Physics 103-02 Exam IV 4 Dec
... Part C: Work the following problem. Show your work, and use words and phrases to describe your reasoning. [10 points] 16. An ideal string is wrapped around a pulley. Hanging from the free end of the string is a mass, m = 4.0 kg. The axle of the pulley is frictionless, but the string does not slip o ...
... Part C: Work the following problem. Show your work, and use words and phrases to describe your reasoning. [10 points] 16. An ideal string is wrapped around a pulley. Hanging from the free end of the string is a mass, m = 4.0 kg. The axle of the pulley is frictionless, but the string does not slip o ...
p250t2f03
... (D) trick question, since the force and acceleration must be zero for motion with constant speed is zero. ___ 3. If the orbital distance of the moon from the earth were larger, then (A) the force of attraction between the earth and the moon would be smaller. (B) the centripetal acceleration of the m ...
... (D) trick question, since the force and acceleration must be zero for motion with constant speed is zero. ___ 3. If the orbital distance of the moon from the earth were larger, then (A) the force of attraction between the earth and the moon would be smaller. (B) the centripetal acceleration of the m ...
hp1f2013_class15_rolling_motion_and_accelerating_frames
... Principle of Equivalence In the example problem, we treated acceleration A in the same way as we treated gravitational acceleration. The Principle of Equivalence states that there is no way to distinguish locally* between a gravitational acceleration and an acceleration of the coordinate system. *L ...
... Principle of Equivalence In the example problem, we treated acceleration A in the same way as we treated gravitational acceleration. The Principle of Equivalence states that there is no way to distinguish locally* between a gravitational acceleration and an acceleration of the coordinate system. *L ...
Chapter 2, 4 &5 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. ...
... Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. ...
File
... Takes many different forms and has many different effects Ex: Your body uses energy provided by the food ...
... Takes many different forms and has many different effects Ex: Your body uses energy provided by the food ...
week_10_homework_kinetic_and_potential_energy
... Initially the trolley is held at rest at position A. It is then released. When it has moved some distance, but before the suspended mass hits the floor, a card attached to the trolley passes through a light gate. A clock controlled by the gate records how long the card blocks the light ...
... Initially the trolley is held at rest at position A. It is then released. When it has moved some distance, but before the suspended mass hits the floor, a card attached to the trolley passes through a light gate. A clock controlled by the gate records how long the card blocks the light ...
Motion with a constant speed - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... and how they caused you to move. ...
... and how they caused you to move. ...
CT8b
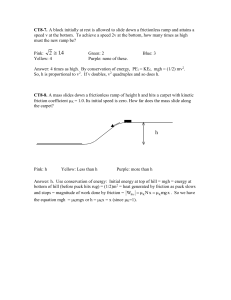
... CT8-8. A mass slides down a frictionless ramp of height h and hits a carpet with kinetic friction coefficient K = 1.0. Its initial speed is zero. How far does the mass slide along the carpet? ...
... CT8-8. A mass slides down a frictionless ramp of height h and hits a carpet with kinetic friction coefficient K = 1.0. Its initial speed is zero. How far does the mass slide along the carpet? ...
Lecture powerpoint
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
Physics
... Q. 2. Under what condition is the scalar product of two non-zero vectors zero ? Q. 3. A body just starts to move when 15 N forces is applied . If 10 N forces is applied on it . Find force of friction . Q. 4. When momentum of a body is doubled , how will its Kinetic-energy changes? Q. 5. Write equati ...
... Q. 2. Under what condition is the scalar product of two non-zero vectors zero ? Q. 3. A body just starts to move when 15 N forces is applied . If 10 N forces is applied on it . Find force of friction . Q. 4. When momentum of a body is doubled , how will its Kinetic-energy changes? Q. 5. Write equati ...
Unit B: Energy Flow in Technological Systems
... 21. A child with a mass of 25.0 kg is at the top of a slide in an amusement park. If the vertical height of the slide is 4.00 m, what is the gravitation potential energy of the child relative to the ground? ...
... 21. A child with a mass of 25.0 kg is at the top of a slide in an amusement park. If the vertical height of the slide is 4.00 m, what is the gravitation potential energy of the child relative to the ground? ...
MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE -
... mathematical analysis Proportion types, systematic vs. random uncertainty, accuracy, % error, metric conversions 1-D kinematics scalar/vector, distance/displacement, speed/velocity, acceleration, kinematics graphs, freefall relative motion/vector addition frames-of-reference, vector addition (1 & 2 ...
... mathematical analysis Proportion types, systematic vs. random uncertainty, accuracy, % error, metric conversions 1-D kinematics scalar/vector, distance/displacement, speed/velocity, acceleration, kinematics graphs, freefall relative motion/vector addition frames-of-reference, vector addition (1 & 2 ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... *An object moving in a straight line at constant speed will continue doing that unless acted on by a force. This force is called friction. It is a force that resists motion between 2 surfaces that are in contact. It always acts opposite to the direction of motion. ...
... *An object moving in a straight line at constant speed will continue doing that unless acted on by a force. This force is called friction. It is a force that resists motion between 2 surfaces that are in contact. It always acts opposite to the direction of motion. ...
Mechanics 105 chapter 12
... Causes displaced mass to to be restored to the equilibrium position. Potential energy Kinetic energy. At equilibrium – large KE but force is now zero. Newton’s first law - keeps moving. ...
... Causes displaced mass to to be restored to the equilibrium position. Potential energy Kinetic energy. At equilibrium – large KE but force is now zero. Newton’s first law - keeps moving. ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.