Electric Field Hockey - Fields and Forces 1
... c. In addition to the puck, let’s decide on a name for the red and blue charges to differentiate them from the puck (later we call them source charges). d. With E-field on, what do you think the black arrows represent? (Can mention that they are not forces). Are they vectors? e. Forces push or pull, ...
... c. In addition to the puck, let’s decide on a name for the red and blue charges to differentiate them from the puck (later we call them source charges). d. With E-field on, what do you think the black arrows represent? (Can mention that they are not forces). Are they vectors? e. Forces push or pull, ...
Chapter 7 - Muddassir
... Mechanical Resonance for the case of swing A swing is the good example of mechanical resonance. It is like a pendulum with a single natural frequency depending on its length. If a series of regular pushes are given to the swing, its motion can be built up enormously. If pushes are given irregularly, ...
... Mechanical Resonance for the case of swing A swing is the good example of mechanical resonance. It is like a pendulum with a single natural frequency depending on its length. If a series of regular pushes are given to the swing, its motion can be built up enormously. If pushes are given irregularly, ...
Document
... which passes over a pulley with radius R and rotational inertia I = ½ MR2. The string moves past the pulley without slipping. The surface of the table is frictionless. What are the tensions in the strings ? ...
... which passes over a pulley with radius R and rotational inertia I = ½ MR2. The string moves past the pulley without slipping. The surface of the table is frictionless. What are the tensions in the strings ? ...
Phy I (AP Phy I) Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
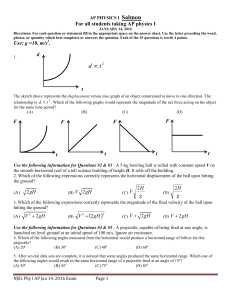
... 8. Once the mass reaches the bottom of the ramp and is stationary, what force would have to be applied parallel to the ramp in order for the mass to move up the ramp at a constant velocity? (A) 8 N (B) 30 N (C) 38 N (D) 46 N 9. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction that would cause this ...
... 8. Once the mass reaches the bottom of the ramp and is stationary, what force would have to be applied parallel to the ramp in order for the mass to move up the ramp at a constant velocity? (A) 8 N (B) 30 N (C) 38 N (D) 46 N 9. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction that would cause this ...
Physics, Mr - TeacherWeb
... Questions 10 – 11: A 2.5 kg block of metal rests on a revolving platform 2.4 m from the center (axis of rotation). The coefficient of static friction (s) between the block and the surface of the platform is 0.1. You use a stopwatch to measure rotation speed and you find that the platform rotates 15 ...
... Questions 10 – 11: A 2.5 kg block of metal rests on a revolving platform 2.4 m from the center (axis of rotation). The coefficient of static friction (s) between the block and the surface of the platform is 0.1. You use a stopwatch to measure rotation speed and you find that the platform rotates 15 ...
Lecture 06: Conservation of Angular Momentum
... A sphere mass m1 and a block of mass m2 are connected by a light cord that passes over a pulley. The radius of the pulley is R, and the mass of the thin rim is M. The spokes of the pulley have negligible mass. The block slides on a ...
... A sphere mass m1 and a block of mass m2 are connected by a light cord that passes over a pulley. The radius of the pulley is R, and the mass of the thin rim is M. The spokes of the pulley have negligible mass. The block slides on a ...
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
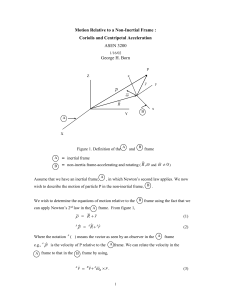
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ ...
... and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ ...
File - Mr. Graham`s AP Physics 1 & AP Physics C
... which the force constant is 5.00 N/m is free to oscillate on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The block is displaced 5.00 cm from equilibrium and released from rest, as shown below. ...
... which the force constant is 5.00 N/m is free to oscillate on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The block is displaced 5.00 cm from equilibrium and released from rest, as shown below. ...
Sliders – High School Worksheet
... 7. Set up the experiment the same as before, except this time position the basket so that it is close enough to the floor in order to land before the box goes over the edge of the table. Measure the distance from the edge of the box to the edge of the table and the distance from the ground to the bo ...
... 7. Set up the experiment the same as before, except this time position the basket so that it is close enough to the floor in order to land before the box goes over the edge of the table. Measure the distance from the edge of the box to the edge of the table and the distance from the ground to the bo ...
Unit 3
... Analyze and evaluate the position, velocity and acceleration in horizontal and vertical frames of reference for projectile motion. Apply the concepts of position, velocity and acceleration developed in Unit One to solve conceptual and quantitative problems for projectile motion in both horizonta ...
... Analyze and evaluate the position, velocity and acceleration in horizontal and vertical frames of reference for projectile motion. Apply the concepts of position, velocity and acceleration developed in Unit One to solve conceptual and quantitative problems for projectile motion in both horizonta ...