Microsoft Word - 12.800 Chapter 10 `06
... whenever the particle is pulled towards the center of attraction and diminishes when the particle is moving away from the center, there will be a constant increase in the amplitude of a “free” oscillation. In fact, all little children recognize this intuitively; this is the basis for “pumping” a swi ...
... whenever the particle is pulled towards the center of attraction and diminishes when the particle is moving away from the center, there will be a constant increase in the amplitude of a “free” oscillation. In fact, all little children recognize this intuitively; this is the basis for “pumping” a swi ...
Linear Impulse − Momentum
... Collision Classifications • Collisions are classified according to whether the kinetic energy changes during the collision. • The two classifications are elastic and inelastic. • In an elastic collision the total kinetic energy of the system is the same before and after the collision. • In an a per ...
... Collision Classifications • Collisions are classified according to whether the kinetic energy changes during the collision. • The two classifications are elastic and inelastic. • In an elastic collision the total kinetic energy of the system is the same before and after the collision. • In an a per ...
Core Lab 4 Newton`s Second Law of Motion - eLearning
... 12. Three students in your class have different ideas about the magnitude of forces and changes in velocity. Carefully read the student arguments and decide which statement is best supported by the evidence. Student A “ The size of an unbalanced force has no affect on the amount of acceleration expe ...
... 12. Three students in your class have different ideas about the magnitude of forces and changes in velocity. Carefully read the student arguments and decide which statement is best supported by the evidence. Student A “ The size of an unbalanced force has no affect on the amount of acceleration expe ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s Second Law When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force. ...
... Newton’s Second Law When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force. ...
Chapter 1 - asmasaid
... Two objects, a ring and a disk, both with equal mass and radii. Each is rotating about an axis through its center, as shown. Which has the greatest rotational inertia, I, a uniform disk or a ring? A) They have the same I, since they both have the same mass and radius B) The disk C) The ring ...
... Two objects, a ring and a disk, both with equal mass and radii. Each is rotating about an axis through its center, as shown. Which has the greatest rotational inertia, I, a uniform disk or a ring? A) They have the same I, since they both have the same mass and radius B) The disk C) The ring ...
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION: SHIFTED ORIGIN AND PHASE
... b. What is the force exerted by the spring on the mass just before it is released? c. Write the equation for the displacement of the mass as a function of time after it is released. d. Calculate the period and frequency of the oscillations. 2. A 3.0 kg mass hangs from a spring. A 0.50 kg body hung b ...
... b. What is the force exerted by the spring on the mass just before it is released? c. Write the equation for the displacement of the mass as a function of time after it is released. d. Calculate the period and frequency of the oscillations. 2. A 3.0 kg mass hangs from a spring. A 0.50 kg body hung b ...
Tri 3 Study Guide 2014
... Describe the three types of acceleration and give an example of each: Type of acceleration Description Example ...
... Describe the three types of acceleration and give an example of each: Type of acceleration Description Example ...
electric circuits
... Second-order linear differential equations have a variety of applications in science and engineering. ...
... Second-order linear differential equations have a variety of applications in science and engineering. ...
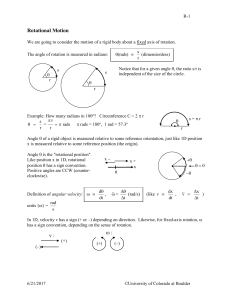
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
Physics 123/5 - UConn Physics
... 4.5 cm in a tree. Subsequent measurements showed that the tree would exert a stopping force of 70N on the straw. What was the straw’s speed when it hit the tree? Since the stopping force (70 N) is so much larger than the weight of the straw (0.0049 N), we may assume that the net work done is essenti ...
... 4.5 cm in a tree. Subsequent measurements showed that the tree would exert a stopping force of 70N on the straw. What was the straw’s speed when it hit the tree? Since the stopping force (70 N) is so much larger than the weight of the straw (0.0049 N), we may assume that the net work done is essenti ...
Forces and Motion
... The fluid friction experienced by objects falling through the air. The product of an object’s mass and velocity. The motion of a falling object when the only force acting on it is gravity. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two surfaces rub against each other. The tendency of an o ...
... The fluid friction experienced by objects falling through the air. The product of an object’s mass and velocity. The motion of a falling object when the only force acting on it is gravity. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two surfaces rub against each other. The tendency of an o ...
Conservation of Momentum
... light is struck from the rear by a compact car with a mass of 975 kg. The two cars become entangled as a result of the collision. If the compact car was moving at a velocity of 22.0 m/s to the north before the collision, what is the velocity of the entangled mass after the collision? ...
... light is struck from the rear by a compact car with a mass of 975 kg. The two cars become entangled as a result of the collision. If the compact car was moving at a velocity of 22.0 m/s to the north before the collision, what is the velocity of the entangled mass after the collision? ...
Newton`s Toy Box - Delta Education
... which the word is defined in the text. acceleration rate at which an object’s velocity changes ...
... which the word is defined in the text. acceleration rate at which an object’s velocity changes ...
Ph201_CH4_worksheet
... 11. Consider the same pulley system in Problem 10. In this case, there is friction (static and/or kinetic) between M2 and the horizontal surface. a. Draw free body diagrams for each mass. ...
... 11. Consider the same pulley system in Problem 10. In this case, there is friction (static and/or kinetic) between M2 and the horizontal surface. a. Draw free body diagrams for each mass. ...
momentum
... • Big player @ 2m/s Small player @ 2 m/s • Big player @ 0.6 m/s Small player @ 6 m/s • Small player @ 2 m/s Bullet @ 100 m/s • Small player @ 100 m/s Bullet @ 4 m/s ...
... • Big player @ 2m/s Small player @ 2 m/s • Big player @ 0.6 m/s Small player @ 6 m/s • Small player @ 2 m/s Bullet @ 100 m/s • Small player @ 100 m/s Bullet @ 4 m/s ...
My Skydiving Mishaps: A Quick Lesson in
... immediate acceleration downwards. What the instructors neglected to mention was that if you miss the first instruction and move your leg off the step, there is a very likely chance that your leg will smack into that very step, as it is in the way of your immediate direction down. And that is indeed ...
... immediate acceleration downwards. What the instructors neglected to mention was that if you miss the first instruction and move your leg off the step, there is a very likely chance that your leg will smack into that very step, as it is in the way of your immediate direction down. And that is indeed ...