Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion Conclusion
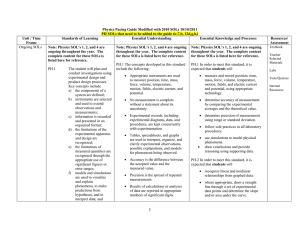
... 4.4 Equilibrium Application of Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
... 4.4 Equilibrium Application of Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
Conditions of Linear Motion
... Anatomical pulley – tendons that pass over bony projections in the body can be considered as anatomical pulleys Composite effects of two or more forces Linear forces – forces applied in the same direction along the same line; these forces can be added by placing vectors head to tail ...
... Anatomical pulley – tendons that pass over bony projections in the body can be considered as anatomical pulleys Composite effects of two or more forces Linear forces – forces applied in the same direction along the same line; these forces can be added by placing vectors head to tail ...
Ch 12 Notes – Teacher2 - Mona Shores Public Schools
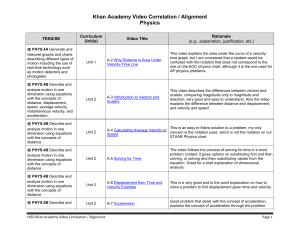
... Regarding Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion • The acceleration of an object is always in the same direction as the net force. • In using Newton’s second law, it is helpful to realize that the units N/kg and m/s2 are equivalent • Newton’s second law also applies when a net force acts in the direction opposi ...
... Regarding Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion • The acceleration of an object is always in the same direction as the net force. • In using Newton’s second law, it is helpful to realize that the units N/kg and m/s2 are equivalent • Newton’s second law also applies when a net force acts in the direction opposi ...
Some Applications of Newton`s Laws. Solving Fnet = ma problems
... an illusion! There is no outward force on the person. Our intuition is failing us. Our intuition about forces was developed over a lifetime of experiences in inertial (non-accelerating) reference frames. If we are suddenly placed in an accelerating reference frame, our brains (wrongly) interpret our ...
... an illusion! There is no outward force on the person. Our intuition is failing us. Our intuition about forces was developed over a lifetime of experiences in inertial (non-accelerating) reference frames. If we are suddenly placed in an accelerating reference frame, our brains (wrongly) interpret our ...
S2-3-06 - In Motion - Lesson Sequence
... a) Contact Forces – involving actual contact between two objects. e.g. Normal forces, Frictional forces, Tensional forces, Spring forces, Air Resistance forces, etc. b) Action at a Distance Forces – forces that affect an object without it. e.g. Gravitational forces, Electrical forces, Magnetic force ...
... a) Contact Forces – involving actual contact between two objects. e.g. Normal forces, Frictional forces, Tensional forces, Spring forces, Air Resistance forces, etc. b) Action at a Distance Forces – forces that affect an object without it. e.g. Gravitational forces, Electrical forces, Magnetic force ...
Physics
... rotating force Fr b. when r is not perpendicular to Fr, then = rFrsin c. torque units are m•N (not N•m—work) First Law: Object remains at rest or uniform rotation as long as no net torque (net) acts on it a. measured as the moment of inertia, I = mr2 b. corrects for mass distribution ( = 1 f ...
... rotating force Fr b. when r is not perpendicular to Fr, then = rFrsin c. torque units are m•N (not N•m—work) First Law: Object remains at rest or uniform rotation as long as no net torque (net) acts on it a. measured as the moment of inertia, I = mr2 b. corrects for mass distribution ( = 1 f ...
Name Reading Science – Newton`s Laws and Roller Coasters In
... Newton’s three laws of motion have been proven over and over again in the last three centuries and they form the underpinnings of many of our current methods of transportation and other scientific inventions. Roller coasters, a modern invention that uses the laws of motion to thrilling ends, are the ...
... Newton’s three laws of motion have been proven over and over again in the last three centuries and they form the underpinnings of many of our current methods of transportation and other scientific inventions. Roller coasters, a modern invention that uses the laws of motion to thrilling ends, are the ...
AP physics final AP test review Mechanics
... constant, and work is zero. Friction, tension, normal force, gravity and the magnetic force are common forces that can act centripetally to cause uniform circular motion. 26. Centripetal Force (A-184 #46) A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a ...
... constant, and work is zero. Friction, tension, normal force, gravity and the magnetic force are common forces that can act centripetally to cause uniform circular motion. 26. Centripetal Force (A-184 #46) A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a ...
IHS ppt 092710 ISA
... back to the starting point, the distance is 4 blocks and the ______ is 0. The use of the terms vector and scalar should be applied to distinguish between the vector quantities of displacement, velocity, and acceleration and the scalar quantities of distance and ______. Motion can be described by a c ...
... back to the starting point, the distance is 4 blocks and the ______ is 0. The use of the terms vector and scalar should be applied to distinguish between the vector quantities of displacement, velocity, and acceleration and the scalar quantities of distance and ______. Motion can be described by a c ...
Forces and acceleration Newton`s 2nd Law
... table below, where Force is the accelerating force (hanger masses times g) and the 2x acceleration is calculated using the above equation, a 2 . t The term M in F=Ma is the total of all masses cart + hanger. ...
... table below, where Force is the accelerating force (hanger masses times g) and the 2x acceleration is calculated using the above equation, a 2 . t The term M in F=Ma is the total of all masses cart + hanger. ...
mi05
... to overcome frictional forces, such as air _______ and friction in the moving parts of the car. Friction is due to the interaction between _______ on the surfaces of materials. Even what looks like a very smooth surface, such as glass or polished metal, is actually very _______ on a microscopic scal ...
... to overcome frictional forces, such as air _______ and friction in the moving parts of the car. Friction is due to the interaction between _______ on the surfaces of materials. Even what looks like a very smooth surface, such as glass or polished metal, is actually very _______ on a microscopic scal ...