Force and Momentum - the SASPhysics.com
... • The principle states: for a system of interacting objects, the total momentum remains constant, provided no external force acts. • Derived by Newton from N3, but in fact ...
... • The principle states: for a system of interacting objects, the total momentum remains constant, provided no external force acts. • Derived by Newton from N3, but in fact ...
Chia Teck Chee and Chia Yee Fei The first part of Newton`s First
... In an attempt to overcome these misconceptions, a computer-integrated demonstration was designed. It is aimed at convincing students that a body will move continuously at constant velocity if there is no net force acting on the moving body and it is initially in motion. The apparatus set-up for the ...
... In an attempt to overcome these misconceptions, a computer-integrated demonstration was designed. It is aimed at convincing students that a body will move continuously at constant velocity if there is no net force acting on the moving body and it is initially in motion. The apparatus set-up for the ...
File
... Acceleration: •a change in velocity •a measurement of how quickly an object is changing speed, direction or both Velocity: The rate of change of a position along a straight line with respect to time Force: strength or energy ...
... Acceleration: •a change in velocity •a measurement of how quickly an object is changing speed, direction or both Velocity: The rate of change of a position along a straight line with respect to time Force: strength or energy ...
Ch_3 Presentation
... Friction is created from the irregularities and differences in materials. Even very smooth surfaces have some microscopic ridges/grooves. These, clash with the opposite surface, and produce opposing forces. ...
... Friction is created from the irregularities and differences in materials. Even very smooth surfaces have some microscopic ridges/grooves. These, clash with the opposite surface, and produce opposing forces. ...
UNIT 2 GCSE PHYSICS 2.1.4 Forces and
... As the object’s velocity increases, an increasing upward drag force acts on it. This causes the resultant force to decrease and so the object’s acceleration decreases (shown by the fact that the gradient of the velocity-time graph decreases). Eventually, when the terminal velocity is reached, the dr ...
... As the object’s velocity increases, an increasing upward drag force acts on it. This causes the resultant force to decrease and so the object’s acceleration decreases (shown by the fact that the gradient of the velocity-time graph decreases). Eventually, when the terminal velocity is reached, the dr ...
1 Introduction: 2 The work of a force:
... For curved paths, however, the magnitude of the normal force is a function of speed. Hence it may be necessary to obtain this speed usingPthe principle of work and energy, and then substitute this quantity into the equation of motion Fn = mv 2 /ρ to obtain the normal force. ...
... For curved paths, however, the magnitude of the normal force is a function of speed. Hence it may be necessary to obtain this speed usingPthe principle of work and energy, and then substitute this quantity into the equation of motion Fn = mv 2 /ρ to obtain the normal force. ...
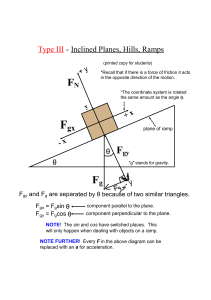
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... This is an example of a system where there are multiple masses, the Atwood machine. We will apply the concept of forces to determine the resulting acceleration. ...
... This is an example of a system where there are multiple masses, the Atwood machine. We will apply the concept of forces to determine the resulting acceleration. ...
Question 7 - Flipped Physics
... a. Determine the acceleration of block A as it descends. b. Block B strikes the floor and does not bounce. Determine the time t = t 1 at which block B strikes the floor. c. Describe the motion of block A from time t = 0 to the time when block B strikes the floor. d. Describe the motion of block A fr ...
... a. Determine the acceleration of block A as it descends. b. Block B strikes the floor and does not bounce. Determine the time t = t 1 at which block B strikes the floor. c. Describe the motion of block A from time t = 0 to the time when block B strikes the floor. d. Describe the motion of block A fr ...
Contact Mechanics
... • Contact pressures (x) 0 for all x R • If R is a planar region, with uniform friction and uniform normal, then all pressure distributions over R are equivalent to • A combination of forces on convex hull of R • If R is polygonal, a combination of forces on the vertices of the convex hull of R ...
... • Contact pressures (x) 0 for all x R • If R is a planar region, with uniform friction and uniform normal, then all pressure distributions over R are equivalent to • A combination of forces on convex hull of R • If R is polygonal, a combination of forces on the vertices of the convex hull of R ...
RevfinQ2010AnsFa06
... Answer: The little calculator. The momenta of the two objects were identical before slowing, and p = mv, so the little calculator must have been going really fast to have the same momentum as the big physics text. Since the two objects slowed to a stop in the same time, the distance traveled is grea ...
... Answer: The little calculator. The momenta of the two objects were identical before slowing, and p = mv, so the little calculator must have been going really fast to have the same momentum as the big physics text. Since the two objects slowed to a stop in the same time, the distance traveled is grea ...
Additional Physics
... To understand what happens to radioactive substances when they decay we need to understand the structure of the atoms from which they are made. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: HT - to explain how the Rutherford and Marsden scattering experiment l ...
... To understand what happens to radioactive substances when they decay we need to understand the structure of the atoms from which they are made. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: HT - to explain how the Rutherford and Marsden scattering experiment l ...
Final Exam Review
... This is a problem with constant acceleration, so we can use the constant acceleration formulas. A: True B: False False: As they get closer, the force of gravity increases and so does the acceleration 13. An unhappy student works out his aggression by attempting to knock down a large wooden bowling p ...
... This is a problem with constant acceleration, so we can use the constant acceleration formulas. A: True B: False False: As they get closer, the force of gravity increases and so does the acceleration 13. An unhappy student works out his aggression by attempting to knock down a large wooden bowling p ...
Practice test_2 Midterm2 (Chapters 6
... Two blocks with masses 2.0 kg and 3.0 kg are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface. A light spring is placed in a horizontal position between the blocks. The blocks are pushed together, compressing the spring, and then released from rest. After contact with the spring ends, the 3.0-kg mass has ...
... Two blocks with masses 2.0 kg and 3.0 kg are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface. A light spring is placed in a horizontal position between the blocks. The blocks are pushed together, compressing the spring, and then released from rest. After contact with the spring ends, the 3.0-kg mass has ...
PHY205 Physics of Everyday Life
... and collides head-on with a mosquito. Which is true? A. The Mack Truck does more damage to the mosquito than the mosquito does to the Mack Truck. B. The mosquito does more damage to the Mack Truck than the Mack Truck does to the mosquito. C. The Mack Truck does the same amount of damage to the mosqu ...
... and collides head-on with a mosquito. Which is true? A. The Mack Truck does more damage to the mosquito than the mosquito does to the Mack Truck. B. The mosquito does more damage to the Mack Truck than the Mack Truck does to the mosquito. C. The Mack Truck does the same amount of damage to the mosqu ...
3rd Law: Force every action force there is an equal and opposite
... 1. How does the mass of a body at rest affect its tendency to remain at rest? Newton’s law of inertia states that an object at rest stays at rest. An object with more mass has a greater tendency to resist changes in its state of motion. 2. How does the force required to move an object change with ma ...
... 1. How does the mass of a body at rest affect its tendency to remain at rest? Newton’s law of inertia states that an object at rest stays at rest. An object with more mass has a greater tendency to resist changes in its state of motion. 2. How does the force required to move an object change with ma ...