Work, Power, and Energy - Atlanta International School Moodle
... Field Lines – Indicate the direction of gravitational force that would act on a point mass at that location. 1. For a gravitational field, the lines will always point inward as gravity is always an attractive force. 2. Note that the field lines are perpendicular to the equipotential lines. http://ww ...
... Field Lines – Indicate the direction of gravitational force that would act on a point mass at that location. 1. For a gravitational field, the lines will always point inward as gravity is always an attractive force. 2. Note that the field lines are perpendicular to the equipotential lines. http://ww ...
Lesson 1 - SchoolRack
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object increas ...
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object increas ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... g = 9.8 m/s2 (from our lab experiment), G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nt-m2/kg2 (from precise gravity force experiments), and Rearth = 6,400 km (since we know the circumference of the earth = 25,000 miles). ...
... g = 9.8 m/s2 (from our lab experiment), G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nt-m2/kg2 (from precise gravity force experiments), and Rearth = 6,400 km (since we know the circumference of the earth = 25,000 miles). ...
Conservation of Momentum Notes
... together), and kinetic energy is conserved. • An ideal situation that is often never quite reached… billiard ball collisions are often used as an example of elastic collisions. • Kinetic (motion) energy is conserved: ...
... together), and kinetic energy is conserved. • An ideal situation that is often never quite reached… billiard ball collisions are often used as an example of elastic collisions. • Kinetic (motion) energy is conserved: ...
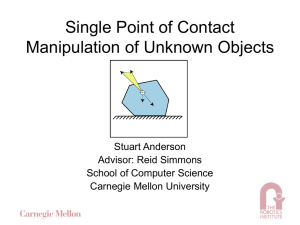
Single Point of Contact Manipulation of Unknown Objects
... constructed from these samples. – Because w’(x) is linear in r we need only sample the minimal and maximal values of r for a given theta. – The number of samples needed for a given maximum error bound grows linearly in the radius of a circle which encloses the contact hull. ...
... constructed from these samples. – Because w’(x) is linear in r we need only sample the minimal and maximal values of r for a given theta. – The number of samples needed for a given maximum error bound grows linearly in the radius of a circle which encloses the contact hull. ...
Lecture-05-09
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backward) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wha ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backward) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wha ...
100 Lec11 06
... Inner core of a larger star collapses into a neutron star of very small radius r = rsun = 7 x 105 km, m = 2 msun,, T = 10 d, rn-star = 10 km Assume no mass is lost in collapse. What is n-star’ rate of rotation? ...
... Inner core of a larger star collapses into a neutron star of very small radius r = rsun = 7 x 105 km, m = 2 msun,, T = 10 d, rn-star = 10 km Assume no mass is lost in collapse. What is n-star’ rate of rotation? ...
EOC_chapter8 - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... the motions of equipment and other astronauts and as a result of venting of materials from the craft. Assume that a 3 500-kg spacecraft undergoes an acceleration of 2.50 μg = 2.45 × 10–5 m/s2 due to a leak from one of its hydraulic control systems. The fluid is known to escape with a speed of 70.0 m ...
... the motions of equipment and other astronauts and as a result of venting of materials from the craft. Assume that a 3 500-kg spacecraft undergoes an acceleration of 2.50 μg = 2.45 × 10–5 m/s2 due to a leak from one of its hydraulic control systems. The fluid is known to escape with a speed of 70.0 m ...
Conceptual Physics
... c. Do you experience an impulse when you catch it and then throw it out again? d. Which impulse is greatest? 88. Why is more impulse delivered during a collision when bouncing occurs than during one when it doesn’t? 89. In terms of momentum conservation, why dies a cannon recoil when fired? 90. What ...
... c. Do you experience an impulse when you catch it and then throw it out again? d. Which impulse is greatest? 88. Why is more impulse delivered during a collision when bouncing occurs than during one when it doesn’t? 89. In terms of momentum conservation, why dies a cannon recoil when fired? 90. What ...
chp. 8
... If the acceleration is small, the speed in increasing gradually. If the acceleration is large, the speed is ...
... If the acceleration is small, the speed in increasing gradually. If the acceleration is large, the speed is ...
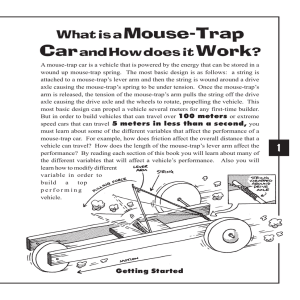
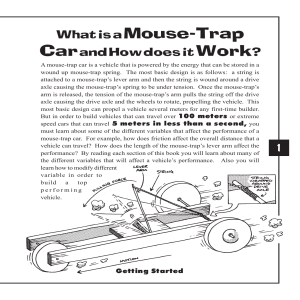
Mouse-Trap Car Worksheet
... If your vehicle does not have enough grip on the floor AND you have too much pulling force your wheels will spin-out! The more “grip” or traction your wheels have on the floor surface, the greater the acceleration that is possible for your vehicle. If you are making a speed-trap or a power pulling v ...
... If your vehicle does not have enough grip on the floor AND you have too much pulling force your wheels will spin-out! The more “grip” or traction your wheels have on the floor surface, the greater the acceleration that is possible for your vehicle. If you are making a speed-trap or a power pulling v ...
Unit 8 Student Notes
... A tossed stone, a cannonball, or any object projected by any means that continues in motion is called a projectile. A thrown stone falls beneath the straight line it would follow with no gravity. The stone curves as it falls. Interestingly, this familiar curve is the result of two kinds of motion oc ...
... A tossed stone, a cannonball, or any object projected by any means that continues in motion is called a projectile. A thrown stone falls beneath the straight line it would follow with no gravity. The stone curves as it falls. Interestingly, this familiar curve is the result of two kinds of motion oc ...
1-2 - Renton School District
... (LITERACY) Students revisit their ideas about force. if this works) ...
... (LITERACY) Students revisit their ideas about force. if this works) ...
Physics - Partners4results
... A. 12 N at 10 meters from the axis of rotation B. 12 N at 5 meters from the axis of rotation C. 6 N at 10 meters from the axis of rotation D. 6 N at 5 meters from the axis of rotation 10. Suppose an ice-skater spins at 3 revs/second. She then changes her body position so that her rotational inertia ...
... A. 12 N at 10 meters from the axis of rotation B. 12 N at 5 meters from the axis of rotation C. 6 N at 10 meters from the axis of rotation D. 6 N at 5 meters from the axis of rotation 10. Suppose an ice-skater spins at 3 revs/second. She then changes her body position so that her rotational inertia ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.