Chapter 5 Lecture
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
Forces_and_Newtons_Laws_powerpoint
... • Friction is the force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. • Friction always acts in the direction opposite an object’s motion. • The two factors that affect friction are the types of surfaces involved and how hard they are pushed together. Not quite enough frict ...
... • Friction is the force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. • Friction always acts in the direction opposite an object’s motion. • The two factors that affect friction are the types of surfaces involved and how hard they are pushed together. Not quite enough frict ...
Document
... Having verified the relationship between the vector potential A and the electric field E, we can now state Maxwell’s Equations in their computational form, which, of course is where we ...
... Having verified the relationship between the vector potential A and the electric field E, we can now state Maxwell’s Equations in their computational form, which, of course is where we ...
Physics Academic v. 2016
... the net torque on the object is zero; Rotational Inertia- The mass property of a rigid body that measures its resistance to changing rotation ...
... the net torque on the object is zero; Rotational Inertia- The mass property of a rigid body that measures its resistance to changing rotation ...
AP Physics - Rose Tree Media School District
... Benchmark # 3 Add and subtract vector quantities in two and three dimenisons. a. Draw vectors graphically, and add and subtract them using the head-tail method to find the resultant. b. Draw vectors mathematically from a common origin, and resolve each into components. c. Add and subtract components ...
... Benchmark # 3 Add and subtract vector quantities in two and three dimenisons. a. Draw vectors graphically, and add and subtract them using the head-tail method to find the resultant. b. Draw vectors mathematically from a common origin, and resolve each into components. c. Add and subtract components ...
Pendulum Periods
... Air resistance is sometimes referred to as a drag force. Experiments have been done with a variety of objects falling in air. These sometimes show that the drag force is proportional to the velocity and sometimes that the drag force is proportional to the square of the velocity. In either case, the ...
... Air resistance is sometimes referred to as a drag force. Experiments have been done with a variety of objects falling in air. These sometimes show that the drag force is proportional to the velocity and sometimes that the drag force is proportional to the square of the velocity. In either case, the ...
Shock and Acceleration Theory
... 5. Plot acceleration vs. time for one of your more interesting foam configurations. Note on the graph what is happening at critical points. 6. Using the information contained in your acceleration vs. time plots, calculate the maximum displacement of the foam for a few interesting examples. One way t ...
... 5. Plot acceleration vs. time for one of your more interesting foam configurations. Note on the graph what is happening at critical points. 6. Using the information contained in your acceleration vs. time plots, calculate the maximum displacement of the foam for a few interesting examples. One way t ...
+ B
... Newton’s Second Law Newton’s second law of motion will be discussed quantitatively in a later chapter, after we have covered acceleration. Acceleration is the rate at which the speed of an object changes. An object with an acceleration of 2 m/s2, for example, is an object whose speed increases by 2 ...
... Newton’s Second Law Newton’s second law of motion will be discussed quantitatively in a later chapter, after we have covered acceleration. Acceleration is the rate at which the speed of an object changes. An object with an acceleration of 2 m/s2, for example, is an object whose speed increases by 2 ...
Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles
... Ex 7: Determine whether the two lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither: a) 3x + y = -4 and 6y – 2x = 12 b) y = 2x + 1 and y = -2x – 3 c) 3y – 15x = -6 and y = 5x + 2 ...
... Ex 7: Determine whether the two lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither: a) 3x + y = -4 and 6y – 2x = 12 b) y = 2x + 1 and y = -2x – 3 c) 3y – 15x = -6 and y = 5x + 2 ...
Semester Exam REVIEW PACKET KEY
... iii. At t = 0, who is faster? Who has a greater positive starting position? Still A (see explanation in part i) and B has the greater positive starting position ...
... iii. At t = 0, who is faster? Who has a greater positive starting position? Still A (see explanation in part i) and B has the greater positive starting position ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... centered in the indicator marker. While keeping the angular velocity constant, record the data for several rotations by clicking on the record button in the software window. 3. Expand the graph of angular position vs. time. 4. Select a straight portion of the graph indicating constant angular veloci ...
... centered in the indicator marker. While keeping the angular velocity constant, record the data for several rotations by clicking on the record button in the software window. 3. Expand the graph of angular position vs. time. 4. Select a straight portion of the graph indicating constant angular veloci ...
4.7.14 Write Equations Parallel and Perpendicular Notes
... • Graphs: Lines Never Intersect and are in the same plane • Equations: ...
... • Graphs: Lines Never Intersect and are in the same plane • Equations: ...
6th entering 7th grade Math - 6Y and 6X Mrs
... grade and will provide students a thorough review of skills needed for seventh grade. lt is important that this packet be completed to the best of their ability. The objective of this assignment is to help them succeed in the next school year. All questions must have work to support the answers. Wor ...
... grade and will provide students a thorough review of skills needed for seventh grade. lt is important that this packet be completed to the best of their ability. The objective of this assignment is to help them succeed in the next school year. All questions must have work to support the answers. Wor ...
Chapter 12 - FIA Science
... According to Newton’s third law of motion, whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. ...
... According to Newton’s third law of motion, whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. ...
New Variational-Lagrangian Thermodynamics of Viscous Fluid Mixtures with Thermomolecular Diffusion
... total entropy flux 8, instead of the entropy flux &‘$due to thermal conduction only. In (3.19) the coefficient $P includes the coupling between l@f and the entropy flux Bi due to both convection and thermal conduction. In order to evaluate the dissipation due to the viscosity properties of the mixtu ...
... total entropy flux 8, instead of the entropy flux &‘$due to thermal conduction only. In (3.19) the coefficient $P includes the coupling between l@f and the entropy flux Bi due to both convection and thermal conduction. In order to evaluate the dissipation due to the viscosity properties of the mixtu ...
9.hamilton11e_ppt_11
... Horizontal velocity projects the object some distance from the release point © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Horizontal velocity projects the object some distance from the release point © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved. ...
Windsor High School Birdsell Conceptual Physics A Windsor High
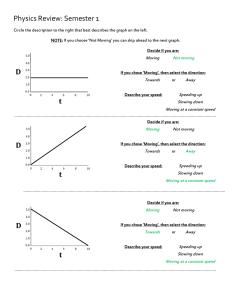
... acceleration,and distance for linear motion B2. Calculate speed,velocity, acceleration, and distance for falling objects B3. Construct graphs for motion B4. Interpret graphs of motion ...
... acceleration,and distance for linear motion B2. Calculate speed,velocity, acceleration, and distance for falling objects B3. Construct graphs for motion B4. Interpret graphs of motion ...
a1_ch01_02
... Solving Equations by 1-2 Adding or Subtracting An equation is a mathematical statement that two expressions are equal. A solution of an equation is a value of the variable that makes the equation true. To find solutions, isolate the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one ...
... Solving Equations by 1-2 Adding or Subtracting An equation is a mathematical statement that two expressions are equal. A solution of an equation is a value of the variable that makes the equation true. To find solutions, isolate the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one ...