Problems for workgroup sessions during week of September 13, 2004
... from 4 to 11 hrs (c) Determine the car's average speed for its entire 11-hour motion. (d) Sketch the velocity versus time graph corresponding to this motion. (e) From the graph below, estimate the average acceleration in the interval from 1 to 3 hours. (f) At what times is the magnitude of the accel ...
... from 4 to 11 hrs (c) Determine the car's average speed for its entire 11-hour motion. (d) Sketch the velocity versus time graph corresponding to this motion. (e) From the graph below, estimate the average acceleration in the interval from 1 to 3 hours. (f) At what times is the magnitude of the accel ...
Chem20u2(5.2) - Mr. Searcy Chemistry 20
... 3. Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. 4. Explain the impact of de Broglie’s wave-particle duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orb ...
... 3. Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. 4. Explain the impact of de Broglie’s wave-particle duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orb ...
THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE The uncertainty principle states
... The uncertainty principle states that a function f on Rn and its Fourier transform fˆ can not both be too highly localized. In the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics, this becomes the statement that both the position and the momentum of a quantum particle cannot be prescribed too accurate ...
... The uncertainty principle states that a function f on Rn and its Fourier transform fˆ can not both be too highly localized. In the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics, this becomes the statement that both the position and the momentum of a quantum particle cannot be prescribed too accurate ...
schoa - Schieck
... ) may not cause ionization of an atom whereas, ultraviolet light (f=10 16 Hz) does. III. The Bohr Model of the Atom & Spectra N: Read p. 174-179: 7. Describe the electron in an atom as Bohr understood it. In the equation: E = -R/n2 a)What does E represent? b) What does n represent? describe any rest ...
... ) may not cause ionization of an atom whereas, ultraviolet light (f=10 16 Hz) does. III. The Bohr Model of the Atom & Spectra N: Read p. 174-179: 7. Describe the electron in an atom as Bohr understood it. In the equation: E = -R/n2 a)What does E represent? b) What does n represent? describe any rest ...
Episode 219 - Teaching Advanced Physics
... accidents, through pile drivers, bullet-proof vests and laser-induced fusion. Momentum is in some ways fundamental. When considering quantum physics, students will meet the idea that light has momentum (but it doesn’t make any sense to use the classical physics definition of mv for light that by def ...
... accidents, through pile drivers, bullet-proof vests and laser-induced fusion. Momentum is in some ways fundamental. When considering quantum physics, students will meet the idea that light has momentum (but it doesn’t make any sense to use the classical physics definition of mv for light that by def ...
Crystal Directions, Wave Propagation and Miller Indices
... Planck’s relationship between energy and frequency requires that light be made up of small “packets” of energy. These packets have come to be known as photons. That is, wave intensity is quantized into basic units given by the frequency and Planck’s constant. If we talk about the power in a light w ...
... Planck’s relationship between energy and frequency requires that light be made up of small “packets” of energy. These packets have come to be known as photons. That is, wave intensity is quantized into basic units given by the frequency and Planck’s constant. If we talk about the power in a light w ...
Sect. 2.5 - TTU Physics
... certain conditions. They aren’t new Laws, but just Newton’s Laws in a different language. ...
... certain conditions. They aren’t new Laws, but just Newton’s Laws in a different language. ...
Formula Sheet - Blank File
... (chose a common origin for all point masses so all positions (all xi and xcm) are relative to that origin.) ...
... (chose a common origin for all point masses so all positions (all xi and xcm) are relative to that origin.) ...
Honors Chemistry Name_________________________________
... 1.Define wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and node. (H.O. p. 278-282) 2. What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and speed of a wave? (Write a mathematical equation.) What is the speed of light (H.O. p. 282) 3. Arrange the following in increasing energy: gamma rays, infrared radiati ...
... 1.Define wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and node. (H.O. p. 278-282) 2. What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and speed of a wave? (Write a mathematical equation.) What is the speed of light (H.O. p. 282) 3. Arrange the following in increasing energy: gamma rays, infrared radiati ...
Chapter 3
... a. The 4 quantum numbers and what they describe b. The difference between orbits (Bohr) and orbitals c. Pauli’s exclusion principle (no two electrons have the same 4 quantum #s) 3. Electron Configuration: a. Aufbau principle (add electrons to lowest energy orbitals first) b. Hund’s rule (1 electron ...
... a. The 4 quantum numbers and what they describe b. The difference between orbits (Bohr) and orbitals c. Pauli’s exclusion principle (no two electrons have the same 4 quantum #s) 3. Electron Configuration: a. Aufbau principle (add electrons to lowest energy orbitals first) b. Hund’s rule (1 electron ...
Chapter 12 Multiple Particle States
... has collapsed? Together with two other physicists, Podolsky and Rosen, Einstein argued that this behavior indicated that quantum theory had to be incomplete. In 1935, they published a paper describing what is now known as the “EPR Paradox” (Einstein et al., 1935). If quantum mechanics is indeed inco ...
... has collapsed? Together with two other physicists, Podolsky and Rosen, Einstein argued that this behavior indicated that quantum theory had to be incomplete. In 1935, they published a paper describing what is now known as the “EPR Paradox” (Einstein et al., 1935). If quantum mechanics is indeed inco ...
Chapter 7 Lect. 1
... 4. Atoms have a minimum energy called the ground state a. Therefore, electrons do not crash into the nucleus b. The ground state of H has its one electron closest to the nucleus c. Energy levels higher than the ground state are called excited states d. The farther the energy level is from the nucle ...
... 4. Atoms have a minimum energy called the ground state a. Therefore, electrons do not crash into the nucleus b. The ground state of H has its one electron closest to the nucleus c. Energy levels higher than the ground state are called excited states d. The farther the energy level is from the nucle ...
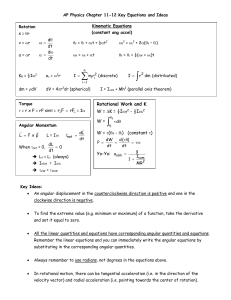
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... To find the extreme value (e.g. minimum or maximum) of a function, take the derivative and set it equal to zero. ...
... To find the extreme value (e.g. minimum or maximum) of a function, take the derivative and set it equal to zero. ...
review
... seen as acting on that particle (e.g. by collapsing a number of superimposed states); and in the case of entangled particles, such action must be on the entangled system as a whole. It thus appears that one particle of an entangled pair "knows" what measurement has been performed on the other, and w ...
... seen as acting on that particle (e.g. by collapsing a number of superimposed states); and in the case of entangled particles, such action must be on the entangled system as a whole. It thus appears that one particle of an entangled pair "knows" what measurement has been performed on the other, and w ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... U U 0 n 0 (0) n1 (1 0 ) n 2 ( 2 0 ) ..... - The equation of partition function for the particle at i=0 ...
... U U 0 n 0 (0) n1 (1 0 ) n 2 ( 2 0 ) ..... - The equation of partition function for the particle at i=0 ...