A Derivation of the Navier
... limit, because of the relatively high particle density, we may, and do, regard temperature (and other intensive properties) as continuous functions. The continuum hypothesis is relevant not just to continuum mechanics, but to all macroscopic physics that deal with continuous systems, including elect ...
... limit, because of the relatively high particle density, we may, and do, regard temperature (and other intensive properties) as continuous functions. The continuum hypothesis is relevant not just to continuum mechanics, but to all macroscopic physics that deal with continuous systems, including elect ...
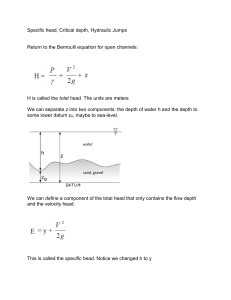
Chapter 7b Specific head_Critical Depth_Hydraulic Jump b
... The flow depth is on the vertical axis as in nature. There’s one flow depth where most of the specific head is held as potential energy (y), and just a little is held as kinetic energy (V2/2g), AND there’s another one where most of the energy is kinetic, and little is potential. There’s also one spe ...
... The flow depth is on the vertical axis as in nature. There’s one flow depth where most of the specific head is held as potential energy (y), and just a little is held as kinetic energy (V2/2g), AND there’s another one where most of the energy is kinetic, and little is potential. There’s also one spe ...
v 1
... The oxygen exchange in the lungs takes place across the membranes of small balloon-like structures called alveoli attached to the branches of the bronchial passages. These alveoli inflate and deflate with inhalation and exhalation It takes some effort to breathe in because these tiny balloons must b ...
... The oxygen exchange in the lungs takes place across the membranes of small balloon-like structures called alveoli attached to the branches of the bronchial passages. These alveoli inflate and deflate with inhalation and exhalation It takes some effort to breathe in because these tiny balloons must b ...
Final Paper DRAFT (as of 5/2) - Edge
... The sensors were chosen to match the pressures and flows within the circulatory system. For this stage of the project, the signals from the sensors need to be analyzed and displayed. LabView was chosen as the platform to perform processing and display, due to its emphasis on data collection and mani ...
... The sensors were chosen to match the pressures and flows within the circulatory system. For this stage of the project, the signals from the sensors need to be analyzed and displayed. LabView was chosen as the platform to perform processing and display, due to its emphasis on data collection and mani ...
CE 3372 Water Systems Design
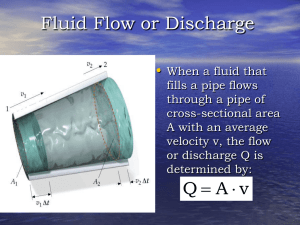
... 1-Dimensional Flow The change of fluid variables (velocity, temp, etc.) in one direction dominates over the change in the other two directions. 2-D and 3-D Change in fluid variables is significant in multiple directions Water is almost always a 3-dimensional flow However, 3D is difficult ...
... 1-Dimensional Flow The change of fluid variables (velocity, temp, etc.) in one direction dominates over the change in the other two directions. 2-D and 3-D Change in fluid variables is significant in multiple directions Water is almost always a 3-dimensional flow However, 3D is difficult ...
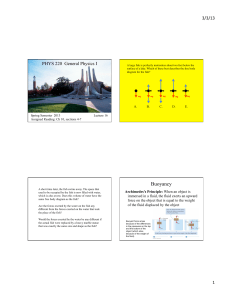
10.7 Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle 10.8 Fluids in Motion
... 1. What is a buoyant force? 2. How does a buoyant force occur? ...
... 1. What is a buoyant force? 2. How does a buoyant force occur? ...
Dynamics and Control of A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
... equipment heat exchanger , is by far the most common type of heat transfer concerned with the used in the chemical and allied industries the present work is the main objective of the . dynamic and control of ashell and heat exchanger constants and steady state gains by experimental work is to determ ...
... equipment heat exchanger , is by far the most common type of heat transfer concerned with the used in the chemical and allied industries the present work is the main objective of the . dynamic and control of ashell and heat exchanger constants and steady state gains by experimental work is to determ ...
2. Patterned Microfluidic Channel
... Each stripe will build up a mobile ion layer with the opposite polarity with respect to its neighbors. In the presence of an electric field, these mobile ion layers will flow against each other. This gives rise to vortex-like flow near the boundaries, but when the channel is sufficiently thick (thic ...
... Each stripe will build up a mobile ion layer with the opposite polarity with respect to its neighbors. In the presence of an electric field, these mobile ion layers will flow against each other. This gives rise to vortex-like flow near the boundaries, but when the channel is sufficiently thick (thic ...
CHAPTER 03
... yield considerable error in which of the following cases? A. when gases are being studied B. when the fluid is traveling very slow C. when you are studying in a vacuum 32.The Bernoulli equation can be modified for compressible flows. True or False A. True B. False 33.An adiabatic process means that ...
... yield considerable error in which of the following cases? A. when gases are being studied B. when the fluid is traveling very slow C. when you are studying in a vacuum 32.The Bernoulli equation can be modified for compressible flows. True or False A. True B. False 33.An adiabatic process means that ...
Notes and Hints for AP Physics Summer Assignment
... a material takes up. The unit of volume will always be cubed because it is 3dimensional (the standard unit is m3). Fluids exert BUOYANT FORCE on objects that are submerged in them. This buoyant force points upward, and it is what causes objects to float. The amount of buoyant force on an object is g ...
... a material takes up. The unit of volume will always be cubed because it is 3dimensional (the standard unit is m3). Fluids exert BUOYANT FORCE on objects that are submerged in them. This buoyant force points upward, and it is what causes objects to float. The amount of buoyant force on an object is g ...
Fluid Mechanics
... FLUIDS IN MOTION • FLUID FLOW: – When a fluid is in motion, the flow can be characterized in one of two ways. The flow is said to be laminar if every particle that passes a particular point moves along the same smooth path traveled by the particles that passed that point earlier. – This path is cal ...
... FLUIDS IN MOTION • FLUID FLOW: – When a fluid is in motion, the flow can be characterized in one of two ways. The flow is said to be laminar if every particle that passes a particular point moves along the same smooth path traveled by the particles that passed that point earlier. – This path is cal ...
Gravity waves on water - UMD Physics
... linear and the force terms are independent of v. For small velocities you might therefore expect that the advective term is negligible, but what exactly does “small” mean? A velocity has dimensions LT −1 , so it is meaningless to say it is “small” in absolute terms. Only dimensionless numbers can be ...
... linear and the force terms are independent of v. For small velocities you might therefore expect that the advective term is negligible, but what exactly does “small” mean? A velocity has dimensions LT −1 , so it is meaningless to say it is “small” in absolute terms. Only dimensionless numbers can be ...
Fluid Mechanics Intro Slides.
... Liquid: A state of matter in which the molecules are relatively free to change their positions with respect to each other but restricted by cohesive forces so as to maintain a relatively fixed volume Gas: a state of matter in which the molecules are practically unrestricted by cohesive forces. A gas ...
... Liquid: A state of matter in which the molecules are relatively free to change their positions with respect to each other but restricted by cohesive forces so as to maintain a relatively fixed volume Gas: a state of matter in which the molecules are practically unrestricted by cohesive forces. A gas ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.