lecture two
... Weight: The force due to gravity. Q:A person has weight 500N on the earth, what is his weight on Fg=w the moon? Location – mass –weight Earth 1kg 9.8N Moon 1kg 1.6N c M Space 1kg 0N w w Friction: resistance force for the relative motion. Static friction: when there is no Dynamic friction: When there ...
... Weight: The force due to gravity. Q:A person has weight 500N on the earth, what is his weight on Fg=w the moon? Location – mass –weight Earth 1kg 9.8N Moon 1kg 1.6N c M Space 1kg 0N w w Friction: resistance force for the relative motion. Static friction: when there is no Dynamic friction: When there ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Mass is the amount of matter in your body • Weight is the amount of force acting on your body • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth ...
... • Mass is the amount of matter in your body • Weight is the amount of force acting on your body • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - Southgate Community School
... We Say: Pressure is the amount of force applied per area of something Ex. 32 psi of tire pressure = 32 lb/in2 We Write: P = F A (Eq. 12) Units for Pressure are N/m2 OR Pa (Pascal) As Pressure increases, Area decreases Ex. Barefeet & Rocks Ex. Snowshoes ...
... We Say: Pressure is the amount of force applied per area of something Ex. 32 psi of tire pressure = 32 lb/in2 We Write: P = F A (Eq. 12) Units for Pressure are N/m2 OR Pa (Pascal) As Pressure increases, Area decreases Ex. Barefeet & Rocks Ex. Snowshoes ...
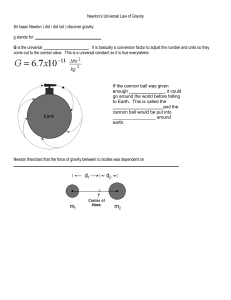
Newton`s Universal Law of Gravity
... Sir Isaac Newton ( did / did not ) discover gravity: g stands for: ________________________________ G is the universal ______________________. It is basically a conversion factor to adjust the number and units so they come out to the correct value. This is a universal constant so it is true everywhe ...
... Sir Isaac Newton ( did / did not ) discover gravity: g stands for: ________________________________ G is the universal ______________________. It is basically a conversion factor to adjust the number and units so they come out to the correct value. This is a universal constant so it is true everywhe ...
2.1 Forces change motion
... Balanced and unbalanced forces • If the net force on an object is zero, the forces acting on the object are balanced. ...
... Balanced and unbalanced forces • If the net force on an object is zero, the forces acting on the object are balanced. ...
Newton*s third Law of Motion
... MASSIVE THAN THE OTHER. THIS IS WHY THE MASSIVE OBJECT MIGHT SEEM TO REMAIN MOTIONLESS. • EXAMPLE: A PERSON WALKING ON THE GROUND. (GROUND/EARTH IS MASSIVE=MOTION IS UNDETECTED) ...
... MASSIVE THAN THE OTHER. THIS IS WHY THE MASSIVE OBJECT MIGHT SEEM TO REMAIN MOTIONLESS. • EXAMPLE: A PERSON WALKING ON THE GROUND. (GROUND/EARTH IS MASSIVE=MOTION IS UNDETECTED) ...
Conceptual Physics
... ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: ...
... ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: ...
Angular Motion Vocabulary
... 20. Universal Gravitation Constant- the universal constant relating force to mass and distance in Newton's law of gravitation Johannes Kepler published his first two laws about planetary motion in 1609, having derived them by analyzing the astronomical observations painstakingly collected by Tycho B ...
... 20. Universal Gravitation Constant- the universal constant relating force to mass and distance in Newton's law of gravitation Johannes Kepler published his first two laws about planetary motion in 1609, having derived them by analyzing the astronomical observations painstakingly collected by Tycho B ...
Skill Phases for
... Chaining angular momentum is transferred in the body from one set of muscle groups to another Lever action for speed or force ...
... Chaining angular momentum is transferred in the body from one set of muscle groups to another Lever action for speed or force ...
05
... at aphelion ( farthest point from the sun) and 80 km/sec at perihelion ( closest point ot the sun). If the earth’s velocity treated as a circle of radius 1.5 × 108 km. and it’s orbital speed as 30 km/sec., find the aphelion distance R of the planet from the Sun ( Focus). 25.Consider a spacecraft to ...
... at aphelion ( farthest point from the sun) and 80 km/sec at perihelion ( closest point ot the sun). If the earth’s velocity treated as a circle of radius 1.5 × 108 km. and it’s orbital speed as 30 km/sec., find the aphelion distance R of the planet from the Sun ( Focus). 25.Consider a spacecraft to ...
Starter Questions: Force and Motion
... What is the formula to calculate force? To which of Newton’s Laws does this formula apply? 7. Give an example of Newton’s First Law (The Law of Inertia) 8. What will have more force, a football player tackling at 10 m/s or a car hitting a wall at 10 m/s? Calculate the following problems. Show ALL yo ...
... What is the formula to calculate force? To which of Newton’s Laws does this formula apply? 7. Give an example of Newton’s First Law (The Law of Inertia) 8. What will have more force, a football player tackling at 10 m/s or a car hitting a wall at 10 m/s? Calculate the following problems. Show ALL yo ...
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits
In classical mechanics, Newton's theorem of revolving orbits identifies the type of central force needed to multiply the angular speed of a particle by a factor k without affecting its radial motion (Figures 1 and 2). Newton applied his theorem to understanding the overall rotation of orbits (apsidal precession, Figure 3) that is observed for the Moon and planets. The term ""radial motion"" signifies the motion towards or away from the center of force, whereas the angular motion is perpendicular to the radial motion.Isaac Newton derived this theorem in Propositions 43–45 of Book I of his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published in 1687. In Proposition 43, he showed that the added force must be a central force, one whose magnitude depends only upon the distance r between the particle and a point fixed in space (the center). In Proposition 44, he derived a formula for the force, showing that it was an inverse-cube force, one that varies as the inverse cube of r. In Proposition 45 Newton extended his theorem to arbitrary central forces by assuming that the particle moved in nearly circular orbit.As noted by astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in his 1995 commentary on Newton's Principia, this theorem remained largely unknown and undeveloped for over three centuries. Since 1997, the theorem has been studied by Donald Lynden-Bell and collaborators. Its first exact extension came in 2000 with the work of Mahomed and Vawda.