chapter FORCES AND NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
... 33. Which one of the following statements concerning the two "gravitational constants" G, the universal gravitational constant, and g the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is true? (a) The values of g and G depend on location. (b) The values of g and G do not depend on location. (c) The ...
... 33. Which one of the following statements concerning the two "gravitational constants" G, the universal gravitational constant, and g the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is true? (a) The values of g and G depend on location. (b) The values of g and G do not depend on location. (c) The ...
1 Topic 3: Applications of Lagrangian Mechanics
... Conservation laws result from symmetries exhibited by mechanical systems - e.g. L independent of time (Hamiltonian), symmetry wrt rotation (angular momentum). This holds generally throught physics { in quantum mechanics and relativity, conservation laws are associated with symmetries in the fundamen ...
... Conservation laws result from symmetries exhibited by mechanical systems - e.g. L independent of time (Hamiltonian), symmetry wrt rotation (angular momentum). This holds generally throught physics { in quantum mechanics and relativity, conservation laws are associated with symmetries in the fundamen ...
Physics 20 - Structured Independent Learning
... electrons of the object and the surface and, therefore, the greater the frictional force. The second factor is the nature of the interaction between object and the surface. If the surface and object are rough in texture, like coarse sandpaper on brushed concrete, the frictional force will be quite d ...
... electrons of the object and the surface and, therefore, the greater the frictional force. The second factor is the nature of the interaction between object and the surface. If the surface and object are rough in texture, like coarse sandpaper on brushed concrete, the frictional force will be quite d ...
Force Motion Pasco Lab
... The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net ...
... The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net ...
Word
... The work W done by a force F that moves its point of application by a distance s in the direction of the force is given by W = F s. Work measures the amount of energy transferred from one thing to another. The SI unit of energy and of work is the joule (J). Work and energy are scalar quantities. Wor ...
... The work W done by a force F that moves its point of application by a distance s in the direction of the force is given by W = F s. Work measures the amount of energy transferred from one thing to another. The SI unit of energy and of work is the joule (J). Work and energy are scalar quantities. Wor ...
2.2 Some Common Speeds
... The laws only apply at speeds much, much less than the speed of ___________. The laws apply equally in ALL inertial frames of reference. FRAME OF REFERENCE ? A frame of reference is best described as “your point of _________________.” An inertial frame of reference is one that is either ____________ ...
... The laws only apply at speeds much, much less than the speed of ___________. The laws apply equally in ALL inertial frames of reference. FRAME OF REFERENCE ? A frame of reference is best described as “your point of _________________.” An inertial frame of reference is one that is either ____________ ...
Ch 8 – Oscillation
... • The amplitude is the maximum distance the mass moves from its equilibrium position. It moves as far on one side as it does on the other. • The time that it takes to make one complete repetition or cycle is called the period of the motion. We will usually measure the period in seconds. • Frequency ...
... • The amplitude is the maximum distance the mass moves from its equilibrium position. It moves as far on one side as it does on the other. • The time that it takes to make one complete repetition or cycle is called the period of the motion. We will usually measure the period in seconds. • Frequency ...
Practice Final
... 4) The fastest airplane is the Lockheed SR-71. If an SR-71 flies 10.0 miles in 15.3 sec, what is its average speed? A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/ ...
... 4) The fastest airplane is the Lockheed SR-71. If an SR-71 flies 10.0 miles in 15.3 sec, what is its average speed? A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/ ...
Chapter 11 Equilibrium - Farmingdale State College
... Remember that if the acceleration is zero, then there is no change of the velocity with time. Most of the cases considered in this chapter deal with bodies that are at rest (v = 0) under the applications of forces. Occasionally we also consider a body that is moving at a constant velocity (also a ca ...
... Remember that if the acceleration is zero, then there is no change of the velocity with time. Most of the cases considered in this chapter deal with bodies that are at rest (v = 0) under the applications of forces. Occasionally we also consider a body that is moving at a constant velocity (also a ca ...
Essential Learning Outcomes (ELOs) Advanced Placement Physics (B & C)
... Determine by what factor a body's rotational inertia changes if all its dimensions are increased by the same factor. b. Students should develop skill in computing rotational inertia so they can find the rotational inertia of: i. A collection of point masses lying in a plane about an axis perpendicul ...
... Determine by what factor a body's rotational inertia changes if all its dimensions are increased by the same factor. b. Students should develop skill in computing rotational inertia so they can find the rotational inertia of: i. A collection of point masses lying in a plane about an axis perpendicul ...
P2 Revision Checklist - The Polesworth School
... Higher tier: Be able to calculate the distance travelled by an object in a given time from its velocitytime graph. Know that when two objects interact, they exert forces on each other that are equal but opposite. Describe friction as a contact force between surfaces. Recall the unit of a force as ne ...
... Higher tier: Be able to calculate the distance travelled by an object in a given time from its velocitytime graph. Know that when two objects interact, they exert forces on each other that are equal but opposite. Describe friction as a contact force between surfaces. Recall the unit of a force as ne ...
REFERENCES - mongolinternet.com
... Law of inertia: a body at rest or a body in motion continues to move at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. Net external force F acting on a body gives it an acceleration a which is in the direction of the force and has magnitude inversely proportional to the mass m of the bo ...
... Law of inertia: a body at rest or a body in motion continues to move at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. Net external force F acting on a body gives it an acceleration a which is in the direction of the force and has magnitude inversely proportional to the mass m of the bo ...
Linear Momentum and Collisions
... rebounds as in figure. The initial and final velocities of the car are vi=-15 m/s and vf = 2.6 m/s, respectively. If the collision lasts for 0.15 s, find (a) the impulse delivered to the car due to the collision (b) the size and direction of the average force exerted on the car ...
... rebounds as in figure. The initial and final velocities of the car are vi=-15 m/s and vf = 2.6 m/s, respectively. If the collision lasts for 0.15 s, find (a) the impulse delivered to the car due to the collision (b) the size and direction of the average force exerted on the car ...
A Unifying Computational Framework for Optimization and
... Treat each leg independently Legs coupled for vertical thrust only Velocity control based on independent leg but position based on the coupled overall velocity of the body ...
... Treat each leg independently Legs coupled for vertical thrust only Velocity control based on independent leg but position based on the coupled overall velocity of the body ...
Science
... move. A student justifies this by answering that the two opposite and equal forces cancel each other. Comment on this logic and explain why the truck does not move. Answer: The logic is that Action and Reaction always act on different bodies, so they can not cancel each other. When we push a massive ...
... move. A student justifies this by answering that the two opposite and equal forces cancel each other. Comment on this logic and explain why the truck does not move. Answer: The logic is that Action and Reaction always act on different bodies, so they can not cancel each other. When we push a massive ...
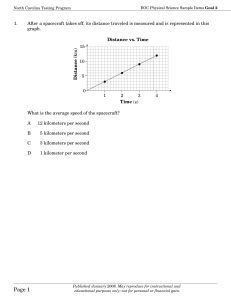
Page 1 - NC Department of Public Instruction
... a. In the absence of a force, an object in motion will remain in motion or an object at rest will remain at rest until acted on by an unbalanced force. b. Change in motion of an object (acceleration) is directly proportional to the unbalanced outside force and inversely proportional to the mass. c. ...
... a. In the absence of a force, an object in motion will remain in motion or an object at rest will remain at rest until acted on by an unbalanced force. b. Change in motion of an object (acceleration) is directly proportional to the unbalanced outside force and inversely proportional to the mass. c. ...
Aim: How do we explain Newton`s 3rd Law?
... 3. A traveler pulls a suitcase of mass 8.00 kg across a level surface by pulling on the handle 20.0 N at an angle of 50.0° relative to horizontal. Friction against the suitcase can be modeled by μk = 0.100. (a) Determine the acceleration of the suitcase. (b) What amount of force applied at the same ...
... 3. A traveler pulls a suitcase of mass 8.00 kg across a level surface by pulling on the handle 20.0 N at an angle of 50.0° relative to horizontal. Friction against the suitcase can be modeled by μk = 0.100. (a) Determine the acceleration of the suitcase. (b) What amount of force applied at the same ...