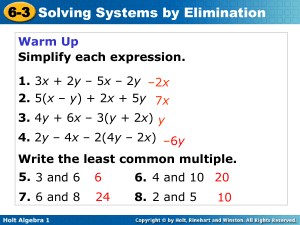
Questions and Problems
... only if no net torque acts on the system. This isn’t the case for either the pulley or the disk: A net torque due to the tension force acts on the pulley as it rotates, and a net torque due to the force of friction acts on the disk as it rolls downhill. For both objects the moment of inertia I remai ...
... only if no net torque acts on the system. This isn’t the case for either the pulley or the disk: A net torque due to the tension force acts on the pulley as it rotates, and a net torque due to the force of friction acts on the disk as it rolls downhill. For both objects the moment of inertia I remai ...
Chapter 21 The Electric Field I: Discrete Charge Distributions
... A –2.0 μC point charge and a 4.0 μC point charge are a distance L apart. Where should a third point charge be placed so that the electric force on that third charge is zero? Picture the Problem The third point charge should be placed at the location at which the forces on the third point charge due ...
... A –2.0 μC point charge and a 4.0 μC point charge are a distance L apart. Where should a third point charge be placed so that the electric force on that third charge is zero? Picture the Problem The third point charge should be placed at the location at which the forces on the third point charge due ...
Chapter 15—Oscillatory Motion MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A body of
... trapeze artist climbs to a point where her center of mass is at the center of the ladder and swings at the system's natural frequency. The angular frequency (in s1) of the system of ladder and woman is a. 1.01. b. 3.07. c. 4.03. d. 8.05. e. 16.2. ANS: B ...
... trapeze artist climbs to a point where her center of mass is at the center of the ladder and swings at the system's natural frequency. The angular frequency (in s1) of the system of ladder and woman is a. 1.01. b. 3.07. c. 4.03. d. 8.05. e. 16.2. ANS: B ...
1 - Sumner
... The scale will read more than 600 N. In general, the scale reads the downward force (N) exerted on it from the object placed on it, in this case, the student. If the student is not accelerating then the upward force on the student IS equal in magnitude to the student’s weight. In reaction to that th ...
... The scale will read more than 600 N. In general, the scale reads the downward force (N) exerted on it from the object placed on it, in this case, the student. If the student is not accelerating then the upward force on the student IS equal in magnitude to the student’s weight. In reaction to that th ...
AB_Activity_03
... Preparation for Teaching a Lab The following pages contain 6 authentic student answers to the Warm-up questions for a 1301 lab problem: Force and Motion. It is the first lab that addresses the physics concept of force. This particular set of solutions was from 2004. During the semester you will coll ...
... Preparation for Teaching a Lab The following pages contain 6 authentic student answers to the Warm-up questions for a 1301 lab problem: Force and Motion. It is the first lab that addresses the physics concept of force. This particular set of solutions was from 2004. During the semester you will coll ...
Orbits - GCSE Science Revision
... through the door but light travels in a straight lines. Describe how we can make light diffract (or bend) and why it will not show this effect when travelling through the door. ...
... through the door but light travels in a straight lines. Describe how we can make light diffract (or bend) and why it will not show this effect when travelling through the door. ...
CP7e: Ch. 7 Problems
... speed of 18.0 rad/s and rolls in a straight line without slipping. If the rotation slows with an angular acceleration of magnitude 1.90 rad/s2, how far does the coin roll before coming to rest? ...
... speed of 18.0 rad/s and rolls in a straight line without slipping. If the rotation slows with an angular acceleration of magnitude 1.90 rad/s2, how far does the coin roll before coming to rest? ...