K-1 Speed©! “Feel the Physics!”
... At the starting line of a race you are at rest, therefore you tend to stay at rest. But when you get the green light, you accelerate as fast as you can go, and feel as though you are ...
... At the starting line of a race you are at rest, therefore you tend to stay at rest. But when you get the green light, you accelerate as fast as you can go, and feel as though you are ...
Answers
... will continue to do so, and rotating objects, (such as tops, flywheels, and gyroscopes) want to keep spinning due to inertia! Rotational inertia keeps gyroscopes, figure skaters (during lightning fast spins), and bike-riders stable, and is used in navigation devices in planes (as turbulence does not ...
... will continue to do so, and rotating objects, (such as tops, flywheels, and gyroscopes) want to keep spinning due to inertia! Rotational inertia keeps gyroscopes, figure skaters (during lightning fast spins), and bike-riders stable, and is used in navigation devices in planes (as turbulence does not ...
Ch2Aug2007
... Since, by definition, a fluid cannot withstand a shear stress without moving, (deformation) a stationary fluid must necessarily be completely free of shear stress (σij=0, i ≠ j). The only non-zero stress is the normal stress, which is referred to as pressure: σii=-p σn = -p, which is compressive, as ...
... Since, by definition, a fluid cannot withstand a shear stress without moving, (deformation) a stationary fluid must necessarily be completely free of shear stress (σij=0, i ≠ j). The only non-zero stress is the normal stress, which is referred to as pressure: σii=-p σn = -p, which is compressive, as ...
Slide 1
... Lets consider a ball being launched across a flat field where the initial and final heights of the ball are the same. Derive an expression for the horizontal distance travelled solely in terms of the initial velocity, acceleration due to gravity, and the angle at which it is fired. ***Hints!!!*** 1 ...
... Lets consider a ball being launched across a flat field where the initial and final heights of the ball are the same. Derive an expression for the horizontal distance travelled solely in terms of the initial velocity, acceleration due to gravity, and the angle at which it is fired. ***Hints!!!*** 1 ...
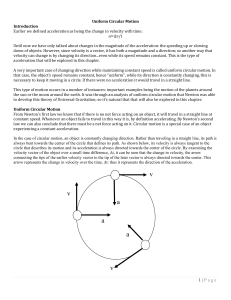
Circular Motion
... • Objects moving in a circle still have a linear velocity = distance/time. • This is often called tangential velocity, since the direction of the linear velocity is tangent to the circle. v ...
... • Objects moving in a circle still have a linear velocity = distance/time. • This is often called tangential velocity, since the direction of the linear velocity is tangent to the circle. v ...
N-body - OU Supercomputing Center for Education & Research
... When N is 2, you have – surprise! – a 2-Body Problem: exactly two particles, each exerting a force that acts on the other. The relationship between the 2 particles can be expressed as a differential equation that can be solved analytically, producing a closed-form solution. So, given the particles’ ...
... When N is 2, you have – surprise! – a 2-Body Problem: exactly two particles, each exerting a force that acts on the other. The relationship between the 2 particles can be expressed as a differential equation that can be solved analytically, producing a closed-form solution. So, given the particles’ ...
Physics
... 1. force can act on contact (collision) or at a distance (gravity) 2. usually multiple forces act on an object the vector sum of all forces = Fnet 3. mass is measured in terms of Newton's laws a. inertial mass = object's resistance to change in motion (first law) b. gravitational mass = gravity's ...
... 1. force can act on contact (collision) or at a distance (gravity) 2. usually multiple forces act on an object the vector sum of all forces = Fnet 3. mass is measured in terms of Newton's laws a. inertial mass = object's resistance to change in motion (first law) b. gravitational mass = gravity's ...
Chapter 06 Momentum
... an unbalanced force must be applied. If you are riding in a car, and you push against the inside of the door; does the car accelerate in the direction of your force? No, Newton’s third law says that your force on the door is balanced by an equal and opposite force that the door applies to you. You a ...
... an unbalanced force must be applied. If you are riding in a car, and you push against the inside of the door; does the car accelerate in the direction of your force? No, Newton’s third law says that your force on the door is balanced by an equal and opposite force that the door applies to you. You a ...
phys1441-spring09
... not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal in magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in the figure. What do you think will happen? ...
... not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal in magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in the figure. What do you think will happen? ...
SPW Chapter 4 PPT
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would ...
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would ...
Physics of Theatre Presentation
... • What kind of forces are we talking about? • If a person is moving at initial speed v, and they stop in a time interval t, they will have an acceleration of a=v/t. The force needed to stop them will have magnitude F=ma, or F=mv/t. • These forces can be as large or larger than the weight of the pers ...
... • What kind of forces are we talking about? • If a person is moving at initial speed v, and they stop in a time interval t, they will have an acceleration of a=v/t. The force needed to stop them will have magnitude F=ma, or F=mv/t. • These forces can be as large or larger than the weight of the pers ...
Offline HW 3 solutions
... 5. Putting Everything Together (Exam-Type Question): Don’t look down! (2 pts) ...
... 5. Putting Everything Together (Exam-Type Question): Don’t look down! (2 pts) ...
1 CHAPTER 22 DIMENSIONS 22.1 Mass, Length and Time Any
... momentum J. We might then say that the dimensions of area could be expressed as E −2 V 2 J 2 . (Verify this!) While agreeing that such a system might be possible, you might feel that it would be totally absurd and there is no point in reading further. But stop! Such a system is not only possible, bu ...
... momentum J. We might then say that the dimensions of area could be expressed as E −2 V 2 J 2 . (Verify this!) While agreeing that such a system might be possible, you might feel that it would be totally absurd and there is no point in reading further. But stop! Such a system is not only possible, bu ...