Unit 8 force - Kowenscience.com
... A rocket can rise into the air because the gases it expels with a downward action force exert an equal but opposite reaction force on the rocket. As long as this upward force, called thrust, is greater than the downward pull of gravity, there is an unbalanced force in the upward direction that cause ...
... A rocket can rise into the air because the gases it expels with a downward action force exert an equal but opposite reaction force on the rocket. As long as this upward force, called thrust, is greater than the downward pull of gravity, there is an unbalanced force in the upward direction that cause ...
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND RAOTATIONAL DYNAMICS Various
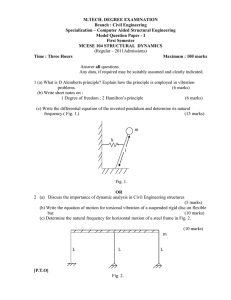
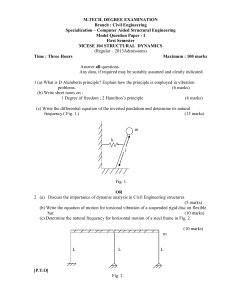
... i.e., angular acceleration of the body in rotational equilibrium will be zero. Partial Equilibrium A body is said to be in partial equilibrium if it is in translational equilibrium and not in rotational equilibrium or the body may be in rotational equilibrium and not in translational equilibrium. Ex ...
... i.e., angular acceleration of the body in rotational equilibrium will be zero. Partial Equilibrium A body is said to be in partial equilibrium if it is in translational equilibrium and not in rotational equilibrium or the body may be in rotational equilibrium and not in translational equilibrium. Ex ...
Problems
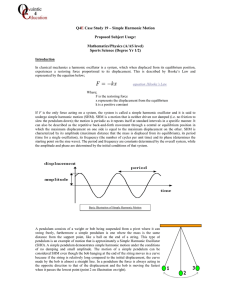
... the end of an ideal spring of negligible mass and start it oscillating. The elapsed time from when the glider first moves through the equilibrium point to the second time it moves through that point is 2.60 s. Find the spring’s force constant. 14.7 . When a body of unknown mass is attached to an idea ...
... the end of an ideal spring of negligible mass and start it oscillating. The elapsed time from when the glider first moves through the equilibrium point to the second time it moves through that point is 2.60 s. Find the spring’s force constant. 14.7 . When a body of unknown mass is attached to an idea ...
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
... Here lT is the total cord length and lCD is the length of cord passing over arc CD on the pulley W. Wang ...
... Here lT is the total cord length and lCD is the length of cord passing over arc CD on the pulley W. Wang ...
Slide 1
... a surface, due to the torque created by gravity when its axis of rotation is not vertical. ...
... a surface, due to the torque created by gravity when its axis of rotation is not vertical. ...
Kinetic energy
... NO!!! Energy in the system is conserved – With every movement, the swing’s chains rub on their hooks and air pushes on the rider – Friction and air resistance cause some of the mechanical energy of the swing to change to thermal energy – With every pass of the swing, the temperature of the hooks and ...
... NO!!! Energy in the system is conserved – With every movement, the swing’s chains rub on their hooks and air pushes on the rider – Friction and air resistance cause some of the mechanical energy of the swing to change to thermal energy – With every pass of the swing, the temperature of the hooks and ...
How do we describe motion?
... As long as Earth doesn’t transfer angular momentum to other objects, its rotation and orbit cannot change. © 2005 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley ...
... As long as Earth doesn’t transfer angular momentum to other objects, its rotation and orbit cannot change. © 2005 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.