Chapter 6
... The rate of change of velocity is the acceleration. Remember that a = Dv/Dt. The acceleration is related to the force by Newton’s 2nd Law (F = ma), so the acceleration of the boulder is less than that of the pebble (for the same applied force) because the boulder is much more massive. ...
... The rate of change of velocity is the acceleration. Remember that a = Dv/Dt. The acceleration is related to the force by Newton’s 2nd Law (F = ma), so the acceleration of the boulder is less than that of the pebble (for the same applied force) because the boulder is much more massive. ...
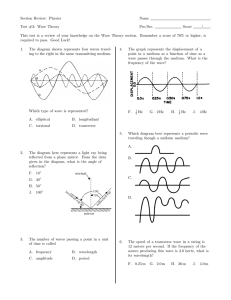
Newtonian Mechanics
... 1. The planets move on elliptical orbits with the sun at one focal point. 2. The radial vector sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The square of the period of revolution is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of the ellipse. Newton started with the results of Galileo and Kepler. His ...
... 1. The planets move on elliptical orbits with the sun at one focal point. 2. The radial vector sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The square of the period of revolution is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of the ellipse. Newton started with the results of Galileo and Kepler. His ...
Answers
... Newton's 2nd Law of Motion can be expressed as force equals mass times acceleration. It explains that force causes acceleration and mass resists acceleration. The more mass, the more force you need to make the object move. Acceleration is calculated by dividing change in velocity (final speed – init ...
... Newton's 2nd Law of Motion can be expressed as force equals mass times acceleration. It explains that force causes acceleration and mass resists acceleration. The more mass, the more force you need to make the object move. Acceleration is calculated by dividing change in velocity (final speed – init ...
Version 001 – Review 1: Mechanics – tubman – (IBII20142015) 1
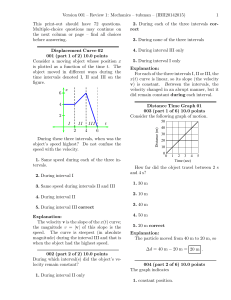
... Frustrated With It All 016 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A disgruntled physics student, frustrated with finals, releases his tensions by bombarding the adjacent building, 12 m away, with water balloons. He fires one at 40◦ from the horizontal with an initial speed of 24.4 m/s. The acceleration of gravit ...
... Frustrated With It All 016 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A disgruntled physics student, frustrated with finals, releases his tensions by bombarding the adjacent building, 12 m away, with water balloons. He fires one at 40◦ from the horizontal with an initial speed of 24.4 m/s. The acceleration of gravit ...
ME1301 Dynamics of Machinery Year/Sem: III/V UNIT
... 1000mm long. The mass of the reciprocating parts is 140kg.On the expansion stroke with the crank at 30°from the top dead center, the gas pressure is 0.7MPa.If the runs at 250rpm, determine; 1. Net force acting on the piston 2.resultant load on the gudgeon pin 3. Thrust on cylinder walls 4. The speed ...
... 1000mm long. The mass of the reciprocating parts is 140kg.On the expansion stroke with the crank at 30°from the top dead center, the gas pressure is 0.7MPa.If the runs at 250rpm, determine; 1. Net force acting on the piston 2.resultant load on the gudgeon pin 3. Thrust on cylinder walls 4. The speed ...
Name:
... 18. In the movie Indiana Jones and the Raiders of the Lost Ark, a large boulder runs downhill after Dr. Jones. Let’s assume that Dr. Jones and the boulder follow the path shown below. Fill in all of the missing information for the boulder in the drawing below. You may assume there is no friction and ...
... 18. In the movie Indiana Jones and the Raiders of the Lost Ark, a large boulder runs downhill after Dr. Jones. Let’s assume that Dr. Jones and the boulder follow the path shown below. Fill in all of the missing information for the boulder in the drawing below. You may assume there is no friction and ...
Slide 1
... A simple clutch consists of two cylindrical plates that can be pressed together to connect two sections of an axle, as needed, in a piece of machinery. The two plates have masses MA = 6.0 kg and MB = 9.0 kg, with equal radii R0 = 0.60 m. They are initially separated. Plate MA is accelerated from res ...
... A simple clutch consists of two cylindrical plates that can be pressed together to connect two sections of an axle, as needed, in a piece of machinery. The two plates have masses MA = 6.0 kg and MB = 9.0 kg, with equal radii R0 = 0.60 m. They are initially separated. Plate MA is accelerated from res ...
ch2_osc_waves
... To start the study of oscillations we will consider an object of mass m attached to a spring with a stiffness k . The object can be displaced from its equilibrium and set to oscillate freely or it can be forced to oscillate by some mechanical means. As the object oscillates it can dissipate energy t ...
... To start the study of oscillations we will consider an object of mass m attached to a spring with a stiffness k . The object can be displaced from its equilibrium and set to oscillate freely or it can be forced to oscillate by some mechanical means. As the object oscillates it can dissipate energy t ...
Textbook Practice Problems
... Have students explore the relationship between mass and inertia by using coins, index cards and a paper cup. How does mass impact the inertia of an object? Does a nickel have more inertial than a penny? (2E, 4D). Or have students explore the relationship between force and mass using “Active Phys ...
... Have students explore the relationship between mass and inertia by using coins, index cards and a paper cup. How does mass impact the inertia of an object? Does a nickel have more inertial than a penny? (2E, 4D). Or have students explore the relationship between force and mass using “Active Phys ...
Lab 3 - Susquehanna Township School District
... Student's grades will consist entirely of a two part marking period exam (70%) and three quizzes (30%). Homework, WebAssigns, labs, and special assignments are held in the highest regard. Any of these assignments done poorly, inadequately, incompletely, or after the deadline will automatically resul ...
... Student's grades will consist entirely of a two part marking period exam (70%) and three quizzes (30%). Homework, WebAssigns, labs, and special assignments are held in the highest regard. Any of these assignments done poorly, inadequately, incompletely, or after the deadline will automatically resul ...
Content Area: Communication Arts
... laboratory write up. Answer Key: 1. Graphs are used MOST OF THE TIME in solid scientific writing. They are appropriate whenever they simplify the presentation of information. In other words, if a graph makes results easier to interpret or a graph’s slope, mean, or critical points provide critical in ...
... laboratory write up. Answer Key: 1. Graphs are used MOST OF THE TIME in solid scientific writing. They are appropriate whenever they simplify the presentation of information. In other words, if a graph makes results easier to interpret or a graph’s slope, mean, or critical points provide critical in ...
AP Physics Pacing Curriculum
... spring oscillators, objects falling in a gravitational field. c. The change in electric potential in a circuit is the change in potential energy per unit charge. 5.B.3.1 The student is able to describe and make qualitative and/or quantitative predictions about everyday examples of systems with inte ...
... spring oscillators, objects falling in a gravitational field. c. The change in electric potential in a circuit is the change in potential energy per unit charge. 5.B.3.1 The student is able to describe and make qualitative and/or quantitative predictions about everyday examples of systems with inte ...
Section 2
... An observer wants to find the instantaneous speed of a car as it passes a pedestrian crossing. He measures the length of the car and finds it to be 3·5 m. He then stands with a stop watch at the crossing, starts timing as the front of the car passes him and stops when the back of the car has passed. ...
... An observer wants to find the instantaneous speed of a car as it passes a pedestrian crossing. He measures the length of the car and finds it to be 3·5 m. He then stands with a stop watch at the crossing, starts timing as the front of the car passes him and stops when the back of the car has passed. ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.