Powerpoint slides
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) ...
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) ...
What If Matter Could Have A Negative Mass
... What If? There is some strange behavior that would come from applying forces to negative masses. For instance, it would become very difficult to control the object. When pushed, the object accelerates towards whatever is pushing it. But this results in the initial force continuing, because the objec ...
... What If? There is some strange behavior that would come from applying forces to negative masses. For instance, it would become very difficult to control the object. When pushed, the object accelerates towards whatever is pushing it. But this results in the initial force continuing, because the objec ...
Ch04CQ5e
... 14. REASONING AND SOLUTION Assuming that the accelerating mechanism remains attached to the rocket, the acceleration will be greater when the rocket is fired horizontally. The accelerating mechanism provides an acceleration that points in the initial direction of motion of the rocket. The net accele ...
... 14. REASONING AND SOLUTION Assuming that the accelerating mechanism remains attached to the rocket, the acceleration will be greater when the rocket is fired horizontally. The accelerating mechanism provides an acceleration that points in the initial direction of motion of the rocket. The net accele ...
File
... 2. A car is stopped at a traffic light. If then travels along straight road so that its distance from the light is given by x(t ) bt 2 ct 3 , where b=2.40 m/s2 and c=0.120 m/s3. a) Calculate the average velocity of the car for the time interval t=0 to t=10 s. b) Calculate the instantaneous veloc ...
... 2. A car is stopped at a traffic light. If then travels along straight road so that its distance from the light is given by x(t ) bt 2 ct 3 , where b=2.40 m/s2 and c=0.120 m/s3. a) Calculate the average velocity of the car for the time interval t=0 to t=10 s. b) Calculate the instantaneous veloc ...
Gravitation and Momentum
... • If a car hits a haystack or the same car hits a wall, momentum is decreased by same impulse – the same products of force and time. • However, impact force is greater into the wall than it is into the haystack as the haystack extends impact time, lessening the impact force. • Impact time is the tim ...
... • If a car hits a haystack or the same car hits a wall, momentum is decreased by same impulse – the same products of force and time. • However, impact force is greater into the wall than it is into the haystack as the haystack extends impact time, lessening the impact force. • Impact time is the tim ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... interval t=tf-ti is equal to the change of the momentum of the particle caused by that force. Impulse is the degree of which an external force changes momentum. ...
... interval t=tf-ti is equal to the change of the momentum of the particle caused by that force. Impulse is the degree of which an external force changes momentum. ...
solutions to problem set 4
... In most problems in this book, the ropes, cords, or cables have so little mass compared to other objects in the problem that their masses can safely be neglected. But if the rope is the only object in the problem, then clearly its mass cannot be neglected. For example, suppose we have a clothesline ...
... In most problems in this book, the ropes, cords, or cables have so little mass compared to other objects in the problem that their masses can safely be neglected. But if the rope is the only object in the problem, then clearly its mass cannot be neglected. For example, suppose we have a clothesline ...
mi08sol
... back to the space craft he moves towards the space ship and it moves towards him. He applies a force to the ship, via the rope. The ship applies a reaction force, equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, to the astronaut. The rate of change of momentum is equal to the net force applied, and so ...
... back to the space craft he moves towards the space ship and it moves towards him. He applies a force to the ship, via the rope. The ship applies a reaction force, equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, to the astronaut. The rate of change of momentum is equal to the net force applied, and so ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion Section 3 What do you think?
... • An agricultural student is designing a support system to keep a tree upright. Two wires have been attached to the tree and placed at right angles to each other (parallel to the ground). One wire exerts a force of 30.0 N and the other exerts a force of 40.0 N. Determine where to place a third wire ...
... • An agricultural student is designing a support system to keep a tree upright. Two wires have been attached to the tree and placed at right angles to each other (parallel to the ground). One wire exerts a force of 30.0 N and the other exerts a force of 40.0 N. Determine where to place a third wire ...
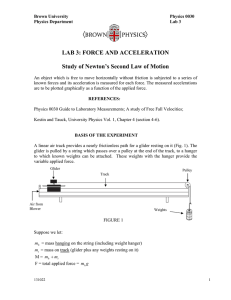
LAB 3: FORCE AND ACCELERATION Study of Newton`s Second
... Practice starting and stopping the glider to get a feel for the speeds involved and the techniques required. Practice releasing the glider from rest (starting at the backstop position and letting go without imparting any initial velocity). Pick a U photocell position near to the rest position, and a ...
... Practice starting and stopping the glider to get a feel for the speeds involved and the techniques required. Practice releasing the glider from rest (starting at the backstop position and letting go without imparting any initial velocity). Pick a U photocell position near to the rest position, and a ...
First Diploma in Engineering Mathematics for Engineering
... v is the final velocity of the object t is the time taken to travel the distance Transpose the equation to make t the subject and then find its value if s = 12 m, u = 3 msˉ¹ and v = 7 msˉ¹. ...
... v is the final velocity of the object t is the time taken to travel the distance Transpose the equation to make t the subject and then find its value if s = 12 m, u = 3 msˉ¹ and v = 7 msˉ¹. ...
Section 6.2 Circular Motion Acceleration
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
Chapter 1, Interactions and Motion 1 Recall the
... 11 Relate the period of oscillation for a block attached to horizontal or vertical spring to the spring constant and the block's mass Graphically represent the motion of an oscillator (position or velocity vs. time) given properties of its behavior ...
... 11 Relate the period of oscillation for a block attached to horizontal or vertical spring to the spring constant and the block's mass Graphically represent the motion of an oscillator (position or velocity vs. time) given properties of its behavior ...
Circular Motion - juan
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
Rotational Inertia
... ~ is the angular acceleration. The moment of inertia of an object depends on the shape of the object and the distribution of its mass relative to the object’s axis of rotation. A uniform disk of mass m is not as hard to set into rotational motion as a “dumbbell” with the same mass and radius. For a ...
... ~ is the angular acceleration. The moment of inertia of an object depends on the shape of the object and the distribution of its mass relative to the object’s axis of rotation. A uniform disk of mass m is not as hard to set into rotational motion as a “dumbbell” with the same mass and radius. For a ...