Physics 121 Exam Sheet - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Newton’s Third Law – The Third Law of Motion: If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B exerts a force, equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction, on body A, i.e.., FAB = FBA, where FAB is the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA is the force exerted on body A by body B. This law is ...
... Newton’s Third Law – The Third Law of Motion: If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B exerts a force, equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction, on body A, i.e.., FAB = FBA, where FAB is the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA is the force exerted on body A by body B. This law is ...
for reference Name Period ______ Date ______ Motion Notes from
... An object at rest will remain at rest, and a moving object will remain at a constant velocity unless unbalanced forces act on it. Newton was first to use the term inertia to describe the tendency of objects to remain in motion or stay at rest. Inertia comes from the Latin word iners, which means ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest, and a moving object will remain at a constant velocity unless unbalanced forces act on it. Newton was first to use the term inertia to describe the tendency of objects to remain in motion or stay at rest. Inertia comes from the Latin word iners, which means ...
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... COURSE CODE: PHYS-1006 COURSE NAME: GENERAL PHYSICS I: MECHANICS FACULTY MEMBER: WENFENG CHEN ...
... COURSE CODE: PHYS-1006 COURSE NAME: GENERAL PHYSICS I: MECHANICS FACULTY MEMBER: WENFENG CHEN ...
You get to explore the possible energy transitions for Hydrogen
... Orbits describe one body falling around another. The less massive object is a satellite of the more massive object. The two bodies orbit a common center of mass. For a much smaller satellite, the center of mass is inside the more massive body. ...
... Orbits describe one body falling around another. The less massive object is a satellite of the more massive object. The two bodies orbit a common center of mass. For a much smaller satellite, the center of mass is inside the more massive body. ...
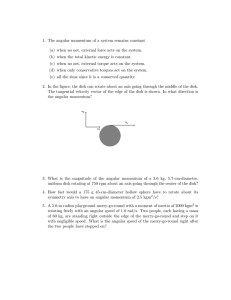
1. The angular momentum of a system remains constant (a) when no
... (a) when no net, external force acts on the system. (b) when the total kinetic energy is constant. (c) when no net, external torque acts on the system. (d) when only conservative torques act on the system. (e) all the time since it is a conserved quantity. 2. In the figure, the disk can rotate about ...
... (a) when no net, external force acts on the system. (b) when the total kinetic energy is constant. (c) when no net, external torque acts on the system. (d) when only conservative torques act on the system. (e) all the time since it is a conserved quantity. 2. In the figure, the disk can rotate about ...
Lecture 17
... plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origin at an arbitrary point P is established. The x-y axes should not rotate and can either be fixed or translate with constant velocity. ...
... plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origin at an arbitrary point P is established. The x-y axes should not rotate and can either be fixed or translate with constant velocity. ...
Physics 111
... • Rotational quantities as vectors • Cross product revisited • Torque as a vector • Angular momentum – conceptual • Newton’s second law in angular form • Angular momentum as a vector • Angular momentum of a system of particles • Angular momentum of a rigid body about a fixed axis • Conservation of a ...
... • Rotational quantities as vectors • Cross product revisited • Torque as a vector • Angular momentum – conceptual • Newton’s second law in angular form • Angular momentum as a vector • Angular momentum of a system of particles • Angular momentum of a rigid body about a fixed axis • Conservation of a ...
Set 5
... 4) Text Problem 11-27 – note that the angular velocity requested is just dϕ/dt, where ϕ is the Euler angle identified in the text. To solve this problem, you will need to use the equations that relate the angular velocity components to the Euler angle time derivatives for force free motion and the e ...
... 4) Text Problem 11-27 – note that the angular velocity requested is just dϕ/dt, where ϕ is the Euler angle identified in the text. To solve this problem, you will need to use the equations that relate the angular velocity components to the Euler angle time derivatives for force free motion and the e ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... elliptical orbit about the earth. Its point of closest approach is 8.37x106 m from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106 m from the center of the earth.The speed of the satellite at the perigee is 8450 m/s. Find the speed at the apogee. ...
... elliptical orbit about the earth. Its point of closest approach is 8.37x106 m from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106 m from the center of the earth.The speed of the satellite at the perigee is 8450 m/s. Find the speed at the apogee. ...
Notes for Newton
... 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of the forces acting on an object equal zero. a. Object in equilibrium are either moving at constant velocity or are at rest ...
... 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of the forces acting on an object equal zero. a. Object in equilibrium are either moving at constant velocity or are at rest ...
You get to explore the possible energy transitions for Hydrogen
... Orbits describe one body falling around another. The less massive object is a satellite of the more massive object. The two bodies orbit a common center of mass. For a much smaller satellite, the center of mass is inside the more massive body. ...
... Orbits describe one body falling around another. The less massive object is a satellite of the more massive object. The two bodies orbit a common center of mass. For a much smaller satellite, the center of mass is inside the more massive body. ...
Rotational Dynamics
... force that is exerted in a very specific way changes the angular velocity of an extended object. Extended object- an object that has a definite shape and size. There is an inverse relationship present here since to get the most effect from the least force, you exert the force as far from the axis of ...
... force that is exerted in a very specific way changes the angular velocity of an extended object. Extended object- an object that has a definite shape and size. There is an inverse relationship present here since to get the most effect from the least force, you exert the force as far from the axis of ...
vocabulary
... A measure of the amount of matter contained in or constituting a physical body. The mass of an object is related to the force required to accelerate it and hence is related to its inertia, and is essential to Newton's laws of motion. In most scientific applications, the SI unit of kilogram is used. ...
... A measure of the amount of matter contained in or constituting a physical body. The mass of an object is related to the force required to accelerate it and hence is related to its inertia, and is essential to Newton's laws of motion. In most scientific applications, the SI unit of kilogram is used. ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
Chapter 10
... position r from axis of rotation , then Torque = r F sin=rFt= rF, where ( is angle between r and F) Ft is component of F to r, while r is distance between the rotation axis and extended line running through F. ris called moment arm of F. Unit of torque: (N.m) Sign of : Positive torque f ...
... position r from axis of rotation , then Torque = r F sin=rFt= rF, where ( is angle between r and F) Ft is component of F to r, while r is distance between the rotation axis and extended line running through F. ris called moment arm of F. Unit of torque: (N.m) Sign of : Positive torque f ...
Quiz 1 Force and Vectors Static Equilibrium Problem Solving
... Methodology for Newton’s 2nd Law I. ...
... Methodology for Newton’s 2nd Law I. ...
Physics I - Rose
... That is, you must pull with a force of 175.5 N to tighten the spark plug. Assess: The force applied on the wrench leads to its clockwise motion. That is why we have used a negative sign for the net torque. ...
... That is, you must pull with a force of 175.5 N to tighten the spark plug. Assess: The force applied on the wrench leads to its clockwise motion. That is why we have used a negative sign for the net torque. ...
Rotational Dynamics
... Newton’s Second Law: Rotational The torque produced by the force is Fr maT r But the tangential acceleration is related to the angular acceleration: aT r ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Rotational The torque produced by the force is Fr maT r But the tangential acceleration is related to the angular acceleration: aT r ...