particle in Magnetic Saddle Point
... We study charged particles moving in two dimensions. From the perspective of solid state physics, this can be realised for electrons in semiconductor quantum wells. For the moment, we will ignore the quantum nature of the electron, and study classical dynamics in two dimensions. Now apply a perpendi ...
... We study charged particles moving in two dimensions. From the perspective of solid state physics, this can be realised for electrons in semiconductor quantum wells. For the moment, we will ignore the quantum nature of the electron, and study classical dynamics in two dimensions. Now apply a perpendi ...
The History of Quantum Mechanics
... This principle is significant for the fact that it explains why matter occupies space exclusively for itself and does not allow other material objects to pass through it, at the same time allowing lights and radiations to pass. It states that no two identical fermions may occupy the same quantum s ...
... This principle is significant for the fact that it explains why matter occupies space exclusively for itself and does not allow other material objects to pass through it, at the same time allowing lights and radiations to pass. It states that no two identical fermions may occupy the same quantum s ...
The buoyant force on an object totally submerged in a fluid depends
... state function ψ that contains all accessible physical information about the system in that state The probability of finding a system within the volume dv at time t is equal to |ψ|2dv Every observable is represented by an operator which is used to obtain information about the observable from the ...
... state function ψ that contains all accessible physical information about the system in that state The probability of finding a system within the volume dv at time t is equal to |ψ|2dv Every observable is represented by an operator which is used to obtain information about the observable from the ...
from last time:
... Quantum mechanics is the basis of solid state physics, which is the basis of our understanding of semiconductors, which is the basis of all electronics and computers! so lets look at atoms now… ...
... Quantum mechanics is the basis of solid state physics, which is the basis of our understanding of semiconductors, which is the basis of all electronics and computers! so lets look at atoms now… ...
Quantum1
... for a particle? •First, remember that a particle is only a particle sort of, and a wave sort of, and it’s not quite like anything you’ve encountered in classical physics. We need to use Fourier’s Theorem to represent the particle as the superposition of many waves. ...
... for a particle? •First, remember that a particle is only a particle sort of, and a wave sort of, and it’s not quite like anything you’ve encountered in classical physics. We need to use Fourier’s Theorem to represent the particle as the superposition of many waves. ...
Slide 1
... • Quantum Theory – describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small ...
... • Quantum Theory – describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small ...
CH101 General Chemistry
... they radiate energy as well. The amount and type of electromagnetic radiation they emit is directly related to their temperature. Black bodies below around 700 K (430 °C) produce very little radiation at visible wavelengths and appear black (hence the name). Black bodies above this temperature, howe ...
... they radiate energy as well. The amount and type of electromagnetic radiation they emit is directly related to their temperature. Black bodies below around 700 K (430 °C) produce very little radiation at visible wavelengths and appear black (hence the name). Black bodies above this temperature, howe ...
hwk9
... 1. A positively charged particle is moving horizontally when it enters the region between the plates of a capacitor, as the drawing illustrates. (a) Draw the trajectory that the particle follows in moving through the capacitor. (b) When the particle is within the capacitor, which of the following fo ...
... 1. A positively charged particle is moving horizontally when it enters the region between the plates of a capacitor, as the drawing illustrates. (a) Draw the trajectory that the particle follows in moving through the capacitor. (b) When the particle is within the capacitor, which of the following fo ...
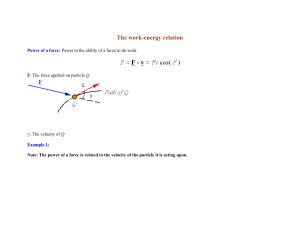
Quantum Mechanics I. Introduction Just before 1900, the classical
... A. Atomic spectra emission lines are a result of electrons moving from a higher to a lower energy level in the atom. ...
... A. Atomic spectra emission lines are a result of electrons moving from a higher to a lower energy level in the atom. ...