PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 12
... • Torques require point of reference • Point can be anywhere • Use same point for all torques • Pick the point to make problem easiest (eliminate unwanted Forces from equation) ...
... • Torques require point of reference • Point can be anywhere • Use same point for all torques • Pick the point to make problem easiest (eliminate unwanted Forces from equation) ...
Document
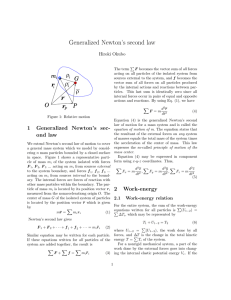
... Equivalently, only the perpendicular distance between the line of force and the axis of rotation, known as the moment arm r, can be used to calculate the torque. t = rF = (rsinq)F ...
... Equivalently, only the perpendicular distance between the line of force and the axis of rotation, known as the moment arm r, can be used to calculate the torque. t = rF = (rsinq)F ...
Slide 1
... rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. ...
... rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... III. Kinetics of Particles: Force, Mass, and Acceleration A. Newton’s Second Law of Motion B. Systems of Units C. Equations of Motion. Dynamic Equilibrium D. Systems of Particles. D’Alembert’s Principle E. Motion of the Mass Center of a System of Particles F. Rectilinear Motion of a Particle G. Cu ...
... III. Kinetics of Particles: Force, Mass, and Acceleration A. Newton’s Second Law of Motion B. Systems of Units C. Equations of Motion. Dynamic Equilibrium D. Systems of Particles. D’Alembert’s Principle E. Motion of the Mass Center of a System of Particles F. Rectilinear Motion of a Particle G. Cu ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid rotating object is ...
... The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid rotating object is ...
Newton`s Laws
... object increases with increased force and decreased with increased mass. • The acceleration of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inverse to the mass. The two people are pushing with the same power so they don't move. ...
... object increases with increased force and decreased with increased mass. • The acceleration of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inverse to the mass. The two people are pushing with the same power so they don't move. ...
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 1 Notes
... angular velocity and acceleration are vector quantities. So far we only talked about the magnitude of these vectors. But as vectors they also have a direction. Both angular velocity and acceleration point along the rotation axis. ...
... angular velocity and acceleration are vector quantities. So far we only talked about the magnitude of these vectors. But as vectors they also have a direction. Both angular velocity and acceleration point along the rotation axis. ...
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
Lecture Notes
... for a special case. A rigid body which consists of a point mass m at the end of a massless rod of length r. We will now derive the same equation for a general case. ...
... for a special case. A rigid body which consists of a point mass m at the end of a massless rod of length r. We will now derive the same equation for a general case. ...
ppt
... case where you can actually do exact solution instead of sampling Really easy for simple particles ...
... case where you can actually do exact solution instead of sampling Really easy for simple particles ...
Worksheet - 2
... g) Acceleration 2.Differences between a) Speed and velocity b) Uniform and Non-uniform speed c) Uniform and Non-uniform velocity d) Uniform acceleration and non-uniform acceleration 3. Define Uniform circular motion 4. What do you mean by the term retardation? Give an example 5. Describe the distanc ...
... g) Acceleration 2.Differences between a) Speed and velocity b) Uniform and Non-uniform speed c) Uniform and Non-uniform velocity d) Uniform acceleration and non-uniform acceleration 3. Define Uniform circular motion 4. What do you mean by the term retardation? Give an example 5. Describe the distanc ...
Expectations for Ch 2 & 3
... analyzed in several ways ¤ How coordinate systems can be used in motion studies ¤ Terms such as displacement, magnitude, vectors ...
... analyzed in several ways ¤ How coordinate systems can be used in motion studies ¤ Terms such as displacement, magnitude, vectors ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ABOUT TEAL
... Make a careful drawing showing where forces act Clearly indicate what axis you are using Clearly indicate whether CW or CCW is positive ...
... Make a careful drawing showing where forces act Clearly indicate what axis you are using Clearly indicate whether CW or CCW is positive ...
Newton`s Laws - strikerphysics11
... to indicate their point of application on an object. In a free-body diagram, all forces are shown as emanating from a common point (the origin) Forces don’t have to be drawn to scale but the diagram should show whether there is a net force. ...
... to indicate their point of application on an object. In a free-body diagram, all forces are shown as emanating from a common point (the origin) Forces don’t have to be drawn to scale but the diagram should show whether there is a net force. ...