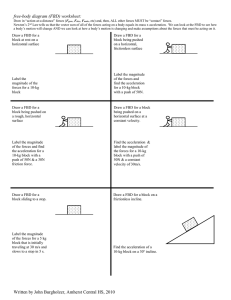
Final 1 Practice
... (e) You measure the speed of the ball at the lowest point of the circle, and find that it is only 7.8 m/s. Determine the work done by air friction on the ball as it swung down from the highest point to the lowest point. ...
... (e) You measure the speed of the ball at the lowest point of the circle, and find that it is only 7.8 m/s. Determine the work done by air friction on the ball as it swung down from the highest point to the lowest point. ...
Set 1
... A car is driven at constant speed over a circular hill and then into a circular valley with the same radius. At the top of the hill the normal force acting on the driver from the car seat is 0 N. The driver mass is 70 kg. What is the magnitude of the normal force acting on the driver from the seat w ...
... A car is driven at constant speed over a circular hill and then into a circular valley with the same radius. At the top of the hill the normal force acting on the driver from the car seat is 0 N. The driver mass is 70 kg. What is the magnitude of the normal force acting on the driver from the seat w ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... – On the moon, the object would have only one-sixth the weight it has on the earth. This is because the force of gravity on the moon is only one-sixth as strong as it is on the earth – If the object were in a gravity-free region of space, its weight would be zero. Its mass, on the other hand, would ...
... – On the moon, the object would have only one-sixth the weight it has on the earth. This is because the force of gravity on the moon is only one-sixth as strong as it is on the earth – If the object were in a gravity-free region of space, its weight would be zero. Its mass, on the other hand, would ...
Packet 4 - Momentum
... 2001M1. A motion sensor and a force sensor record the motion of a cart along a track, as shown above. The cart is given a push so that it moves toward the force sensor and then collides with it. The two sensors record the values shown in the above graphs. a. Determine the cart's average acceleration ...
... 2001M1. A motion sensor and a force sensor record the motion of a cart along a track, as shown above. The cart is given a push so that it moves toward the force sensor and then collides with it. The two sensors record the values shown in the above graphs. a. Determine the cart's average acceleration ...
Chapter 12 Notes
... Gravity is the weakest universal force, but it is the most effective over long distances. Earth’s gravitational force keeps the moon in a nearly circular orbit. The gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth causes ocean tides. ...
... Gravity is the weakest universal force, but it is the most effective over long distances. Earth’s gravitational force keeps the moon in a nearly circular orbit. The gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth causes ocean tides. ...
Newton`s 3rd Law
... A common misconception is that a rocket is propelled by the impact of exhaust gases against the atmosphere. In fact, in the early 1900s before the advent of rockets, many people thought that sending a rocket to the moon was impossible because of the absence of an atmosphere for the rocket to push a ...
... A common misconception is that a rocket is propelled by the impact of exhaust gases against the atmosphere. In fact, in the early 1900s before the advent of rockets, many people thought that sending a rocket to the moon was impossible because of the absence of an atmosphere for the rocket to push a ...
Gravity Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation states that every
... proportional to the square of the distance between them If two uniform spheres or point particles have masses m 1 and m 2 and their centers of separated by a distance the magnitude of the gravitational force is F = G m1 m2 / r 2 where G is the gravitational constant which has been measured to be G = ...
... proportional to the square of the distance between them If two uniform spheres or point particles have masses m 1 and m 2 and their centers of separated by a distance the magnitude of the gravitational force is F = G m1 m2 / r 2 where G is the gravitational constant which has been measured to be G = ...
Systems of Particles
... Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which can slide on a horizontal, frictionless surface, are attached to three 200-mm-long strings, which are tied to a ring G. Initially, the spheres rotate clockwise about the ring with a relative velocity of 0.8 m/s and the ring moves along the x-axis with ...
... Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which can slide on a horizontal, frictionless surface, are attached to three 200-mm-long strings, which are tied to a ring G. Initially, the spheres rotate clockwise about the ring with a relative velocity of 0.8 m/s and the ring moves along the x-axis with ...
Physics - Teachers
... study of matter, energy, force, and motion, and the way they relate to each other The study of matter, motion, energy and forces. ...
... study of matter, energy, force, and motion, and the way they relate to each other The study of matter, motion, energy and forces. ...
Core Lab 4 Newton`s Second Law of Motion - eLearning
... “ The bigger the pull or the push, the bigger the change in motion experienced by an object. There is a linear relationship between the size of the exerted force and the acceleration experienced by an object.” Student C “The amount of mass to be moved is also important. If the mass is increased and ...
... “ The bigger the pull or the push, the bigger the change in motion experienced by an object. There is a linear relationship between the size of the exerted force and the acceleration experienced by an object.” Student C “The amount of mass to be moved is also important. If the mass is increased and ...
motion in two dimension
... two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of directions the object can move along, but there are only three independent dimensions in space . What does independent dimension mean? In the Cartesian coordinate system the directions of x, y and z axis are inde ...
... two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of directions the object can move along, but there are only three independent dimensions in space . What does independent dimension mean? In the Cartesian coordinate system the directions of x, y and z axis are inde ...
Wednesday, June 24, 2015
... Newton’s Three Laws Motion 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forces, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity. 2nd law of motion: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force exerte ...
... Newton’s Three Laws Motion 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forces, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity. 2nd law of motion: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force exerte ...
integrated-science-5th-edition-tillery-solution
... measure of inertia, and inertia exists everywhere. A change of motion, acceleration, always results from an unbalanced force everywhere in the known universe. Finally, forces of the universe always come in pairs. Of the two forces one force is always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to t ...
... measure of inertia, and inertia exists everywhere. A change of motion, acceleration, always results from an unbalanced force everywhere in the known universe. Finally, forces of the universe always come in pairs. Of the two forces one force is always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to t ...
First--Inertia (see above for this law in detail)
... When the net force is zero, there are balanced forces and there is no change in motion. To achieve a net force of zero means that an applied force balances the force of friction so that the combined force acting on the object is zero. (Ex. Tug-of-War, when there is a deadlock and no one is able to m ...
... When the net force is zero, there are balanced forces and there is no change in motion. To achieve a net force of zero means that an applied force balances the force of friction so that the combined force acting on the object is zero. (Ex. Tug-of-War, when there is a deadlock and no one is able to m ...