Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
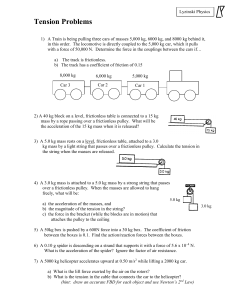
... between the boxes is 0.1. Find the action/reaction forces between the boxes. 6) A 0.10 g spider is descending on a strand that supports it with a force of 5.6 x 10–4 N. What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s ...
... between the boxes is 0.1. Find the action/reaction forces between the boxes. 6) A 0.10 g spider is descending on a strand that supports it with a force of 5.6 x 10–4 N. What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s ...
Newton`s First Law (Law of Inertia)
... Now let's say that the mass of the sled stays at 50 kg and that another dog is added to the team. If we assume the second dog pulls with the same force as the first (100 N), the total force would be 200 N and the acceleration would be 4 m/s2. Finally, let's imagine that a second dog team is attached ...
... Now let's say that the mass of the sled stays at 50 kg and that another dog is added to the team. If we assume the second dog pulls with the same force as the first (100 N), the total force would be 200 N and the acceleration would be 4 m/s2. Finally, let's imagine that a second dog team is attached ...
Motion, Work , and Power
... MOTION Motion- A change in position in a certain amount of time In order to describe motion, you need a frame of reference to compare it with ...
... MOTION Motion- A change in position in a certain amount of time In order to describe motion, you need a frame of reference to compare it with ...
Newton_s Laws AP
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
A Net Force
... Since the length of the vectors for FN and Fg are the same length, the net force in the vertical direction should be zero as we would expect. This also means that FN = Fg. ...
... Since the length of the vectors for FN and Fg are the same length, the net force in the vertical direction should be zero as we would expect. This also means that FN = Fg. ...
+ v 2 - Cloudfront.net
... Calculations: First, put the stamped-out disk (call it disk S) back into place to form the original composite plate (call it plate C). Because of its circular symmetry, the center of mass comS for disk S is at the center of S, at x =-R. Similarly, the center of mass comC for composite plate C is at ...
... Calculations: First, put the stamped-out disk (call it disk S) back into place to form the original composite plate (call it plate C). Because of its circular symmetry, the center of mass comS for disk S is at the center of S, at x =-R. Similarly, the center of mass comC for composite plate C is at ...
Final Exam Practice questions
... is increased until the object starts moving. If the surface is kept at this angle, the object (assume k < s) a) slows down b) moves at uniform speed c) speeds up d) impossible to tell e) none of these 5) A 4.0 kg hollow sphere of radius 5.0 cm starts from rest and rolls without slipping down a 30 ...
... is increased until the object starts moving. If the surface is kept at this angle, the object (assume k < s) a) slows down b) moves at uniform speed c) speeds up d) impossible to tell e) none of these 5) A 4.0 kg hollow sphere of radius 5.0 cm starts from rest and rolls without slipping down a 30 ...
Ch. 4
... • Downward force is weight. • a = weight/mass • but an object with twice the mass will have twice the weight… • so the accelerations are the same… • We call this acceleration “g”. • g is about 10m/s/s downward. ...
... • Downward force is weight. • a = weight/mass • but an object with twice the mass will have twice the weight… • so the accelerations are the same… • We call this acceleration “g”. • g is about 10m/s/s downward. ...
RevfinQans111fa02
... 2. You know the acceleration of a particle at all times. What do you know about the direction of the velocity of the particle? A: You know nothing about the direction of the velocity. B: You know that the direction of the velocity is either parallel to, anti-parallel to, or at right angles to the di ...
... 2. You know the acceleration of a particle at all times. What do you know about the direction of the velocity of the particle? A: You know nothing about the direction of the velocity. B: You know that the direction of the velocity is either parallel to, anti-parallel to, or at right angles to the di ...
Course: 8th Pre-AP Science - H. Wright
... 2 Roller coasters use the laws of motion to thrilling ends. They are the best use of Newton’s Laws of Motion. Roller coasters are known for their twists, turns, and loops. They seem to defy everything we know about how people and objects move. Roller coaster designers, however, use Newton’s laws to ...
... 2 Roller coasters use the laws of motion to thrilling ends. They are the best use of Newton’s Laws of Motion. Roller coasters are known for their twists, turns, and loops. They seem to defy everything we know about how people and objects move. Roller coaster designers, however, use Newton’s laws to ...
AP Physics 1- Circular Motion and Rotation Practice Problems FACT
... Q4. An object of mass 5 kg moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s in a circular path of radius 2 m. Find the object’s acceleration and the net force responsible for the motion. Q5. A 10.0 kg mass is attached to a string that has a breaking strength of 200N. If the mass is whirled in a horizontal circle ...
... Q4. An object of mass 5 kg moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s in a circular path of radius 2 m. Find the object’s acceleration and the net force responsible for the motion. Q5. A 10.0 kg mass is attached to a string that has a breaking strength of 200N. If the mass is whirled in a horizontal circle ...
Training - studentorg
... with your team prior to going into the classroom. • This presentation does not contain the entire lesson—only selected experiments that may be difficult to visualize and/or understand. ...
... with your team prior to going into the classroom. • This presentation does not contain the entire lesson—only selected experiments that may be difficult to visualize and/or understand. ...
doc
... system axis. Note that if the line of action should go through the axis, d will be zero, and thus the Torque about that axis will also be zero. The direction of the torque (“thumb”) is always perpendicular to the plane defined by the force vector and d(in the direction defined by the axis). ...
... system axis. Note that if the line of action should go through the axis, d will be zero, and thus the Torque about that axis will also be zero. The direction of the torque (“thumb”) is always perpendicular to the plane defined by the force vector and d(in the direction defined by the axis). ...
Name: ___________ Date: ____________ Period: _______ 7th
... 1) An automobile is at rest on a level road Which of the following is false? a) No forces act on the car. b) The resultant force on the car is zero. c) The normal force is equal to the weight of the car. 2) The car in problem 1) will remain at rest until: a) a forward force of any magnitude is appli ...
... 1) An automobile is at rest on a level road Which of the following is false? a) No forces act on the car. b) The resultant force on the car is zero. c) The normal force is equal to the weight of the car. 2) The car in problem 1) will remain at rest until: a) a forward force of any magnitude is appli ...
Prof
... 13- A 200-g block is attached to a horizontal spring and executes simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.250 s. If the total energy of the system is 2.00 J, find (a) the force constant of the spring and (b) the amplitude of the motion. 14- A block–spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.5 ...
... 13- A 200-g block is attached to a horizontal spring and executes simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.250 s. If the total energy of the system is 2.00 J, find (a) the force constant of the spring and (b) the amplitude of the motion. 14- A block–spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.5 ...
newtons laws
... related to the mass of the object and the net force applied to the object. • a = Fnet / m or Fnet = ma • 1 Newton = the force required to accelerate a 1 kg by 1m/s2 (N = kg•m/s2) http://www.gaston.k12.nc.us/resources/teachers/webquests/Art/webquest/resour1.jpg ...
... related to the mass of the object and the net force applied to the object. • a = Fnet / m or Fnet = ma • 1 Newton = the force required to accelerate a 1 kg by 1m/s2 (N = kg•m/s2) http://www.gaston.k12.nc.us/resources/teachers/webquests/Art/webquest/resour1.jpg ...























