Study Sheet for Chemistry and Physics Chemistry Atomic Structure
... while the object falls. When these 2 factors balance out – terminal velocity is reached. The object falling is now BALANCED! Free fall –ONLY possible in a vacuum! No forces can act on the object as it falls. Projectile Motion – an object that is thrown will accelerate horizontally and then verticall ...
... while the object falls. When these 2 factors balance out – terminal velocity is reached. The object falling is now BALANCED! Free fall –ONLY possible in a vacuum! No forces can act on the object as it falls. Projectile Motion – an object that is thrown will accelerate horizontally and then verticall ...
Angular momentum and magnetic moment
... angular momentum and magnetic moment. This was first measured for an electron by Stern and Gerlach in 1922. Early interpretation of this observation were based on a model of a particle spinning around its axis. This prompted the name spin. However, its was quickly pointed out that rotational speed a ...
... angular momentum and magnetic moment. This was first measured for an electron by Stern and Gerlach in 1922. Early interpretation of this observation were based on a model of a particle spinning around its axis. This prompted the name spin. However, its was quickly pointed out that rotational speed a ...
Regular Note
... obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus? Trick Question! Each force is the same size. For every ac ...
... obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus? Trick Question! Each force is the same size. For every ac ...
Derivation of equations of motion
... Gravitational field strength was introduced in Standard Grade and is defined as. The force acting per unit mass on an object in the field. A gravitational field is a model by which the effects of gravitation can be explained. The force acting on a mass in the field is always attractive. We can repre ...
... Gravitational field strength was introduced in Standard Grade and is defined as. The force acting per unit mass on an object in the field. A gravitational field is a model by which the effects of gravitation can be explained. The force acting on a mass in the field is always attractive. We can repre ...
Chapter 3: Forces Review
... B.their velocities C.their shapes D.the distance between them E.more than one of the above (A and D) ...
... B.their velocities C.their shapes D.the distance between them E.more than one of the above (A and D) ...
Unit 4 Practice Test: Rotational Motion
... increases so does its vertical component. When F is large enough so that its vertical component is equal to the weight of the child, the child’s feet leave the ground. 36. Mass resists changes in translational motion, and moment of inertia resists changes in rotational motion. 37. The second conditi ...
... increases so does its vertical component. When F is large enough so that its vertical component is equal to the weight of the child, the child’s feet leave the ground. 36. Mass resists changes in translational motion, and moment of inertia resists changes in rotational motion. 37. The second conditi ...
R - Life Learning Cloud
... The marks for the parts of questions are shown in round brackets, e.g. (2). There are 7 questions in this question paper. The total mark for this paper is 75. Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled. You must show sufficient working to make y ...
... The marks for the parts of questions are shown in round brackets, e.g. (2). There are 7 questions in this question paper. The total mark for this paper is 75. Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled. You must show sufficient working to make y ...
3.1.2 In Class or Homework Exercise 1. The brakes of a car apply a
... You bend your knees in order to lengthen the time over which you come to a stop. Doing this reduces the average force applied to your body ( J F t ) while applying the required impulse to stop you. If you were to land without bending your knees, the time would be short. This would require a larg ...
... You bend your knees in order to lengthen the time over which you come to a stop. Doing this reduces the average force applied to your body ( J F t ) while applying the required impulse to stop you. If you were to land without bending your knees, the time would be short. This would require a larg ...
Force Balanced and unbalanced
... Notice that when the forces are balanced, the object might still be moving, but the objects are not accelerating, instead they have a constant velocity. Hence, once in motion – it’s always in motion unless acted upon by what? Another Force. ...
... Notice that when the forces are balanced, the object might still be moving, but the objects are not accelerating, instead they have a constant velocity. Hence, once in motion – it’s always in motion unless acted upon by what? Another Force. ...
ysics P2 Graded Task Bungee Jumping with equations
... A Bungee jumper has a mass of 80Kg and jumps off a platform 80m in the air. The jumper takes 6 seconds to fall, just stopping to touch the ground with their hand. The jumper accelerates for the first 2 seconds to 20m/s. They then reach a steady speed for 2 seconds and then slow down to a stop in the ...
... A Bungee jumper has a mass of 80Kg and jumps off a platform 80m in the air. The jumper takes 6 seconds to fall, just stopping to touch the ground with their hand. The jumper accelerates for the first 2 seconds to 20m/s. They then reach a steady speed for 2 seconds and then slow down to a stop in the ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... When mass is in kilograms and acceleration is in m/s2, the unit of force is in newtons (N). One newton is equal to the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at one ...
... When mass is in kilograms and acceleration is in m/s2, the unit of force is in newtons (N). One newton is equal to the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at one ...
Circular Motion Web Lab
... 8. Thinking Mathematically: Explore the quantitative dependencies of the acceleration upon the speed and the radius of curvature. Then answer the following questions. a. For the same speed, the acceleration of the object varies _____________ (directly, inversely) with the radius of curvature. b. For ...
... 8. Thinking Mathematically: Explore the quantitative dependencies of the acceleration upon the speed and the radius of curvature. Then answer the following questions. a. For the same speed, the acceleration of the object varies _____________ (directly, inversely) with the radius of curvature. b. For ...
Newtons Laws Part 1b - student
... forces. Draw a free body diagram. If there is motion, choose one axis in the direction of motion. Identify all forces that act on the object, and draw them on the diagram. Model: Constant Force ...
... forces. Draw a free body diagram. If there is motion, choose one axis in the direction of motion. Identify all forces that act on the object, and draw them on the diagram. Model: Constant Force ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
香港考試局
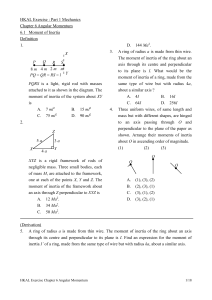
... objects are moving with instantaneous velocities as shown in the above diagram. The total angular momentum about the point O at this instant is A. 4 kg m2 s-1. B. C. 84 kg m2 s-1. D. ...
... objects are moving with instantaneous velocities as shown in the above diagram. The total angular momentum about the point O at this instant is A. 4 kg m2 s-1. B. C. 84 kg m2 s-1. D. ...