Q1 CP Physics Answer Section
... ____ 12. A ball is pushed with an initial velocity of 4.0 m/s. The ball rolls down a hill with a constant acceleration of 1.6 m/s2. The ball reaches the bottom of the hill in 8.0 s. What is the ball's velocity at the bottom of the hill? a. 10 m/s b. 12 m/s c. 16 m/s d. 17 m/s ____ 13. A bird, accel ...
... ____ 12. A ball is pushed with an initial velocity of 4.0 m/s. The ball rolls down a hill with a constant acceleration of 1.6 m/s2. The ball reaches the bottom of the hill in 8.0 s. What is the ball's velocity at the bottom of the hill? a. 10 m/s b. 12 m/s c. 16 m/s d. 17 m/s ____ 13. A bird, accel ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... Rotation has several terms that have similar properties to terms in linear motion. Distance gets replaced with angle, speed with angular speed, acceleration with angular acceleration, mass with moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with ang ...
... Rotation has several terms that have similar properties to terms in linear motion. Distance gets replaced with angle, speed with angular speed, acceleration with angular acceleration, mass with moment of inertia, force with torque, kinetic energy with rotational kinetic energy, and momentum with ang ...
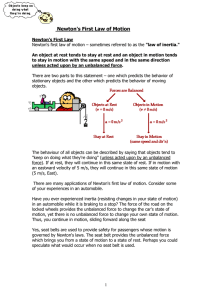
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Newton's Second Law of Motion Newton's Second Law Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if ...
... Newton's Second Law of Motion Newton's Second Law Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if ...
Lesson 10 notes - Angular Measurement - science
... point above the car, your upper half will be seen to be trying to follow a tangential path while the car turns to the left. Watching a marble roll on the surface of a table in a train as the train corners: again, if the train turns to the left, the marble will appear to drift off to the right. It is ...
... point above the car, your upper half will be seen to be trying to follow a tangential path while the car turns to the left. Watching a marble roll on the surface of a table in a train as the train corners: again, if the train turns to the left, the marble will appear to drift off to the right. It is ...
ce-phy ii
... 1 What physical quantity does the area of the shaded region represent? A. B. C. D. ...
... 1 What physical quantity does the area of the shaded region represent? A. B. C. D. ...
Notes - Net Forces and Applications of Newton`s Laws
... 1. Weight – a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object; direction is down (toward the earth’s center); symbol is W W=mg Where W is the weight of the object in Newtons, m is the mass of the object in kilograms, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. Advanced Look at Weight It is easy ...
... 1. Weight – a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object; direction is down (toward the earth’s center); symbol is W W=mg Where W is the weight of the object in Newtons, m is the mass of the object in kilograms, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. Advanced Look at Weight It is easy ...
to - GEOCITIES.ws
... A student wanted to find out if the temperature of water affected the amount of sugar that would dissolve in it. He put 50 mL of water into each of four identical jars. He changed the temperatures of the water in the jars until he had one at 0°C, one at 50°C, one at 75°C, and one at 95°C. He then di ...
... A student wanted to find out if the temperature of water affected the amount of sugar that would dissolve in it. He put 50 mL of water into each of four identical jars. He changed the temperatures of the water in the jars until he had one at 0°C, one at 50°C, one at 75°C, and one at 95°C. He then di ...
AP Physics 1 Investigation 2: Newton`s Second Law
... cart and the falling mass are included in the total inertial mass of the system being affected by the gravitational force on the falling mass. During the investigation, all masses to be used as falling masses should be placed in the cart when not pulling the cart. Students will be tempted to have th ...
... cart and the falling mass are included in the total inertial mass of the system being affected by the gravitational force on the falling mass. During the investigation, all masses to be used as falling masses should be placed in the cart when not pulling the cart. Students will be tempted to have th ...
Edmund Taylor Whittaker. 1873-1956
... Whittaker's first long paper, 'On the connexion of algebraic functions with automorphic functions', (R.2) was the definitive edition of his Trinity fellowship thesis and Smith's Price essay. If u is a many-valuedfunction of z, defined by an equationf(u, z) = 0, then it may be possible to find a vari ...
... Whittaker's first long paper, 'On the connexion of algebraic functions with automorphic functions', (R.2) was the definitive edition of his Trinity fellowship thesis and Smith's Price essay. If u is a many-valuedfunction of z, defined by an equationf(u, z) = 0, then it may be possible to find a vari ...
Newton`s Laws Multiple Choice: 1. The resistance of an object to
... e. Forces always cause objects to move. f. An object can experience two or more forces and not accelerate. g. A contact force results from the physical contact between two objects. h. A field force results from the action of two objects which are positioned some distance away. i. Spring and tension ...
... e. Forces always cause objects to move. f. An object can experience two or more forces and not accelerate. g. A contact force results from the physical contact between two objects. h. A field force results from the action of two objects which are positioned some distance away. i. Spring and tension ...
Learning Objectives for AP Physics
... (1) Identify by inspection the center of mass of a symmetrical object. (2) Locate the center of mass of a system consisting of two such objects. (3) Use integration to find the center of mass of a thin rod of non-uniform density b) Students should be able to understand and apply the relation between ...
... (1) Identify by inspection the center of mass of a symmetrical object. (2) Locate the center of mass of a system consisting of two such objects. (3) Use integration to find the center of mass of a thin rod of non-uniform density b) Students should be able to understand and apply the relation between ...
PHY–309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 10. Non
... with the right support. Thus, there is no normal force on the right and of the bridge. Instead, the right end is pulled up by the two chains of net tension T ; we do not know the magnitude of this tension force but we do know its direction: along the chains themselves, θ = 40◦ above the horizontal. ...
... with the right support. Thus, there is no normal force on the right and of the bridge. Instead, the right end is pulled up by the two chains of net tension T ; we do not know the magnitude of this tension force but we do know its direction: along the chains themselves, θ = 40◦ above the horizontal. ...
Chapter 10 Rotational Motion
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...