Lecture8 (Equilibrium)
... • A force cannot be seen, only the effect of a force on a body may be seen. • Force Units: S.I. Unit ,Newton, (N) or (kN) • Force is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. ...
... • A force cannot be seen, only the effect of a force on a body may be seen. • Force Units: S.I. Unit ,Newton, (N) or (kN) • Force is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. ...
Work and Energy - Blue Valley Schools
... Experiment 18 15. Place the Motion Detector about one meter from the Force Sensor, along the line of the spring. Be sure there are no nearby objects to interfere with the distance measurement. ...
... Experiment 18 15. Place the Motion Detector about one meter from the Force Sensor, along the line of the spring. Be sure there are no nearby objects to interfere with the distance measurement. ...
I L - IBPhysicsLund
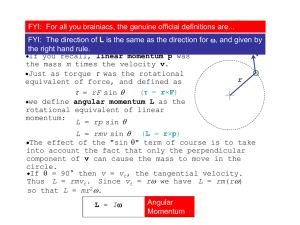
... FYI: You may recall Topic doing the same when we looked at linear 2.2thing Extended ...
... FYI: You may recall Topic doing the same when we looked at linear 2.2thing Extended ...
AP Quiz #z15 AP FR Quiz #15 Energy Concepts
... Arianna: “I think the boy pushed harder on the girl because he is bigger, so she ended up with more kinetic energy than he did.” Boris: “I disagree. They pushed equally hard on each other, but the girl moved farther while they were pushing on each other, so she ended up with more kinetic energy.” Ca ...
... Arianna: “I think the boy pushed harder on the girl because he is bigger, so she ended up with more kinetic energy than he did.” Boris: “I disagree. They pushed equally hard on each other, but the girl moved farther while they were pushing on each other, so she ended up with more kinetic energy.” Ca ...
Work and Energy combined
... Well, the law of conservation of energy always works – it is the law, after all. What happens is that the energy of the ball is transformed into energy forms that do not contribute to the bounce height. We call these transformations energy losses. They are not really energy losses, however, in the ...
... Well, the law of conservation of energy always works – it is the law, after all. What happens is that the energy of the ball is transformed into energy forms that do not contribute to the bounce height. We call these transformations energy losses. They are not really energy losses, however, in the ...
lectures 2015
... where M is the total mass, mi is the mass of the disc at height hi Ask yourself what is going on, and write it down in words in just one or perhaps two sentences. Try to understand the problem qualitatively before ...
... where M is the total mass, mi is the mass of the disc at height hi Ask yourself what is going on, and write it down in words in just one or perhaps two sentences. Try to understand the problem qualitatively before ...
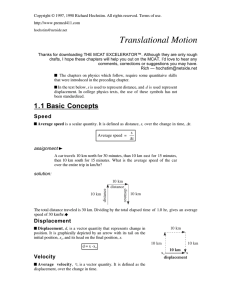
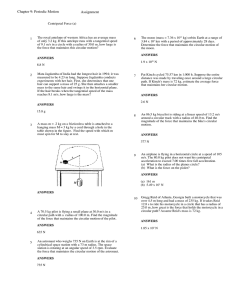
Translational Motion
... To find the instantaneous velocity we will need to know v¥ and v¶ at t = 1.0 s. Since vx = 20 m/s at all times, v¥ at t = 1.0 s is 20 m/s. Since the acceleration is a uniform -10 m/s,¤ the change in velocity during any one second interval will be -10 m/s. Since vºy is 20 m/s ,v¶ at t = 1.0 s is 10 ...
... To find the instantaneous velocity we will need to know v¥ and v¶ at t = 1.0 s. Since vx = 20 m/s at all times, v¥ at t = 1.0 s is 20 m/s. Since the acceleration is a uniform -10 m/s,¤ the change in velocity during any one second interval will be -10 m/s. Since vºy is 20 m/s ,v¶ at t = 1.0 s is 10 ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
Force and Laws of Motion
... Force:- Force may be defined as an influence, which tend to change state, speed, direction and shape of a body. It has both magnitude and direction and is therefore, a vector quantity. It may also be defined as an external agency, which changes the speed and direction of a body. It can also change t ...
... Force:- Force may be defined as an influence, which tend to change state, speed, direction and shape of a body. It has both magnitude and direction and is therefore, a vector quantity. It may also be defined as an external agency, which changes the speed and direction of a body. It can also change t ...
2009 Q6 - Loreto Balbriggan
... A skateboarder with a total mass of 70 kg starts from rest at the top of a ramp and accelerates down it. The ramp is 25 m long and is at an angle of 20 to the horizontal. The skateboarder has a velocity of 12.2 m s–1 at the bottom of the ramp. ...
... A skateboarder with a total mass of 70 kg starts from rest at the top of a ramp and accelerates down it. The ramp is 25 m long and is at an angle of 20 to the horizontal. The skateboarder has a velocity of 12.2 m s–1 at the bottom of the ramp. ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.