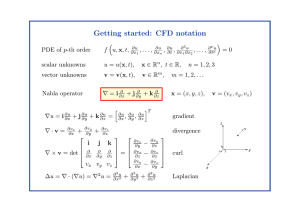
THE EQUATIONS OF FLUID DYNAMICS—DRAFT
... hand side is the rate of change of mass in the volume V and the right hand side represents in and out flow through the boundaries of V . Since the volume is fixed in space we can take R the derivative H inside the integral, and by applying the divergence theorem ( V ∇ · adv = S a · nds) to the bound ...
... hand side is the rate of change of mass in the volume V and the right hand side represents in and out flow through the boundaries of V . Since the volume is fixed in space we can take R the derivative H inside the integral, and by applying the divergence theorem ( V ∇ · adv = S a · nds) to the bound ...
Fluids
... A Fluid can easily deform to any shape. It is defined as any substance that deforms continuously under a shear. If you think about a piece of ice (solid water), unless the ice melts, no amount of pushing on the ice will cause it to deform enough to let your finger inside until it reaches its breakin ...
... A Fluid can easily deform to any shape. It is defined as any substance that deforms continuously under a shear. If you think about a piece of ice (solid water), unless the ice melts, no amount of pushing on the ice will cause it to deform enough to let your finger inside until it reaches its breakin ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology Abstract: Authors: A
... respectively. In the former, an external field is applied to magnetize the elements, and in the latter, they are permanently magnetized. The field produced by the magnetized elements permeates into the flow cell giving rise to an attractive force on magnetic particles that flow through it. The syste ...
... respectively. In the former, an external field is applied to magnetize the elements, and in the latter, they are permanently magnetized. The field produced by the magnetized elements permeates into the flow cell giving rise to an attractive force on magnetic particles that flow through it. The syste ...
Balanced Flow
... The types of atmospheric flows describe here have the following characteristics: 1) Steady state (meaning that the flows do not change with time) 2) No vertical velocity component 3) Natural coordinate system (constant pressure surfaces) These are “idealized” flows, created by balances of horizontal ...
... The types of atmospheric flows describe here have the following characteristics: 1) Steady state (meaning that the flows do not change with time) 2) No vertical velocity component 3) Natural coordinate system (constant pressure surfaces) These are “idealized” flows, created by balances of horizontal ...
Molecular Dynamics
... Transport Coefficients • Thermal conductivity can be computed through energy-current correlation using Green-Kubo formula; or nonequilibrium simulation by directly computing the energy current ...
... Transport Coefficients • Thermal conductivity can be computed through energy-current correlation using Green-Kubo formula; or nonequilibrium simulation by directly computing the energy current ...
Chap 4-che 312
... 3. Flow past sphere, long cylinder, disks - For each particular shape of object and orientation of the object with the direction of the flow, a relation of Cd vs Re exists. ...
... 3. Flow past sphere, long cylinder, disks - For each particular shape of object and orientation of the object with the direction of the flow, a relation of Cd vs Re exists. ...
Equation of Fluid Motion
... velocity, it is a one-dimensional flow which is studied very simply. Let us applied the principle of conservation of momentum (2) to the infinitesimal, cylindrical element of fluid having the cross-sectional area dA and length ds which lay along the streamline. We assume that tension t is described ...
... velocity, it is a one-dimensional flow which is studied very simply. Let us applied the principle of conservation of momentum (2) to the infinitesimal, cylindrical element of fluid having the cross-sectional area dA and length ds which lay along the streamline. We assume that tension t is described ...
L15
... • so far we have considered only “ideal” liquids liquids that can flow without any resistance to the flow • “real” liquids (like ketchup) have a property called viscosity which is a tendency for the liquid to resist flowing ...
... • so far we have considered only “ideal” liquids liquids that can flow without any resistance to the flow • “real” liquids (like ketchup) have a property called viscosity which is a tendency for the liquid to resist flowing ...
Isentropic and Ideal Gas Density Relationships
... Case 1. Isentropic flow is "assumed". Hence, the pressure and density are strict functions of each other. ...
... Case 1. Isentropic flow is "assumed". Hence, the pressure and density are strict functions of each other. ...
Compressible Flow
... T11. High temperature effects in compressible flows are found when analyzing for example very strong shocks or nozzle flows with extremely high total pressure and total enthalpy. What is the root cause of these effects and what do we mean by equilibrium gas? What kind of thermodynamic relations are ...
... T11. High temperature effects in compressible flows are found when analyzing for example very strong shocks or nozzle flows with extremely high total pressure and total enthalpy. What is the root cause of these effects and what do we mean by equilibrium gas? What kind of thermodynamic relations are ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.











![L 15 Fluids [4] Bernoulli`s principle WIND](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016758540_1-efd75f7a7777372eeb0885c6e88a0e4b-300x300.png)