Physics 37
... 2. A 5.80-kg blob of bubble gum moves to the right with an initial velocity vi = 12.3 m/s. It collides with a 3.2-kg blob of bubble gum initially at rest. After the collision they stick together and move to the right with some final velocity. What percent of the initial kinetic energy of the system ...
... 2. A 5.80-kg blob of bubble gum moves to the right with an initial velocity vi = 12.3 m/s. It collides with a 3.2-kg blob of bubble gum initially at rest. After the collision they stick together and move to the right with some final velocity. What percent of the initial kinetic energy of the system ...
When spring is stretched or compressed it has elastic potential energy.
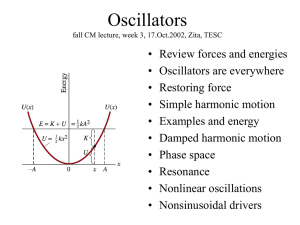
... harmonic motion will not vibrate forever. Friction, or some such force, will decrease the velocity and amplitude of the motion. This is called damped harmonic motion. ...
... harmonic motion will not vibrate forever. Friction, or some such force, will decrease the velocity and amplitude of the motion. This is called damped harmonic motion. ...
Work & Energy
... length is 12 m. If Tarzan starts at an angle of 30 degrees with respect to the vertical and has no initial speed, what is his speed at the bottom of the arc? ...
... length is 12 m. If Tarzan starts at an angle of 30 degrees with respect to the vertical and has no initial speed, what is his speed at the bottom of the arc? ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d / t 3. Constant speed – speed stays the same the entire trip 4. Average speed – total distance divided by t ...
... 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d / t 3. Constant speed – speed stays the same the entire trip 4. Average speed – total distance divided by t ...
week_9_homework_work_and_energy_conservation_markscheme
... Straight line finishing at (1.8, 0) (+ or – 1 small square) (1) Starting at (0, 5) (+ or – 1 small square) (1) ...
... Straight line finishing at (1.8, 0) (+ or – 1 small square) (1) Starting at (0, 5) (+ or – 1 small square) (1) ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
... Think about how to find x(t) near the bottom of potential well. ...
... Think about how to find x(t) near the bottom of potential well. ...
Document
... Work is force x distance Only the force parallel to the displacement applies to the work ...
... Work is force x distance Only the force parallel to the displacement applies to the work ...
Document
... The next step in discovering the law of conservation of energy was made by René Descartes, the French philosopher. He developed the idea that motion is conserved in all physical interactions. Descartes expressed motion by multiplying an object’s mass by its velocity. In contrast, the German philosop ...
... The next step in discovering the law of conservation of energy was made by René Descartes, the French philosopher. He developed the idea that motion is conserved in all physical interactions. Descartes expressed motion by multiplying an object’s mass by its velocity. In contrast, the German philosop ...
Circular Motion
... Always points toward the center of the circular motion. Period (T) = time needed for an object to make one complete revolution Distance traveled = circumference Circumference = 2πr = πd ...
... Always points toward the center of the circular motion. Period (T) = time needed for an object to make one complete revolution Distance traveled = circumference Circumference = 2πr = πd ...
Forces and Motion Vocabulary Words
... Force = Mass x Acceleration By increasing or decreasing the mass or acceleration of an object you change the force applied by that object ...
... Force = Mass x Acceleration By increasing or decreasing the mass or acceleration of an object you change the force applied by that object ...
R07
... Figure shows the cross-section of masonary dan. Determine the distance of the centroid from the vertical face. ...
... Figure shows the cross-section of masonary dan. Determine the distance of the centroid from the vertical face. ...
Energy of the universe is conserved Mechanical Energy
... 1. The graphs above show the force a person exerts on a box sliding on a frictionless surface without air drag with respect to both time and position. a. Find the work done by the person on the box for the first 6 meters of pushing. ...
... 1. The graphs above show the force a person exerts on a box sliding on a frictionless surface without air drag with respect to both time and position. a. Find the work done by the person on the box for the first 6 meters of pushing. ...
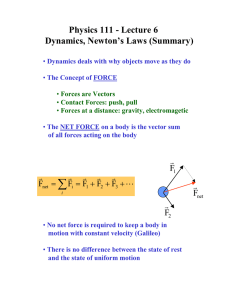
Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary)
... Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary) • Dynamics deals with why objects move as they do • The Concept of FORCE • Forces are Vectors • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the body ...
... Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary) • Dynamics deals with why objects move as they do • The Concept of FORCE • Forces are Vectors • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the body ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.