teacher background information force
... planet is known as weight. There is no such thing as weightlessness, since gravity exists everywhere in the universe! When you step on a bathroom scale (spring scale), you are determining the magnitude of the gravitational force Earth is exerting on you. The greater the mass of a body, the greater i ...
... planet is known as weight. There is no such thing as weightlessness, since gravity exists everywhere in the universe! When you step on a bathroom scale (spring scale), you are determining the magnitude of the gravitational force Earth is exerting on you. The greater the mass of a body, the greater i ...
Period 3 Activity Sheet: Motion and Forces
... 1) Add one 0.5 kg mass to the cart and allow it to run along the track with the fan set at high speed. How does the cart’s acceleration now compare to its acceleration with the force set at high speed but without added mass? 2) Add a second 0.5 kg mass to the cart. How does the acceleration now comp ...
... 1) Add one 0.5 kg mass to the cart and allow it to run along the track with the fan set at high speed. How does the cart’s acceleration now compare to its acceleration with the force set at high speed but without added mass? 2) Add a second 0.5 kg mass to the cart. How does the acceleration now comp ...
A x
... force bringing bob back to eqlbm position = F = -mgsin For small angles, sin = s/L x/L F = -mg = -mgx/L, i.e. F x Compare with F = -kx, means k mg/L OR k/m = g/L . But k/m = 2 So 2 = g/L Since T = 2(m/k) = 2(L/g) Period of simple pendulum T = 2(L/g) ...
... force bringing bob back to eqlbm position = F = -mgsin For small angles, sin = s/L x/L F = -mg = -mgx/L, i.e. F x Compare with F = -kx, means k mg/L OR k/m = g/L . But k/m = 2 So 2 = g/L Since T = 2(m/k) = 2(L/g) Period of simple pendulum T = 2(L/g) ...
Chapter 11 Force and Newton`s Laws
... Texture – A rougher surface = greater friction. A smoother surface = less friction. Mass/Weight – The greater the mass or weight of an object, the more friction it will create. Fluids – Fluids reduce friction by preventing surfaces from coming into contact. ...
... Texture – A rougher surface = greater friction. A smoother surface = less friction. Mass/Weight – The greater the mass or weight of an object, the more friction it will create. Fluids – Fluids reduce friction by preventing surfaces from coming into contact. ...
Chapter 4 Kinetics of a particle
... Therefore, any path Fc dr is a function of initial and end points only, It is defined as the change of potential energy, P.E. P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point ...
... Therefore, any path Fc dr is a function of initial and end points only, It is defined as the change of potential energy, P.E. P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point ...
Lecture06-09
... apparent weight may be more or less than your actual weight. In this case the “apparent weight” is the sum of the gravitational attaction (actual weight) and the force required to accelerate the body, as specified ...
... apparent weight may be more or less than your actual weight. In this case the “apparent weight” is the sum of the gravitational attaction (actual weight) and the force required to accelerate the body, as specified ...
The Web of Newton`s Laws
... safely. The lack of friction is not only an inconvenience but can also be dangerous. There are also applications where the presence of friction is an inconvenience, such as in machines. Oil and other lubricants are used to reduce friction and make these devices run more efficiently. In this lab you ...
... safely. The lack of friction is not only an inconvenience but can also be dangerous. There are also applications where the presence of friction is an inconvenience, such as in machines. Oil and other lubricants are used to reduce friction and make these devices run more efficiently. In this lab you ...
Newton`s Laws
... an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force. This statement contradicted Aristotle’s teaching and was considered a radical idea at the time. However, Newton proposed that there was, in fact, an unrecognized force of resistance between objects t ...
... an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force. This statement contradicted Aristotle’s teaching and was considered a radical idea at the time. However, Newton proposed that there was, in fact, an unrecognized force of resistance between objects t ...
document
... class. They are discussing an object that is being acted upon by two individual forces (both in a vertical direction); the free-body diagram for the particular object is shown at the right. During the discussion, Anna Litical suggests to Noah Formula that the object under discussion could be moving. ...
... class. They are discussing an object that is being acted upon by two individual forces (both in a vertical direction); the free-body diagram for the particular object is shown at the right. During the discussion, Anna Litical suggests to Noah Formula that the object under discussion could be moving. ...
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
... A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of iner ...
... A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of iner ...
Kinematics
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
document
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
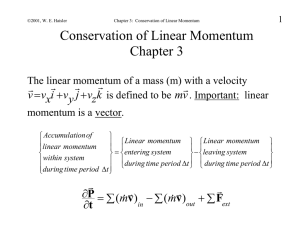
Chapter 3
... Chapter 3 The linear momentum of a mass (m) with a velocity v vxi v y j vzk is defined to be mv . Important: linear momentum is a vector. ...
... Chapter 3 The linear momentum of a mass (m) with a velocity v vxi v y j vzk is defined to be mv . Important: linear momentum is a vector. ...
Centripetal force and Centrifugal force
... track of which is which, chances are anyone who has heard of the two concepts remembers that one is the tendency of objects in rotation to move inward, and the other is the tendency of rotating objects to move outward. It may come as a surprise, then, to learn that there is no such thing, strictly s ...
... track of which is which, chances are anyone who has heard of the two concepts remembers that one is the tendency of objects in rotation to move inward, and the other is the tendency of rotating objects to move outward. It may come as a surprise, then, to learn that there is no such thing, strictly s ...
Chapter 4
... start at exactly the same instant, and they both stop at exactly the same instant. They are equal in time. ...
... start at exactly the same instant, and they both stop at exactly the same instant. They are equal in time. ...
f - Edublogs
... You pull on a box with an applied force of 30 N. The coefficient of friction is 0.4. If the mass of the box is 2 kg, what is its acceleration? 1. Draw the box and all FOUR forces acting on it. 2. Write what you know and don’t know. 3. Write the equations, Fnet = ma and f = mN 4. Calculate the Norma ...
... You pull on a box with an applied force of 30 N. The coefficient of friction is 0.4. If the mass of the box is 2 kg, what is its acceleration? 1. Draw the box and all FOUR forces acting on it. 2. Write what you know and don’t know. 3. Write the equations, Fnet = ma and f = mN 4. Calculate the Norma ...