ch13_lecture
... the object relative to the equilibrium position In the absence of friction, an object in simple harmonic motion will oscillate between ±A on each side of the equilibrium position ...
... the object relative to the equilibrium position In the absence of friction, an object in simple harmonic motion will oscillate between ±A on each side of the equilibrium position ...
Motion & Newton`s Laws
... Sliding Friction • Sliding friction occurs when two surfaces slide past each other. ...
... Sliding Friction • Sliding friction occurs when two surfaces slide past each other. ...
Example 11-3.
... 11.2 Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator We get our OSE for the total mechanical energy of a simple harmonic oscillator by considering a mass attached to a spring on a horizontal, frictionless surface: E = mv2/2 + kx2/2 (here I am using x instead of s). At the equilibrium position (x=0), the e ...
... 11.2 Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator We get our OSE for the total mechanical energy of a simple harmonic oscillator by considering a mass attached to a spring on a horizontal, frictionless surface: E = mv2/2 + kx2/2 (here I am using x instead of s). At the equilibrium position (x=0), the e ...
Chapter 7
... A 3 kg mass has an initial velocity, v = (5i - 3j) m/s. What is the kinetic energy at this time? The velocity changes to (8i + 4j) m/s. What is the change in kinetic energy? How much work was done? ...
... A 3 kg mass has an initial velocity, v = (5i - 3j) m/s. What is the kinetic energy at this time? The velocity changes to (8i + 4j) m/s. What is the change in kinetic energy? How much work was done? ...
Review1 - UCF Physics
... Drawing a FBD of forces on an object (on, not by) 1. Choose the object to analyze. Draw it as a dot. 2. What forces physically touch this object? This object, not some other 3. What “action at a distance” forces act on the object? Gravity is the only one for this PHYS2053 4. Draw these forces as ar ...
... Drawing a FBD of forces on an object (on, not by) 1. Choose the object to analyze. Draw it as a dot. 2. What forces physically touch this object? This object, not some other 3. What “action at a distance” forces act on the object? Gravity is the only one for this PHYS2053 4. Draw these forces as ar ...
Instructions - People Server at UNCW
... and UB = 560 kJ. What is the heat transferred to the gas during this process? [The units are in kPa and m3.] ...
... and UB = 560 kJ. What is the heat transferred to the gas during this process? [The units are in kPa and m3.] ...
Transport Homework Package
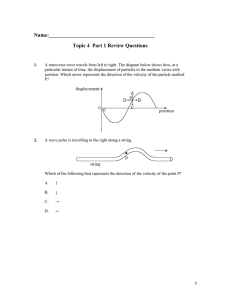
... 5. Look at the pairs of forces acting on the objects below. In each case, state the resultant force and the direction in which it is acting. (a) ...
... 5. Look at the pairs of forces acting on the objects below. In each case, state the resultant force and the direction in which it is acting. (a) ...
Gravitational Potential Energy
... that must be done on the mass to increase its speed to 11.5 meters per second? ...
... that must be done on the mass to increase its speed to 11.5 meters per second? ...
work and energy
... decreased nor increased It can change from one form to another It can be transferred from one body to another, but IT CAN NOT BE CREATED NOR DESTROYED ...
... decreased nor increased It can change from one form to another It can be transferred from one body to another, but IT CAN NOT BE CREATED NOR DESTROYED ...
Gravitational Potential Energy (PE)
... At pt.A, the reference level is the At pt.B, the reference level is the At pt.C, the reference level is the They all have a value of zero for Potential Energy. (PE = 0) ...
... At pt.A, the reference level is the At pt.B, the reference level is the At pt.C, the reference level is the They all have a value of zero for Potential Energy. (PE = 0) ...
Part I
... • In addition to a System, we also talk about the system environment. System interacts with environment at it’s boundaries. ...
... • In addition to a System, we also talk about the system environment. System interacts with environment at it’s boundaries. ...
APPLICATION OF FORCES
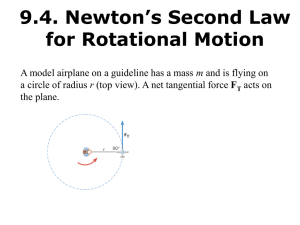
... • M.O.I – resistance of a body to a change of state when rotating • Angular Velocity – the rate of movement in rotation (its speed) • Newton’s 1st Law of Angular Motion: • ‘a rotating body will continue to turn about its axis with constant angular momentum unless an external force acts upon it. ...
... • M.O.I – resistance of a body to a change of state when rotating • Angular Velocity – the rate of movement in rotation (its speed) • Newton’s 1st Law of Angular Motion: • ‘a rotating body will continue to turn about its axis with constant angular momentum unless an external force acts upon it. ...
Unit 7 Review
... 15. Neglecting friction, if a child exerts a force of 85 N on the handle of a wagon that makes a 35 angle with the horizontal, how far is the wagon pulled when 280 J of work are done? ...
... 15. Neglecting friction, if a child exerts a force of 85 N on the handle of a wagon that makes a 35 angle with the horizontal, how far is the wagon pulled when 280 J of work are done? ...
Physics Year Long Plan
... affected by a change in speed or height, or stretch/compression (qualitatively) solve various problems involving all forms of energy using the law of conservation of energy describe the effect of friction on mechanical ...
... affected by a change in speed or height, or stretch/compression (qualitatively) solve various problems involving all forms of energy using the law of conservation of energy describe the effect of friction on mechanical ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.