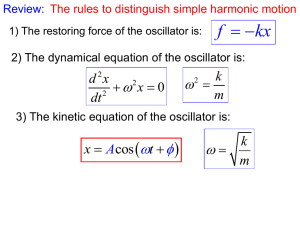
Simple Harmonic Motion
... B free oscillation. C resonance. D stationary waves. (Total for Question = 1 mark) ...
... B free oscillation. C resonance. D stationary waves. (Total for Question = 1 mark) ...
ParticleSystems - Computer Science and Engineering
... particles, they should obey conservation of momentum As it happens, the springs will also conserve energy, as the kinetic energy of motion can be stored in the deformation energy of the spring and later restored In practice, our simple implementation of the particle system will guarantee conservatio ...
... particles, they should obey conservation of momentum As it happens, the springs will also conserve energy, as the kinetic energy of motion can be stored in the deformation energy of the spring and later restored In practice, our simple implementation of the particle system will guarantee conservatio ...
RGch10
... Differential equations describe how physical quantities change, often with time or position. The rate of change of a physical quantity, y , with time t is written as dy /dt . The rate of change of a physical quantity, y , with position x is written as dy /dx . A rate of change can itself change. For ...
... Differential equations describe how physical quantities change, often with time or position. The rate of change of a physical quantity, y , with time t is written as dy /dt . The rate of change of a physical quantity, y , with position x is written as dy /dx . A rate of change can itself change. For ...
SOLVING SYSTEMS BY GRAPHING INTRODUCTION The objective
... second line. What did we find out about the point (zero, five) when we substituted it into the equations? It was a solution for the first line but not the second. What do you notice about the point (two, zero)? This point lies on the second line but not the first. What did we find out about the poin ...
... second line. What did we find out about the point (zero, five) when we substituted it into the equations? It was a solution for the first line but not the second. What do you notice about the point (two, zero)? This point lies on the second line but not the first. What did we find out about the poin ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... Thus the Lorentz condition on the potentials makes the electric charges and magnetic monopoles time independent. The equation (3) indicates that the electric charges or magnetic monopoles cannot be created or destroyed but they can be transferred from one position to other. However, in pair producti ...
... Thus the Lorentz condition on the potentials makes the electric charges and magnetic monopoles time independent. The equation (3) indicates that the electric charges or magnetic monopoles cannot be created or destroyed but they can be transferred from one position to other. However, in pair producti ...
The 5?
... Walter is a waiter at the Towne Diner. He earns a daily wage of $50, plus tips that are equal to 15% of the total cost of the dinners he serves. What was the total cost of the dinners he ...
... Walter is a waiter at the Towne Diner. He earns a daily wage of $50, plus tips that are equal to 15% of the total cost of the dinners he serves. What was the total cost of the dinners he ...
Chapter 2
... §1-4 forced oscillations The mechanical energy of a damped oscillator decreases in time as a result of resistive force. The diminished mechanical energy is possible to be compensated by applying an external force that does positive work on the system. If the external force varies periodically F (t ...
... §1-4 forced oscillations The mechanical energy of a damped oscillator decreases in time as a result of resistive force. The diminished mechanical energy is possible to be compensated by applying an external force that does positive work on the system. If the external force varies periodically F (t ...
Chapter 8 Rigid Body Rotation: Axis Direction Fixed - RIT
... Chapter 8 begins the discussion of rigid bodies, a system of particles with fixed relative positions. Previously we have dealt with movement of a particle: if a rigid body does not rotate it usually can just be treated by these earlier techniques. In Chapter 8 we discuss only rotations about an axis ...
... Chapter 8 begins the discussion of rigid bodies, a system of particles with fixed relative positions. Previously we have dealt with movement of a particle: if a rigid body does not rotate it usually can just be treated by these earlier techniques. In Chapter 8 we discuss only rotations about an axis ...
Section 3.1.jnt - Lone Star College
... decreasing at a rate of 4 units per minute. At what rate is the x – coordinate changing as the particle passes through the point (-1,0)? ...
... decreasing at a rate of 4 units per minute. At what rate is the x – coordinate changing as the particle passes through the point (-1,0)? ...
Section 2 Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... • Newton’s law of gravitation accounts for ocean tides. • High and low tides are partly due to the gravitational force exerted on Earth by its moon. • The tides result from the difference between the gravitational force at Earth’s surface and at Earth’s ...
... • Newton’s law of gravitation accounts for ocean tides. • High and low tides are partly due to the gravitational force exerted on Earth by its moon. • The tides result from the difference between the gravitational force at Earth’s surface and at Earth’s ...
Oscillations and Waves
... • To do calculations with simple harmonic motion • To analyze simple harmonic motion using energy • To apply the ideas of simple harmonic motion to different physical situations • To analyze the motion of a simple pendulum • To examine the characteristics of a physical pendulum • To explore how osci ...
... • To do calculations with simple harmonic motion • To analyze simple harmonic motion using energy • To apply the ideas of simple harmonic motion to different physical situations • To analyze the motion of a simple pendulum • To examine the characteristics of a physical pendulum • To explore how osci ...
Waves - TeacherWeb
... Resonance, occurs when small forces are applied at regular intervals to a vibrating or oscillating object and the amplitude or vibration increases The addition of small forces at specific times increases the amplitude Pushing a stuck car, trampoline, diving board etc. Resonance can be very destructi ...
... Resonance, occurs when small forces are applied at regular intervals to a vibrating or oscillating object and the amplitude or vibration increases The addition of small forces at specific times increases the amplitude Pushing a stuck car, trampoline, diving board etc. Resonance can be very destructi ...
Document
... Daisy’s Flowers sells a rose bouquet for $39.95 plus $2.95 for every rose. A competing florist sells a similar bouquet for $26.00 plus $4.50 for every rose. Find the number of roses that would make both florists' bouquets cost the same price. What is the price? Write an equation for each service. Le ...
... Daisy’s Flowers sells a rose bouquet for $39.95 plus $2.95 for every rose. A competing florist sells a similar bouquet for $26.00 plus $4.50 for every rose. Find the number of roses that would make both florists' bouquets cost the same price. What is the price? Write an equation for each service. Le ...