Motion With Constant Acceleration
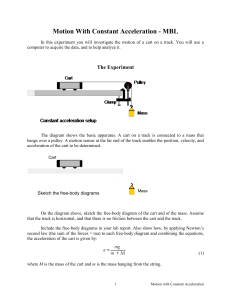
... Record a set of data where you start with the cart near the pulley, and you give it a quick push so it moves away from the pulley. From one of the graphs, determine the acceleration for the motion when the cart is moving away from the pulley. Compare this with the acceleration you measure for the ca ...
... Record a set of data where you start with the cart near the pulley, and you give it a quick push so it moves away from the pulley. From one of the graphs, determine the acceleration for the motion when the cart is moving away from the pulley. Compare this with the acceleration you measure for the ca ...
Final exam review problems
... IA = 500 kg·m2 (satellite) mB = 2 kg (small weights) What should be the extension length d to slow the satellite as required? ...
... IA = 500 kg·m2 (satellite) mB = 2 kg (small weights) What should be the extension length d to slow the satellite as required? ...
NewtonsLaws
... applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. • The forces of a force pair do not cancel because they act on different objects. • According to the law of conservation of momentum, momentum is conserved during a collision unless an outside force acts on the colliding objects. ...
... applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. • The forces of a force pair do not cancel because they act on different objects. • According to the law of conservation of momentum, momentum is conserved during a collision unless an outside force acts on the colliding objects. ...
Chapter 02 Motion
... 20. A boy on a skateboard pushes off the ground with his foot. He and the skateboard accelerate down the sidewalk due to the force A. he exerts against the ground. B. between the skateboard wheels and the ground. C. the ground exerts against his foot. D. of gravity acting on the skateboard. ...
... 20. A boy on a skateboard pushes off the ground with his foot. He and the skateboard accelerate down the sidewalk due to the force A. he exerts against the ground. B. between the skateboard wheels and the ground. C. the ground exerts against his foot. D. of gravity acting on the skateboard. ...
English Physics Book 2012-web copy
... the speed of the car and is displayed on the car’s speedometer. ...
... the speed of the car and is displayed on the car’s speedometer. ...
Chapter 11 - UCF Physics
... space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to 5.00 m. ...
... space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to 5.00 m. ...
Rotational Motion
... however, either rotate together as a rigid object or independent of one another. For this lab, we will only be using the upper disc in our rotation studies. The bottom disc should remain fixed to the base of the apparatus. The hanging mass (mh = 25 g), which generates tension in the string, runs ove ...
... however, either rotate together as a rigid object or independent of one another. For this lab, we will only be using the upper disc in our rotation studies. The bottom disc should remain fixed to the base of the apparatus. The hanging mass (mh = 25 g), which generates tension in the string, runs ove ...
Applied Maths Introductory Module Workbook
... A car of mass 150kg is accelerating in a race. If the car engine provides a thrust of 200N, and the drag, or resistance, is 180N find i) The net force in the direction of motion ii) The acceleration of the car iii) The speed of the car after travelling 100m, assuming the car starts from rest. iv) If ...
... A car of mass 150kg is accelerating in a race. If the car engine provides a thrust of 200N, and the drag, or resistance, is 180N find i) The net force in the direction of motion ii) The acceleration of the car iii) The speed of the car after travelling 100m, assuming the car starts from rest. iv) If ...
lcp 14: the physics of star trek
... Moreover, teleportation, a la Star Trek seems to contradict the second law of thermodynamics (see: "The Notion of Energy"). ...
... Moreover, teleportation, a la Star Trek seems to contradict the second law of thermodynamics (see: "The Notion of Energy"). ...
Chapter – 12 Simple Harmonic Motion
... Q 31. A uniform plate of mass M stays horizontally and symmetrically on two wheels rotating in opposite directions (figure). The separation between the wheels is L. The friction coefficient between each wheel and the plate is µ. Find the time period of oscillation of the plate if it is slightly disp ...
... Q 31. A uniform plate of mass M stays horizontally and symmetrically on two wheels rotating in opposite directions (figure). The separation between the wheels is L. The friction coefficient between each wheel and the plate is µ. Find the time period of oscillation of the plate if it is slightly disp ...
Work and Energy in One Dimension
... and provide a general framework for appreciating the concept of energy and its usefulness in all areas of science. We present these ideas for one-dimensional motion, the theme of the previous two chapters, leaving the generalization to more than one dimension for the next chapter. A major goal of th ...
... and provide a general framework for appreciating the concept of energy and its usefulness in all areas of science. We present these ideas for one-dimensional motion, the theme of the previous two chapters, leaving the generalization to more than one dimension for the next chapter. A major goal of th ...
force - Willmar Public Schools
... Static friction is the friction force that acts on objects that are not moving. Static friction always acts in the direction opposite to that of the applied force. Without this static friction, your feet would slip out from under you, making it difficult to walk. Sliding friction is a force that op ...
... Static friction is the friction force that acts on objects that are not moving. Static friction always acts in the direction opposite to that of the applied force. Without this static friction, your feet would slip out from under you, making it difficult to walk. Sliding friction is a force that op ...
Final Momentum NRG Review
... 22. A popular swinging-balls apparatus consists of an aligned row of identical elastic balls that are suspended by strings so they barely touch each other. When two balls are lifted from one end and released, they strike the row and two balls pop out from the other end. If instead one ball popped ou ...
... 22. A popular swinging-balls apparatus consists of an aligned row of identical elastic balls that are suspended by strings so they barely touch each other. When two balls are lifted from one end and released, they strike the row and two balls pop out from the other end. If instead one ball popped ou ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.