Newton`s Second Law
... Place the cart on the Dynamics Track so the hook end of the Force Sensor points away from the Motion Sensor. The cart will be pulled away from the sensor. The cart must remain a minimum distance away from the sensor. The minimum distance from the sensor to its target is dependent upon the motion sen ...
... Place the cart on the Dynamics Track so the hook end of the Force Sensor points away from the Motion Sensor. The cart will be pulled away from the sensor. The cart must remain a minimum distance away from the sensor. The minimum distance from the sensor to its target is dependent upon the motion sen ...
Lecture 06: Conservation of Angular Momentum
... Linear motion: apply force to a mass The force causes the linear momentum to change The net force acting on a body is the time rate of change of its linear momentum ...
... Linear motion: apply force to a mass The force causes the linear momentum to change The net force acting on a body is the time rate of change of its linear momentum ...
Document
... We will consider effect of uniform motion on different quantities & laws of physics. We will establish a relationship between the space & time coordinates in two inertial frames of reference. The basic relations were obtained by Galileo & are ...
... We will consider effect of uniform motion on different quantities & laws of physics. We will establish a relationship between the space & time coordinates in two inertial frames of reference. The basic relations were obtained by Galileo & are ...
mr10Tsol
... difficult to tilt it, and you feel it exerting a large force on you. When a person sitting on the rotating stool tries to tilt the wheel they also feel the force that it exerts on them, but they are not held stationary to the ground by friction, so they begin to rotate with the stool. Angular moment ...
... difficult to tilt it, and you feel it exerting a large force on you. When a person sitting on the rotating stool tries to tilt the wheel they also feel the force that it exerts on them, but they are not held stationary to the ground by friction, so they begin to rotate with the stool. Angular moment ...
Quantum electrodynamics: one- and two-photon processes Contents December 19, 2005
... We take as basis dimensions length (l), mass (m), and time (t). Two common unit systems are m.k.s. (meter, kilogram, second), which is used in the S.I. system, and c.g.s. (centimeter, gram, second), which is used in the Gaussian unit system. The atomic units system has the Bohr radius (a0 ) for leng ...
... We take as basis dimensions length (l), mass (m), and time (t). Two common unit systems are m.k.s. (meter, kilogram, second), which is used in the S.I. system, and c.g.s. (centimeter, gram, second), which is used in the Gaussian unit system. The atomic units system has the Bohr radius (a0 ) for leng ...
TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS
... where: C = 2.00 and vc and fc are both measured in lbf/in2. What numerical value should be used for C if vc and fc are both measured in MPa? a. 6.02 b. 0.166 c. 2.00 d. 0.500 e. 1.00 17. If the mass of an object is 13.2 lbm on earth, what is the weight on the moon where the acceleration of gravity i ...
... where: C = 2.00 and vc and fc are both measured in lbf/in2. What numerical value should be used for C if vc and fc are both measured in MPa? a. 6.02 b. 0.166 c. 2.00 d. 0.500 e. 1.00 17. If the mass of an object is 13.2 lbm on earth, what is the weight on the moon where the acceleration of gravity i ...
physics 220 - Purdue Physics
... •Magnitude of the velocity vector is constant, but direction is constantly changing •At any instant of time, the direction of the instantaneous velocity is tangent to the path ...
... •Magnitude of the velocity vector is constant, but direction is constantly changing •At any instant of time, the direction of the instantaneous velocity is tangent to the path ...
force
... Balanced forces do not cause change in motion They are equal in size and opposite in direction ...
... Balanced forces do not cause change in motion They are equal in size and opposite in direction ...
Concept Questions
... The time derivative that appears in the second term in the above expression, the time derivative of the momentum of a mass element in the center-of mass-frame, is equal to the force acting on that element which include both inertial and fictitious forces, ...
... The time derivative that appears in the second term in the above expression, the time derivative of the momentum of a mass element in the center-of mass-frame, is equal to the force acting on that element which include both inertial and fictitious forces, ...
Rotary Motion
... the distance, r, of the object(s) from the axis of rotation. To test this hypothesis, you will need the data from several groups that positioned the weights at different distances along the rod. If that is not feasible, you will have to repeat Part 3 at least five more times, changing the distance t ...
... the distance, r, of the object(s) from the axis of rotation. To test this hypothesis, you will need the data from several groups that positioned the weights at different distances along the rod. If that is not feasible, you will have to repeat Part 3 at least five more times, changing the distance t ...
Force
... Contact forces 接 觸力 involve physical contact between two objects Field forces 場力 act through empty space ...
... Contact forces 接 觸力 involve physical contact between two objects Field forces 場力 act through empty space ...
dynamics intro power..
... The shell is fired from a gun leaving the barrel with a velocity of +770 m/s. The gun barrel is 1.5m long. Assume that the force, and the acceleration, of the shell is constant while the shell is in the gun barrel. What is the force on the shell while it is in the gun ...
... The shell is fired from a gun leaving the barrel with a velocity of +770 m/s. The gun barrel is 1.5m long. Assume that the force, and the acceleration, of the shell is constant while the shell is in the gun barrel. What is the force on the shell while it is in the gun ...
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum
... Rotating about a Fixed Axis • Angular momentum as analogue of linear momentum (What could we conclude?) • Scalar expressions for angular momentum, the relation of torque and angular momentum, and conservation of angular momentum ...
... Rotating about a Fixed Axis • Angular momentum as analogue of linear momentum (What could we conclude?) • Scalar expressions for angular momentum, the relation of torque and angular momentum, and conservation of angular momentum ...
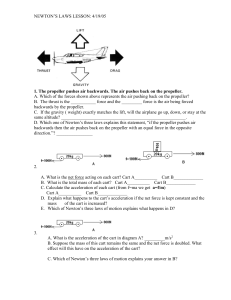
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
... B. The thrust is the ___________ force and the _________ force is the air being forced backwards by the propeller. C. If the gravity ( weight) exactly matches the lift, will the airplane go up, down, or stay at the same altitude? _______________________________________________________. D. Which one ...
... B. The thrust is the ___________ force and the _________ force is the air being forced backwards by the propeller. C. If the gravity ( weight) exactly matches the lift, will the airplane go up, down, or stay at the same altitude? _______________________________________________________. D. Which one ...