Chapter 7 Rotational Motion 7.1 Angular Quantities Homework # 51
... 03. A truck engine slows down from 3700 rpm to 1800 rpm in 4.25 s. How many revolutions were made by the engine during this time? 04. A car, with 26-inch (66.0-cm)-diameter wheels, accelerates from rest to 72.5 km/h (45.0 mi/h) in 295 m. a.) What is the angular displacement of the wheels? b.) What i ...
... 03. A truck engine slows down from 3700 rpm to 1800 rpm in 4.25 s. How many revolutions were made by the engine during this time? 04. A car, with 26-inch (66.0-cm)-diameter wheels, accelerates from rest to 72.5 km/h (45.0 mi/h) in 295 m. a.) What is the angular displacement of the wheels? b.) What i ...
Force and Motion
... the same direction. • Example: You’re pushing a cabinet across the room with a force of 15 N. You’re friend is pulling with a force of 10 N. • What is the NET FORCE? • What direction is the cabinet moving? ...
... the same direction. • Example: You’re pushing a cabinet across the room with a force of 15 N. You’re friend is pulling with a force of 10 N. • What is the NET FORCE? • What direction is the cabinet moving? ...
Momentum - ClassZone
... A moving object has a property that is called momentum (moh-MEHN-tuhm). Momentum is a measure of mass in motion; the momentum of an object is the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum is similar to inertia. To calculate an object’s momentum, you can use the following formula: momentum = mas ...
... A moving object has a property that is called momentum (moh-MEHN-tuhm). Momentum is a measure of mass in motion; the momentum of an object is the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum is similar to inertia. To calculate an object’s momentum, you can use the following formula: momentum = mas ...
Solutions for HW chapter 18
... 37- REASONING The electric field is given by Equation 18.2 as the force F that acts on a test charge q0, divided by q0. Although the force is not known, the acceleration and mass of the charged object are given. Therefore, we can use Newton’s second law to determine the force as the mass times the a ...
... 37- REASONING The electric field is given by Equation 18.2 as the force F that acts on a test charge q0, divided by q0. Although the force is not known, the acceleration and mass of the charged object are given. Therefore, we can use Newton’s second law to determine the force as the mass times the a ...
Powerpoint Slides - Faculty Web Sites
... When you strike a wall, does it hurt your hand? You might say the wall struck you. Newton would say the force you applied to the wall was the same as that which the wall applied to you. The wall is bigger and more massive, therefore has more inertia and was not harmed as much as you. If you push on ...
... When you strike a wall, does it hurt your hand? You might say the wall struck you. Newton would say the force you applied to the wall was the same as that which the wall applied to you. The wall is bigger and more massive, therefore has more inertia and was not harmed as much as you. If you push on ...
Test 3 Preparation Questions
... volumes. They are both placed in a swimming pool filled with water. The wood floats on the surface and the iron sinks to the bottom. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning the buoyant forces acting on the two objects? (A) The floating wood has a greater buoyant force on it since ...
... volumes. They are both placed in a swimming pool filled with water. The wood floats on the surface and the iron sinks to the bottom. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning the buoyant forces acting on the two objects? (A) The floating wood has a greater buoyant force on it since ...
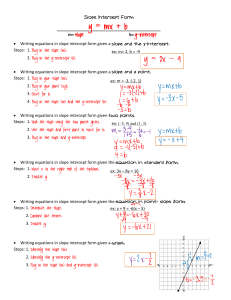
ALGEBRA I
... Recognize point-slope form Write an equation of a line in point-slope form Write an equation of a line in point slope form given: 1.) A point and a slope 2.) 2 points 3.) A point and the nature of the line 4.) Graph Transform any linear equation from one of the following forms to any other form: 1.) ...
... Recognize point-slope form Write an equation of a line in point-slope form Write an equation of a line in point slope form given: 1.) A point and a slope 2.) 2 points 3.) A point and the nature of the line 4.) Graph Transform any linear equation from one of the following forms to any other form: 1.) ...
First 5 chapters
... Overview.............................................................................................. 37 Two Concepts ...................................................................................... 38 Newton’s Second Law ....................................................................... ...
... Overview.............................................................................................. 37 Two Concepts ...................................................................................... 38 Newton’s Second Law ....................................................................... ...
Physics 201: Lecture 1
... In many real systems, nonconservative forces are present The system is no longer ideal Friction/drag force are common nonconservative forces In this case, the mechanical energy of the system diminishes in time, the motion is said to be damped The amplitude decreases with time The blue dashed lines ...
... In many real systems, nonconservative forces are present The system is no longer ideal Friction/drag force are common nonconservative forces In this case, the mechanical energy of the system diminishes in time, the motion is said to be damped The amplitude decreases with time The blue dashed lines ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued
... In the collision of bullet and block, tension in string and weight are external forces but the net external force is zero. Therefore, momentum is conserved. Because the bullet is stopped in the block by friction, energy is not conserved in collision. But, after the collision, only gravity (a conserv ...
... In the collision of bullet and block, tension in string and weight are external forces but the net external force is zero. Therefore, momentum is conserved. Because the bullet is stopped in the block by friction, energy is not conserved in collision. But, after the collision, only gravity (a conserv ...
4 Newton`s Laws
... 7. Highlight the points on your graph that follow a straight line (the slope should be negative because the cart is accelerating towards the motion sensor). Do NOT include the end points of ...
... 7. Highlight the points on your graph that follow a straight line (the slope should be negative because the cart is accelerating towards the motion sensor). Do NOT include the end points of ...
Lab 5 – Circular Motion and Forces
... Once you have become proficient at whirling the stopper so that the mark on the string stays even with the bottom of the tube, you’re ready to take data. 3. In the data table on the workshe ...
... Once you have become proficient at whirling the stopper so that the mark on the string stays even with the bottom of the tube, you’re ready to take data. 3. In the data table on the workshe ...