Conservation of Momentum and Energy
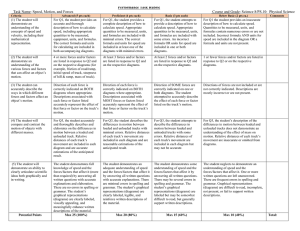
... There are several things that must be done in preparation for the experiments. Most importantly is to check if the track is level. Levels are provided for this purpose. Take one, and place it over the track’s feet at one end of the track. First, place it along the length of the track and observe the ...
... There are several things that must be done in preparation for the experiments. Most importantly is to check if the track is level. Levels are provided for this purpose. Take one, and place it over the track’s feet at one end of the track. First, place it along the length of the track and observe the ...
Ch 7 momentum notes
... momentum is a vector quantity ........has both magnitude and direction momentum can be canceled by equal and opposite momentum *if no net force or net impulse acts on a system, the momentum of that system cannot change -momentum of a system cannot change unless it is acted on by external forces -a s ...
... momentum is a vector quantity ........has both magnitude and direction momentum can be canceled by equal and opposite momentum *if no net force or net impulse acts on a system, the momentum of that system cannot change -momentum of a system cannot change unless it is acted on by external forces -a s ...
03 Linear Systems and Matrices
... • Use matrix operations to find the total sales of each product for each store ...
... • Use matrix operations to find the total sales of each product for each store ...
Color
... …because the seesaw has rotational inertia! Newton’s first law of rotational motion A rigid object that’s not wobbling and that is free of outside torques rotates at constant angular velocity. ...
... …because the seesaw has rotational inertia! Newton’s first law of rotational motion A rigid object that’s not wobbling and that is free of outside torques rotates at constant angular velocity. ...
6.3 Logarithmic Functions
... Now Let’s Apply the Definition to Solve. Here are the steps: 1. Set the logarithm equal to y 2. Rewrite the logarithm in exponential form Logarithmic form: y = logb x ...
... Now Let’s Apply the Definition to Solve. Here are the steps: 1. Set the logarithm equal to y 2. Rewrite the logarithm in exponential form Logarithmic form: y = logb x ...
Sample problem
... Practice Problem: If x is the displacement of a particle, and d is the distance the particle traveled during that displacement, which of the following is always a true statement? a) d = |x| b) d < |x| c) d > |x| d) d > |x| e) d < |x| ...
... Practice Problem: If x is the displacement of a particle, and d is the distance the particle traveled during that displacement, which of the following is always a true statement? a) d = |x| b) d < |x| c) d > |x| d) d > |x| e) d < |x| ...
Chapter 5 – Linking Forces to Momentum and Energy
... Answer to Essential Question 12.1: This estimated time is less than the actual time. The closer the block gets to the equilibrium position, the smaller the force that is exerted on it by the spring, and the smaller the magnitude of the block’s acceleration. Because the block generally has a smaller ...
... Answer to Essential Question 12.1: This estimated time is less than the actual time. The closer the block gets to the equilibrium position, the smaller the force that is exerted on it by the spring, and the smaller the magnitude of the block’s acceleration. Because the block generally has a smaller ...
Chapter 9: Linear Momentum
... • In many situations, such as a bullet hitting a carrot, we cannot use Newton’s second law to solve problems because we know very little about the complicated forces involved. • In this chapter, we shall introduce momentum and impulse, and the conservation of momentum, to solve such problems. ...
... • In many situations, such as a bullet hitting a carrot, we cannot use Newton’s second law to solve problems because we know very little about the complicated forces involved. • In this chapter, we shall introduce momentum and impulse, and the conservation of momentum, to solve such problems. ...
Performance Task Rubric Task Name: Speed, Motion, and Forces
... (Q1) If you wanted to know if a truck was coming down the hill at an unsafe speed, what measurements and calculations could you use? (Q2) What variables would VDOT need to include when designing a runaway ramp that would effectively reduce the speed of a runaway truck? (Q3) How might a loaded truck ...
... (Q1) If you wanted to know if a truck was coming down the hill at an unsafe speed, what measurements and calculations could you use? (Q2) What variables would VDOT need to include when designing a runaway ramp that would effectively reduce the speed of a runaway truck? (Q3) How might a loaded truck ...
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3
... The angle of the ramp θ and the speed of the block before it starts up the ramp is v0 . The block will slide up to some height h above the floor before stopping. Show that h is independent of m and θ by deriving an expression for h in terms of v0 and g. ...
... The angle of the ramp θ and the speed of the block before it starts up the ramp is v0 . The block will slide up to some height h above the floor before stopping. Show that h is independent of m and θ by deriving an expression for h in terms of v0 and g. ...
Mathematical Structure of Analytic Mechanics
... (2) We just assumed that a force F = F(x) depending only on coordinates is described as thegradient of a potential function U. One can investigate what force fields can be describedin this way. A force field is called conservative, if for any trajectory ...
... (2) We just assumed that a force F = F(x) depending only on coordinates is described as thegradient of a potential function U. One can investigate what force fields can be describedin this way. A force field is called conservative, if for any trajectory ...
Advancing Physics A2
... Kepler’s laws are described in the student's book (page 36) but are not in the specification. They are summarised below: 1 a planet moves in an ellipse with the Sun at one focus 2 the line from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times 3 square of orbital time is proportional to cub ...
... Kepler’s laws are described in the student's book (page 36) but are not in the specification. They are summarised below: 1 a planet moves in an ellipse with the Sun at one focus 2 the line from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times 3 square of orbital time is proportional to cub ...
Chapter 11 Clickers
... both ends. The radius of the cylinder is r. At what angular speed must the this cylinder rotate to have the same total kinetic energy that it would have if it were moving horizontally with a speed v without rotation? v2 a) 2r ...
... both ends. The radius of the cylinder is r. At what angular speed must the this cylinder rotate to have the same total kinetic energy that it would have if it were moving horizontally with a speed v without rotation? v2 a) 2r ...
Chapter 8 (1, 3, 6, 7, 13, 19, 22, 39, 40, 44, 45, 52, 54, 56, 57, 63, 65
... the right, showing the bullet the instant before it hits the door. The physical situation is identical to that of a point mass mg moving in a circular path of radius r with tangential speed t = i. For that situation the angular momentum is ...
... the right, showing the bullet the instant before it hits the door. The physical situation is identical to that of a point mass mg moving in a circular path of radius r with tangential speed t = i. For that situation the angular momentum is ...